Achieving the Dream at Tulsa Community College
advertisement

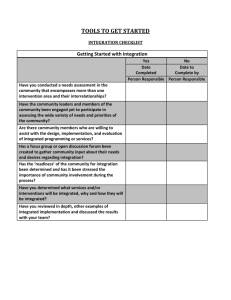
The Four Components What’s Wrong? Why? (Quantitative Data) (Focus Group Student Data) Revised Interventions New Interventions Policy Changes Assess Impact 60% reported ACT scores; average ACT composite score = 19.6 77% were tested for remedial needs 18% enrolled in developmental English/writing 29% enrolled in developmental reading 67% enrolled in developmental math Developmental Placement (based on entry-level assessment) 30% 40% 17% 591 788 329 13% 263 Graduation Rate by Number of Developmental Areas Required 591 789 329 263 Graduation Rate By Writing Placement 1628 126 218 Graduation Rate by Reading Placement 1404 263 305 Graduation Rate By Math Placement 648 48 143 1133 1972 1485 989 968 781 717 Persistence Rate 100 80 60 40 20 0 100% 71% 78% 53% 52% 46% 45% Male (N=800) Female (N=1172) 42% 36% 33% 39% *The one Native Hawaiian was removed from the dataset The Four Components What’s Wrong? Why? (Quantitative Data) (Focus Group Student Data) Goals • Persistence (Year 2 – 4 ) • Developmental Reading (Year 3 – 4 ) • Developmental Math (Year 4 ) Revised Interventions New Interventions Policy Changes Assess Impact The Four Components What’s Wrong? Why? (Quantitative Data) (Focus Group Student Data) Goals • Persistence (Year 2 – 4 ) • Developmental Reading (Year 3 – 4 ) • Developmental Math (Year 4 ) Revised Interventions New Interventions Policy Changes Assess Impact Three focus groups per campus 12 total groups 101 total students Students volunteered and were accepted if they had completed their first semester in fall 2007 and had re-enrolled in spring 2008. 4% African American males in both AtD cohort and focus groups 44% Tulsa Achieves students Mean average age was • 22.7 years for focus groups (more 18 year olds with Tulsa Achieves) • 24.5 years for AtD cohort Mean average age of non-Tulsa Achieves students was 25.8 years. Adjusting to college Balancing school and life Textbook issues Tulsa Achieves implementation issues Communication issues with instructors Choosing courses All six barriers/challenges were identified on all four campuses. Service Barriers Adjustment Barriers Academic Barriers 82% of all barriers/challenges fell into one of three clusters. Instructional Issues • Communication issues with instructors • Instructional quality • Understanding instructor’s course requirements Student Issues • Choosing courses • Meeting academic workload • Using Blackboard and MyTCC email • Academically underprepared • Lacking computer proficiency • Course placement Textbook issues Poor customer service Financial Aid service Confusing enrollment process Limited times and locations of classes Finding locations on campus Adjusting to college life Balancing school and life Time management Lack of motivation The Four Components What’s Wrong? Why? (Quantitative Data) (Focus Group Student Data) Goals • Persistence (Year 2 – 4 ) Top Persistence Barriers: 1. Adjusting to college 2. Balancing school and life • Developmental Reading (Year 3 – 4 ) • Developmental Math (Year 4 ) 3. Textbook issues 4. Tulsa Achieves implementation issues 5. Communication issues with instructors 6. Choosing courses Revised Interventions New Interventions Policy Changes Questions • How do we revise current interventions to directly address common barriers? • What new interventions can be implemented to address common barriers? Assess Impact Orientation 1. ◦ ◦ Fall 2008: Strategies for Academic Success Expand orientation to all students Multiple delivery options Options for testing out Advising 2. ◦ ◦ 3. Compiling current interventions Collaborating with student services and registration Tulsa Achieves Implementation Persistence Barriers Understanding Instructor’s Course Communication with Instructors Adjusting to College Motivation Adjustment Academic Meeting Academic Workload Time Management Balancing School & Life Teaching Styles Strategies for Academic Success The Four Components What’s Wrong? Why? (Quantitative Data) (Focus Group Student Data) Goals • Persistence (Year 2 – 4 ) Top Persistence Barriers: 1. Adjusting to college 2. Balancing school and life • Developmental Reading (Year 3 – 4 ) • Developmental Math (Year 4 ) 3. Textbook issues 4. Tulsa Achieves implementation issues 5. Communication issues with instructors 6. Choosing courses Revised Interventions New Interventions Policy Changes Questions • How do we revise current interventions to directly address common barriers? • What new interventions can be implemented to address common barriers? • What policy changes need to be made to address common barriers? Assess Impact Ensure dual credit for dual enrollment - Seniors, at least, should be able to take college classes rather than high school elective classes for dual credit. Align Oklahoma's K-12 test outcomes with national standards Allow Oklahoma community colleges to offer teacher education in math and science, to reduce the number of unqualified, or marginally qualified, math and science teachers in Oklahoma classrooms Rescind required $13 per credit hour fee on all developmental courses Provide timely statewide reports tracking student transfer The Four Components What’s Wrong? Why? (Quantitative Data) (Focus Group Student Data) Goals Top Persistence Barriers: • Persistence (Year 2 – 4 ) 1. Adjusting to college 2. Balancing school and life 3. Textbook issues • Developmental Reading (Year 3 – 4 ) • Developmental Math (Year 4 ) 4. Tulsa Achieves implementation issues 5. Communication issues with instructors Revised Interventions New Interventions Policy Changes Questions • How do we revise current interventions to directly address common barriers? • What new interventions can be implemented to address common barriers? 6. Choosing courses • What policy changes need to be made to address common barriers? Assess Impact Assessments Formative: • To what extent did interventions (or policy changes) effectively address common barriers? Summative: • To what extent did interventions increase persistence? The Four Components What’s Wrong? Why? (Quantitative Data) (Focus Group Student Data) Goals Top Persistence Barriers: • Persistence (Year 2 – 4 ) 1. Adjusting to college 2. Balancing school and life 3. Textbook issues • Developmental Reading (Year 3 – 4 ) • Developmental Math (Year 4 ) 4. Tulsa Achieves implementation issues 5. Communication issues with instructors Revised Interventions New Interventions Policy Changes Questions • How do we revise current interventions to directly address common barriers? • What new interventions can be implemented to address common barriers? 6. Choosing courses • What policy changes need to be made to address common barriers? Assess Impact Assessments Formative: • To what extent did interventions (or policy changes) effectively address common barriers? Summative: • To what extent did interventions increase persistence? Research AtD.org and other sites for interventions that work for community colleges Complete a list of TCC existing interventions Identify specific advising components that address student identified barriers Develop assessment protocols Identify systemic and standard methods of collaboration and communication TCC’s goal is to achieve a 3% increase in student persistence each year.