The Appendicular Skeleton

The Appendicular Skeleton
Resident Orientation Course 2012
By Dr. Totakhil
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
The Appendicular Skeleton
• 2 pairs of limbs and 2 girdles
– Pectoral (shoulder) girdle attaches upper limbs
– Pelvic (hip) girdle secures lower limbs
• 3-Segmented limbs
Upper = arm
Arm
Forearm
Hand
Lower = Leg
Thigh
Leg
Foot
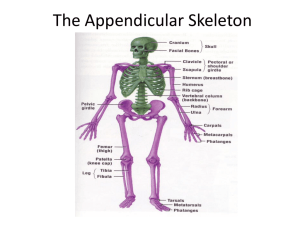
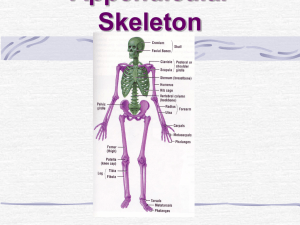
Pectoral Girdle
(Shoulder Girdle)
• Clavicle – anterior: collar bone
– Sternal end attaches to the manubrium medially
– Acromial end articulates with the scapula laterally
• Scapula – posterior: shoulder blade
• Glenoid cavity articulates with the humerus
• Acromium articulates with clavicle
• Coracoid process projects anteriorly
Scapula
Scapulae: triangular, paired, does not connect in back (adds thoracic flexibility)
Upper Extremity
• Arm or Brachium = upper arm
– Between shoulder and elbow (humerus)
• Forearm or Antebrachium
– Radius & ulna
• Hand includes:
– Wrist (carpus)
– Palm (metacarpus)
– Fingers (phalanges)
Arm
• Humerus is the only bone
– Head of humerus fits into glenoid cavity of scapula
– Distal & medially, trochlea articulates with the ulna
– Distal & laterally capitulum articulates with the radius
– Medial & lateral epicondyles
Muscles of the Shoulder Girdle
Anterior Compartment Flexors
Posterior Compartment Flexors
Forearm
• Consists of 2 bones the radius and ulna
• These bones articulate with each other proximally and distally
• An interosseous membrane is between these 2 bones
Radius
• Long bone situated on the lateral side of the forearm
• Together with the ulna, it provides attachment for the forearm muscles
• It consists of an articular head above, which articulates with the humerus and ulna to form the elbow joint
• Consists of an articular surface below, which articulates with the carpal bones to form the wrist
• Its lower end rotates around the ulna, whose position is fixed, to supinate and pronate the forearm and hand
Ulna
• Long bone situated on the medial side of the forearm.
• Together with the radius, they provide attachment for the forearm muscles
• Consists of a large trochlear surface above, which articulates with the humerus to form the elbow joint
• Consists of a small head below, which articulates with the radius to form the radioulnar joint
Radius is thinner proximally, like a spool of thread, and wide distally; ulna is slightly longer and looks like a monkey wrench (supposedly!)
Anatomic Position
• In the anatomical position:
– Radius is lateral (thumb side); with pronation the palm faces posteriorly and the bones cross
• Prone: body lying face down
– You can remember prone if you think about how you would fall forward onto your face if you passed out
• Supine: body lying face up
Proximal and Distal Joints of the
Forearm
Muscles of the Forearm
Muscles of the Forearm
Hand
• Wrist: consists of 8 carpal bones
– Articulate above with the radius at the radiocarpal joint
– Articulate with each other at the intercarpal joints
– Articulate below with the metatarsals at the carpometacarpal joints
Hand
• Hand: consists of 5 metacarpals bones
– The 1st metacarpal lies laterally, providing a base for the thumb
– The 5th metacarpal lies medially, forming a base for the little finger
– Proximally they articulate with the carpal bones at the carpometacarpal joints
– Distally they articulate with the proximal phalanges at the metacarpophalangeal joints
Hand
• Fingers (or digits) consist of miniature long bones called phalanges:
– Thumb has 2 bones: proximal and distal
– The other fingers have 3 bones: proximal, middle, distal
Pelvic Girdle
• Strongly attached to axial skeleton (sacrum)
• More stable than pectoral (shoulder) girdle
• Less freedom of movement
• Made up of the paired hip bones
– “Bony pelvis” is basin-like structure: hip bones plus the axial sacrum and coccyx
Differences Between Male and Female
Pelvis
Male Pelvis
Heavier
Female Pelvis
Lighter and thinner
Heart shaped pelvic inlet
Round or oval shaped pelvic inlet
Prominent muscle and ligament attachments
Less prominent muscle and ligament attachments
Sub-pubic angle is less than
90 degrees
Sub-pubic angle is greater than 90 degrees
Longer narrower pelvic cavity Shorter wider pelvic cavity
Hip bone (Os Coxae): 3 separate bones in childhood which fuse
Ilium
• Iliac crest
• Anterior superior iliac spine
• Greater sciatic notch
• Forms part of
“acetabulum”
(hip socket) which receives ball-shaped head of femur
• Body
• Ramus
• Ischial spine
• Ischial tuberosity
• Part of hip socket
Ischium
Pubis
• Joins medially in pubic symphysis
• Forms “obturator foramen” (large hole) with ischium
• Part of hip socket
• Thigh: femur
• Leg (Lower Leg)
– Tibia
– Fibula
• Foot
Lower Limb
Thigh
• Femur: Longest bone in the body
– It consists of a head above, which articulates with the hip bone to form the hip joint
– Has two large condyles below, which articulate with the tibia and patella to form the knee joint
Patella
• The patella, the largest sesamoid bone in the body
• It is embedded in the tendon of quadriceps femoris, and is located anterior to the knee-joint
• Its outline is somewhat in the shape of an inverted triangle
• It is separated from the femur by the suprapatellar bursa
Leg
• Tibia
– The larger and medial of the two bones of the leg
– It consists of two expanded extremities joined by a shaft
• Fibula
– Lateral and more slender of the two bones of the leg
Foot
• Tarsus: 7 tarsal bones
– Talus: articulates with tibia and fibula anteriorly and calcaneus posteriorly
– Calcaneus: heel bone
– Other bones: Cuboid, navicular, and 3 cunieforms (medial, intermediate and lateral)
• 5 metatarsals
• 14 phalanges
– Great toe is called the hallux
Muscles of the Foot
Any Questions??
References
• www. rci.rutgers.edu