2_ANATOMY_Bones_and_joints_of_the_upper_limb
advertisement
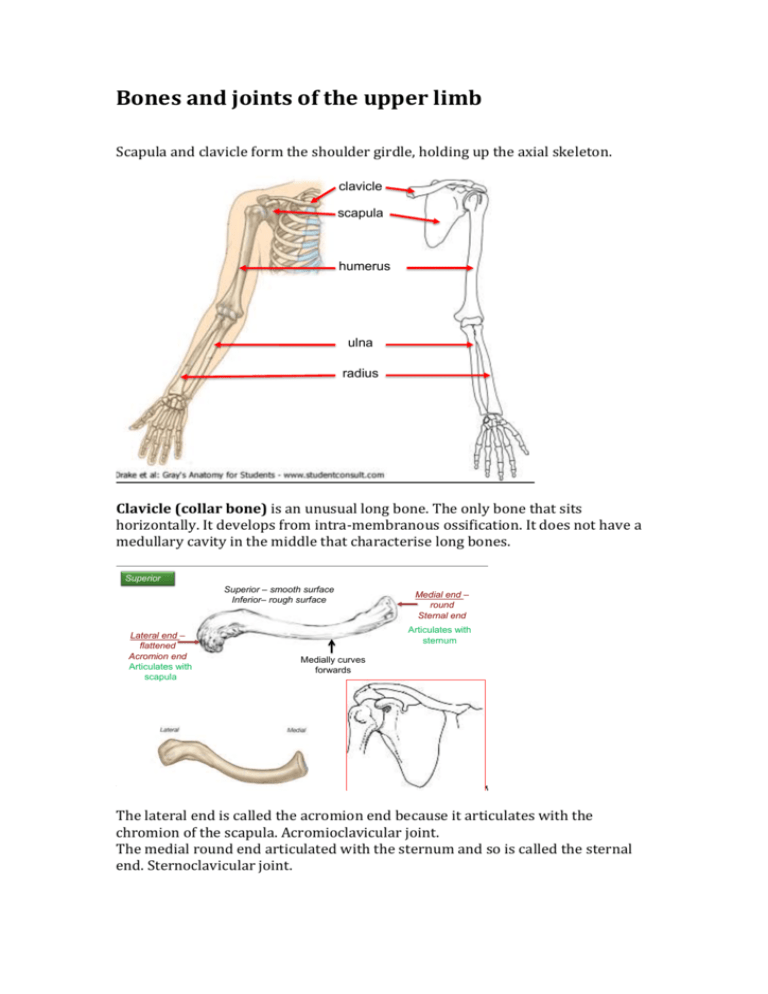
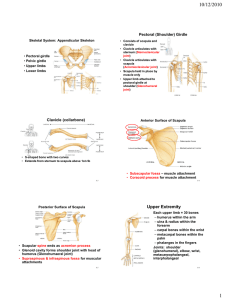
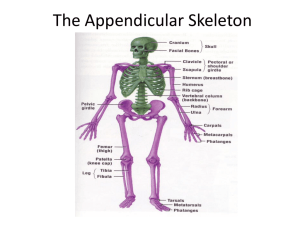
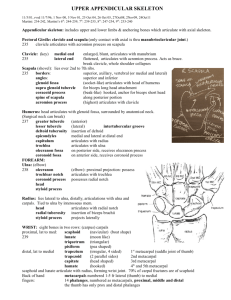
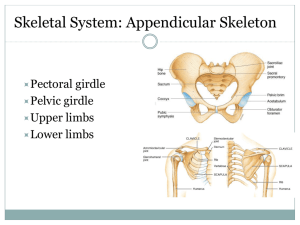
Bones and joints of the upper limb Scapula and clavicle formof thethe shoulder girdle,limb holding up the axial skeleton. Bones upper clavicle scapula humerus ulna radius Clavicle (collar bone) is an unusual long bone. The only bone that sits horizontally. It develops from intra-membranous ossification. It does not have a medullary cavity in the middle that characterise long bones. clavicle Superior Superior – smooth surface Inferior– rough surface Lateral end – flattened Acromion end Articulates with scapula Medial end – round Sternal end Articulates with sternum Medially curves forwards The lateral end is called the acromion end because it articulates with the chromion of the scapula. Acromioclavicular joint. The medial round end articulated with the sternum and so is called the sternal end. Sternoclavicular joint. The curvature changes between 2/3 and 1/3 and this is the weakest point – most likely to fracture. When bones change from round to flat, this is appoint of fracture. Scapula is an irregular bone. Flat bone in a triangular shape. The lateral and medial border meet at a medial angle. Greys anatomy. Scapula Posterior Anterior Corocoid process Superior Acromion Subscapular fossa Supraspinous fossa Glenoid fossa Infraspinous fossa Medial Lateral Glenoid fossa lateral Humerus. Also called the funny bone. Long bone, has a head with an anatomical neck and the surgical neck (where breakages occur). The greater tubercle is more lateral. The greater and lesser tubercles are created by pressure. The grove between the tubercles is the intertubercular groove or sulcus. Most medial bump on the distal head of the humerus is the medial epicondyle. the flexors come form here. The one on the other side is the later epicondyle and is where the extensors come from. The trochlear is the pulley where the ulna articulates. Capitulum is lateral. It articulates with the radius. Humerus Anterior head Greater tubercle anatomical neck surgical neck Lesser tubercle Intertubercular groove Lateral epicondyle Medial epicondyle Capitulum Trochlear Ulna is in line with the 5th digit. It is more medial than the radius. It articulates with the trochlea at the trochlea notch. The most proximal point is olecranon. The head of the ulna is at the bottom, the radius is the reverse. Head is distal. At the base there is the olecranon at the very top, which extends posteriorinferiorally; then the trochlear notch, coronoid process and the ulnar tuberosity. The head (inferioally) is the styloid process. Bones are separated by interosseous membrane. Ulna and Radius Anterior PROXIMAL head neck Olecranon Trochlear notch Coronoid process Ulnar tuberosity radial tuberosity Interosseous membrane (fibrous joint) Radius (lat) BASE Styloid process Ulna (med) HEAD Styloid process Ulnar notch The radius articulates with the capitulum. It is shorter and more lateral. It’s head is proximal. It is circular – controls rotation. It has a head and then a thinned neck. It has a bulge, called the radial tuberosity. The styloid process articulates with the carpal bones. It articulates with the ulna in the proximal radial-ulna joint. With the ulnar notch. In-between the radius and the ulna is the interosseous membrane which is a fibrous joint. The hand Radius and ulna. Carpus – wrist of hand. 2 rows of 4 very short bones. It forms a tunnel shape (carpal tunnel syndrome). Some Lovers Try Positions that they can’t handle. Metacarpals. Are numbered laterally to medially. 1-5. The head of these bones are the knuckles. There are 14 phalanges in the hand. There is a proximal, middle and distal phalanges. The thumb (first digit) doesn’t have a middle phalange. JOINTS Joint means articulation. 1. fibrous joints. 2. cartilaginous joints 3. synovial joints Tissues that lies between the articulating surfaces is synovium, which increases the range of movement. Lined by articular or hyaline cartilage. Inside the joint capsule is the synovial cavity, filled with oil like synovial fluid. Then there are ligaments. Ligament – joins bone to bone. Uniaxial joint – movement in only one plane. Eg. gliding joint between carpal bones. They are synovial, gliding joints. Two flat surfaces that glide on each other. Or hinge joints, like between the ulna and humerus. Biaxial – two. Eg. condyloid joints between radius and the carpal bones or in the metacarpal bones. Multiaxial – more than two. Eg. ball and socket joints at humerus and scapula. Also saddle joints, between first metacarpal and other carpal bones. The only one in the body, Elbow is a hinge joint. Between the capitulum and trochlea with radius and ulna. Proximal radial ulna joint and distal radio-ulna joint. Need to know basic movement.