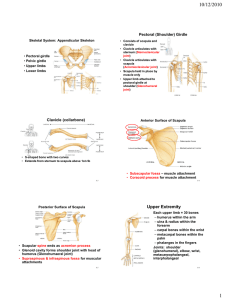
symphysis pubis
advertisement

Upper extremity • Consists of shoulder girdle, upper arms, lower arms, wrists, & hand. Shoulder girdle • Shoulder girdle: clavicle & scapula • Forms ONE joint with trunk called sternoclavicalar joint: sternum & clavicle. • Sternum joins with clavicle at the acromial end. • Scapula attaches to the trunk by MUSCLES, not a bony joint. Head Humerus • Upper arm bone • Long bone • Proximally, the head of the humerus articulates with the with scapula & the capitulum of the humerus articulates with the radius & ulna Capitulum Forearm • Radius (on thumb side) & ulna (on pinkie side) • Ulna articulates proximally with humerus & radius and distally with a fibrocartilaginous disk. – Does NOT articulate with carpal bones. • Radius articulates proximally with humerus and ulna. • Radius articulates distally with head of ulna, and 2 carpal bones (scaphoid & lunate) Fibrocartilaginous disk between ulna and carpals. Carpal bones • 8 bones • Ligiments bind carpals in 2 rows of 4 bones: – Pisiform; triquetrum; lunate; scaphoid – Hamate; capitate; trapezoid; trapezium Metacarpals • 5 metacarpals • Wide range of movement between thumb metacarpals & trapezium. • Heads of metacarpals articulate with phalanges. Trapezium Lower extremity • Hip, thigh, lower leg, ankle, & foot constitute lower extremities. Pelvic Girdle • Ligaments bind the coxal bones (hips) to the sacrum posteriorly and to each other anteriorly. • Ilium makes up the upper part of the hip • Ischium is lower • Pubis is lower mid portion of hip – Joint between coxal bones called symphysis pubis softens prior to delivery of a baby. Ilium Ischium http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/meded/grossanatomy/learnem/bones/main_bone.htm Pubis symphysis pubis Male vs Female • Male – tilted backward – narrow pelvic inlet – Pubic arch less than 90 degree angle – narrow and long sacrum – immovable coccyx – thick and heavy bones • Female – Tilted forward – Wide, oval pelvic inlet – Pubic arch more than 90 degrees – Wider and shorter sacrum – movable coccyx – thin and light bones Male Female Femurs • Longest & heaviest bones • Articulates with coxals & tibia Patella • Located in the tendon of the quadriceps. Lower leg • Tibia: largest & stronger of the two lower leg bones – Proximally articulates with femur to form knee joint – Distally articulates with fibula and tallus • Fibula: smaller – Proximally articulates with lateral condyle of tibia lateral condyle Foot • Strong ligaments and tendons hold foot bones together – This gives foot an arch – When they weaken, flat foot results • Tarsals: calcaneus, talus, navicular, 3 cuneiforms, cuboid. • Metatarsal: 5 – Articulate with phalanges