The Upper Limb aka The Arm
advertisement

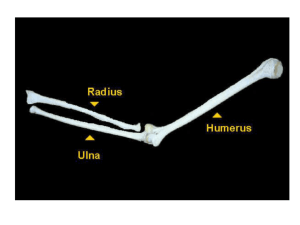
The Upper Limb aka The Arm This is going to take some studying! Bones of the upper limb (30/per limb) Arm and Forearm • Humerus • Radius • Ulna Wrist (8) • Scaphoid • Lunate • Triquetral • Pisiform • Trapezium • Trapezoid • Capitate • Hamate – Just call them carpals! Palm/Hand • Metacarpals (5) • Phalanges (14) • Proximal • Middle • Distal Humerus • Largest bone of upper limb • Articulates with radius and ulna distally • Proximally articulates with scapula at shoulder AFV Posterior view Humerus Points to know • Head – meets glenoid cavity Posterior view Humerus Points to know • Greater tuberosity – Lateral tuberosity – Muscle attachment! Posterior view Humerus Points to know • Lesser tuberosity – medial point of muscle attachment Posterior view Humerus Points to know • Deltoid tuberosity – Roughened site for rotator cuff attachment Posterior view Humerus Points to know • Trochlea – Articulation for the ulna Posterior view Humerus Points to know • Capitulum – “ball like” attachment for radius Posterior view Humerus Points to know • Epicondyles – Ulnar n. runs behind medial epicondyle Humerus • Coronoid fossa – Anterior fossa allows for ulna to articulate when flexion happens • Olecranon fossa – Posterior fossa allows for ulna to articulate when extension happens Antebrachium or Forearm • Proximally articulate with humerus • Distally articulate with carpal bones • Radius and Ulna • Attach twice at radioulnar joints • Interosseous membrane between the two Ulna What comes after L? • Forms the Elbow! • Olecranon process • Coronoid process – Together form the hinge joint with humerus Ulna info • While a large part of elbow, very little influence on wrist • Separated by fribrocartilaginous disc from wrist • Distally ends in head and styloid process • Where else did we see styloid process? Radius major forearm bone • That at proximal end wide distally – (Opposite ulna) • Very little contribution to elbow • Large influence on wrist! • Meaning: You move the radius, the hand will move! Radius markings • Head like a nail Radius markings • Head like a nail • Radial tuberosity – anchors bicep Radius markings • Styloid process is distall – anchors ligaments to wrist Radius markings • Head like a nail • Radial tuberosity – anchors bicep • Styloid process is distall – anchors ligaments to wrist “Getting a Grip” questions 1. According to the author, what made Richard Owen a genius? 2. What is the theme of this book? 3. What pattern does Owen recognize? 4. What does Darwin claim is responsible for the similarities in animal limbs? 5. What about the lung fish is not a coincidence at all? 6. Why is Ichthyostega a “let down?” What is connected to the wristwatch? (The distal forearm ) The Wrist • 8 bones – connected by ligaments • 2 rows of marble sized bones • Form roof for median nerve and tendons to travel through http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aqImkDgD wHU The Wrist This hollow area comparable to a tunnel Carpal Tunnel Syndrome • Overuse of tendons cause them to swell • Press on median n What do you think this causes? The Palm & The Ollll Metacarpals • • • • No names just numbers 1-5 Lateral to medial Metacarpals heads form knuckles Phalanges! • 14 total/hand • Thumb only has two phalanges Proximal Intermediate Distal