Power Point notes

The Government at
Work
The Bureaucracy
Chapter 15
Bureaucracy
Large, complex administrative structure that handles the everyday business of an organization
In gov’t – includes those non-elected positions
Efficient & effective way to organize
Yet often criticized for being slow & inefficient & sometimes inhumane
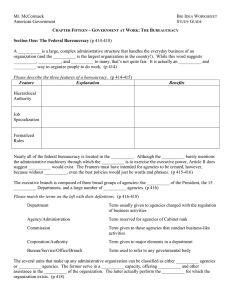
3 Features of a bureaucracy
1.
Hierarchical authority
2. Job specialization – each bureaucrat
3. Formalized rules
Federal Bureaucracy
Today: 4.1 million work for the federal gov’t (2013)
Most in the executive branch
Divided into three areas in Executive Branch
Executive Office of the President
Executive Departments – 15 cabinet departments
Independent Agencies
(See page 429)
Remember – Congress & federal court system have their own bureaucracies
Its all in a name…
Department – Cabinet level departments
Agency, administration – major unit, near –Cabinet status
Commission – typically connected to business activities
Also can be investigative & advisory bodies
Corporation, authority – conduct “business-like” activities often w/ a board & a manager
Bureau – major element of “it”
Can also be called service, administration, office, branch, division
Staff vs. Line agencies
Staff agencies – are the support personnel
Line agencies – actually perform the tasks
In gov’t – we see the line agencies doing the work
Staff agencies in gov’t help them do this through advising, budgeting, purchasing, management & planning
EPA is a line agency
National Security Council is a staff agency
Executive Office of the
President - EOP
“the President’s right arm”
Several separate agencies staffed by approx. 1800 to help the President be chief executive (2013)
White House Office
National Security Council
Office of Management & Budget
Office of National Drug Control Policy
Council of Economic Advisors …& more
White House Office
President’s key personal & political staff
“the West Wing” - Near the Oval Office & Cabinet Room
Chief of Staff, Press Secretary
Counselor to the President, senior advisors
Deputy assistants – foreign policy, defense, homeland security, the economy, political affairs, congressional relations, speech writing
Appointment & Scheduling Assistant, Physician
1 st Lady’s Chief of Staff & press secretary
National Security Council
Staff agency that advises President on domestic & military matters and on most foreign policy issues; often at short notice
VP, National Security Advisor, Secretaries of State,
Treasury, Defense; may also include Director of National
Intelligence & Chairman of Joint Chiefs
Has small staff of experts
Much of their work is super top secret
All have highest level of security clearances
Office of Management
& Budget
OMB – largest & 2 nd most influential unit in the Executive
Office
Primary goal – preparing annual Federal Budget
Federal fiscal year – Oct 1 st thru Sept 30 th
Each agency submits budget requests
OMB reviews & crafts President’s proposed budget
Then monitors gov’t spending
Also oversees the agencies enforcing laws & double checks legislative proposals to make sure they are in line with the President’s policy positions
Assists preparing executive orders & veto messages
Rest of the EOP
Office of National Drug Control Policy
Council of Economic Advisors
Helps prepare annual Economic Report to Congress
Domestic Policy Council
Council on Environmental Quality
Office of the Vice President
Office of the US Trade Representative
Office of Science & Technology
Office of Administration
The Cabinet
Executive Departments authorized by Congress
Today: 15, newest is Homeland Security
Heads are called Secretaries, except for Attorney General for DoJ
Serve as primary between the departments & President
Under or Deputy secretaries & assistant secretaries also appointed by the President
Each department divided into subunits & often even smaller groupings than that
Both staff agencies & line agencies
Picking the Cabinet
Nominated by the President
Confirmed by the Senate
Factors considered include:
Supporters of the President
Professional qualifications & experience
Balancing geography
Interest groups
Management style
More recently – gender, race, ethnicity considerations
What you will do…
Receive your Cabinet assignment
Research & be ready to report back on the following:
Purpose or mission of department
At least one Current event of the department
Roles of the deputy/ under secretaries
Subunits of the department
Current budget and # of employees
*** ½ page report for classmates is advised***
Independent Agencies
Agencies not connected to any of the 15 executive departments
They do not fit within any of the given departments
Sometimes to protect them from politics
Some need to be as they are regulatory commissions
Of course, still answer to the President
But several are free of Presidential control
Three main groups of independent agencies…
1 - Independent Executive
Agencies
Include most of the non-Cabinet agencies
Include very large “near-Cabinet” status ones
General Services Adm. (GSA); NASA, EPA
Include some that do good works & get good PR
Peace Corps, Small Business Adm., NTSB
Some get very little notice & are relatively small
American Battle Monuments Commission
2 – Independent Regulatory
Commissions
11 agencies that regulate important aspects of the nation’s economy
These are largely beyond the President’s control
Congress designed them to be so independent
Boards or commissions have 5-7 members with staggered terms
Must have both major parties represented
Also have quasi- legislative & judicial powers
Make regulations & impose fines & penalties
See page 447 for the 11 of these…
3 – Gov’t Corporations
Set up by Congress to carry out business-like activities & are under the President’s control
Today more than 50 of them exist
Resembles a private business
Has a board of directors & general manager
Any income goes back into itself
Difference: funded by the Gov’t & subject to review by the OMB
FDIC, US Postal Service, Amtrak, TVA
Working for the Gov’t
Office of Personnel Management (OPM) oversees all federal employees
Is an Independent Executive Agency
Is a staff agency
Civil Service System – from the Pendleton Act, 1883
90% of federal employees are in the “classified service”
So must take the Civil Service Exam
(Different from the Selective Service System = the draft
Males, 18 – 26 years old must still be registered)