Plate Tectonics Vocab.
advertisement

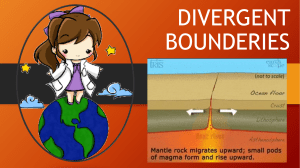
Plate Tectonics The process where the lithosphere plunges back into the interior of the Earth. A seed fern that lived 250 million years ago found on several continents. • “ The preserved remains or traces of an ancient organism. The theory that links together the ideas of Continental Drift and Ocean Floor Spreading. It explains how the Earth has changed over time V -shaped valley on the ocean floor caused by a convergent plate boundary The theory, proposed by Alfred Wegener that the continents were once joined together and have since drifted apart. An undersea mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced. A constructive (divergent) plate boundary The movement of material caused by differences in temperature The process in which old ocean floor is pushed away from a midocean ridge by the formation of new ocean floor Plate movement occurs at the A hippo-like reptile who would not have been able to swim vast oceans Irregularly shaped pieces of the Earth’s crust The branch of geology that deals with the movements that shaped the Earth’s crust. and float on convection currents in the mantle. The name that Alfred Wegener gave to Earth's one huge landmass that existed 300 million years ago. Means All Earth A German scientist that developed the theory of continental drift. He did not have any proof although he based his theory on the fact that the continents looked like pieces of a puzzle that fit together. The edges of Earth's plates where two or more plates meet. What takes place when two plates move apart? When two plates move apart When two plates move toward each other. When two plates move past each other or up and down. When two plates move past each other or up and down. The flat space between the mid-ocean ridges at a divergent boundary, it consists of new ocean floor. A v-shaped valley formed at a subduction zone (convergent boundary) Underwater mountain chains - formed at a divergent boundary due to the build up of magma.









![[Template] Plate Tectonic Theory Study Guide Key](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/025492312_1-d52b662e3fd9fff7ce3751c2658d705b-300x300.png)
