changing seasons
advertisement

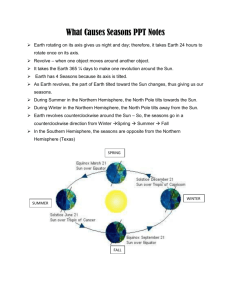
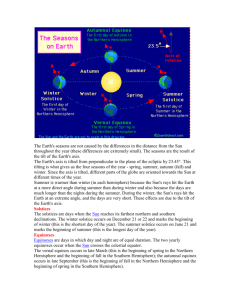
CHANGING SEASONS By Stacee Green Texas Essesntials Knoledge and Skills (TEKS) • (b)Knowledge and skills. • (13) Science concepts. The student knows components of our solar system. The student is expected to: • (A) identify and illustrate how the tilt of the Earth on its axis as it rotates and revolves around the Sun causes changes in seasons and the length of a day; QUESTIONS TO THINK ABOUT Essesntial Question • Why do the seasons change? Unit Question • What are the differences between the four seasons? Content To Be Learned • Students will be able to identify defining characteristics and describe the differences between fall, spring, summer, and winter. • Students will learn and understand new vocabulary terms. • Students will understand what happens to the earth to make the seasons change. Class Activities • Students in groups will pick out different clothes that are worn for each season. • Signs of Autumn-a global project on the internet, which enables students to learn about the changing seasons around the world. • Seasons Story Book- students make a story book individually including the four seasons and add pictures of relevant seasonal items. Students will present their books to the class. • I will read the book Ro Everything There is a Season by Leo Dillion and Diane Dillo to the whole class. Class Activities • Have students work in pairs with the Earth in Motion Flash Interactive, which introduces the basic concepts behind the seasons. As the students use the interactive activity, they will create a vocabulary list of relevant terms. http://www.teachersdomain.org/resources/ess05/sc i/ess/eiu/seasonsgame/index.html • Students will review these vocabulary words as a class and write out the definitions for them individually: Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, equator, North Pole, South Pole, axis, rotation, day, night, orbit, year, summer, winter, autumn, spring, equinox, solstice, and revolution. What is the Cause of the Seasons? • • • • The primary cause of the seasons is by the tilt of the Earth’s axis of rotation. The Earth is tilted on its axis at a 23.5 degree angle, as it moves around the sun to cause the seasons. When the Earth revolves around the sun, the Earth’s axis is tilted away from the sun for part of the year and toward the sun for part of the year. Summer occurs when the Northern Hemisphere tilts toward the sun and during this time, the Southern Hemisphere is tilted away from the sun this half experiences winter. • • • • • • Two Types of Solstice Summer Solstice is the first day of summer and known as the longest day of the year, which is June 21st. Winter Solstice is the first day of winter and the shortest day of the year, which is December 21st. Two Types of Equinox Autumnal equinox is the beginning of fall and occurs on September 21st. Vernal equinox is the beginning of spring and starts on March 21st. Terms • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Northern Hemisphere - the half of the earth that is north of the equator. Southern Hemisphere- the half of the earth that is south of the equator. Equator- an imaginary circle around the middle of the earth, halfway between the North Pole and the South Pole. North Pole- the northern end of the earth’s axis. South Pole- the southern end of the earth’s axis. Axis- a straight line about which an object turns or seems to turn. Rotation-a turning round a center or axis. Day Night Orbit-the curved, usually elliptical, path of a heavenly body, planet, or satellite about another body in space. Summer-the warmest season of the year between spring and fall. Winter-the coldest of the four seasons. FallSpring-season after winter, when plants begin to grow. Equinox-either of the two times in the year when the center of the sun crosses the equator, and day and night are of equal length in all parts of the earth. Solstice-either of the two times in the year when the sun is at its times in the year when the sun is at its greatest distance from the equator. Revolution-a complete cycle. What goes with what season? REFERENCES • Seasons (Science U) • The Youth Online Club – Seasons • http://www.globe.gov/fsl/elementaryglob e/seasons/EGLOBE_SeasonsActivity2. pdf