Chapter 7 Section 4
advertisement

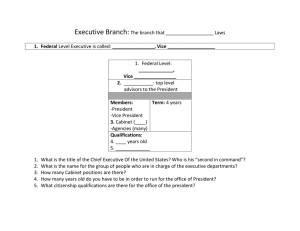
Executive Cabinet Cabinet – group of advisors to the President that includes all of the heads of the 15 top-level executive departments First Lady – The President’s Wife Federal Bureaucracy – The agencies and employees of the executive branch, all of the agencies that work within the top level departments Bureaucrat- employees who work within the government agencies Executive Agencies- Agencies that do not operate within other government department, but have a specialized area of their own Government Corporations – ran like private businesses, but are owned and operated by the Federal Government Regulatory Boards / Commissions – Agencies that enforce the rules for certain industries Independent Agencies – federal boards or commissions that are not part of any cabinet department Political Appointees – People who the President chooses to fill a position, often only hold the position while the President is in office Civil Service Workers – career federal employees, hold their employment until retirement Civil Service System – the practice of using a series of exams and merit to hire government workers • Spoils System – giving jobs to people as a reward for political support • Merit System – jobs are given to people based on Civil Service Exam Scores and other standards set forth by the Office of Personnel Management Advisors, clerks, and Secretaries who help the President to do their job 5 Most Important Offices in the EOP: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ White House Office Office of Management and Budget National Security Council Office of Administration Council of Economic Advisers Group of about 500 people who work directly for the president (includes political advisors, personal secretaries, speech writers, ect..) Person in charge of this department is known as the Chief of Staff (Cyrus on Scandal) They help the President to prepare the budget and monitor spending among government agencies Helps to regulate Foreign Policy Made up of the following people: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Vice-President Secretary of Defense Secretary of State Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Individuals who are seeking information under the Freedom of Information Act The Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) is a law that gives you the right to access information from the federal government. It is often described as the law that keeps citizens in the know about their government. http://www.foia.gov/ Consists of 3 advisors that assist the President on topics of employment, tax policy, inflation, and foreign trade ◦ President names the members, but the Senate must approve them The heads of all of the top level executive departments Head of the Justice Department is called the Attorney General, all others are called secretaries Vice-Presidents and other high raking officials are often asked to join the Cabinet The Department of Homeland Security ◦ Created in 2002 as a reaction to the attacks on 9/11 ◦ Focuses on preventing terrorist attacks on American soil ◦ First secretary named by George W. Bush was PA Governor Tom Ridge • ABSOLUTELY NOTHING !!!! • The cabinet developed out of tradition and need • Dates back to George Washington, who only had 4 cabinet members in his cabinet • President sets the rules for meetings 1. 2. 3. Turn new laws into action by setting rules and procedures Run day to day business of the federal government Regulate activities within the United States, set standards President appoints directors of these agencies with Congressional Approval Operate separate from the President, Leaders are Presidentially Appointed, but the President cannot fire them Types of Agencies: ◦ Executive Agencies ◦ Government Corporations ◦ Regulatory Commissions Agencies that do not operate within other government department, but have a specialized area of their own Example: NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) United States Postal Service To protect the citizens from dangerous or inappropriate actives in certain industries Examples: ◦ Food and Drug Administration (FDA)- inspects food and pharmaceutical industries in the US ◦ Federal Communications Commission (FCC)regulates television and radio broadcasts Political appointees are chosen by the President and usually only hold their position until the end of the President’s term Civil Service Workers are hired based on merit and exam scores, often hold their positions for life Known as the Civil Service Reform Act of 1883 Created after the assassination of James Garfield Limited the amount of positions a President could give to their supporters Created the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) which administers tests and sets standards for hiring federal employees Federal employees are hired based on test scores and other criteria set forth by the OPM