Treatment of common cold
advertisement

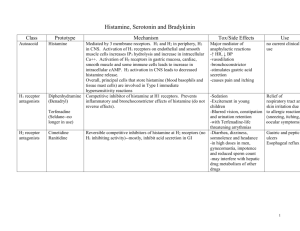
Treatment of common cold By Dr.Mohamed Abd AlMoneim Attia A. Nasal Decongestants • This group of drugs is used to treat the initial symptoms of irritation of the nasal mucosa (e.g. nasal Stuffiness, runny nose). • Agents that stimulate sympathetic responses or block parasympathetic responses are useful in treating nasal congestion. • Agents that block the action of histamine (Antihistaminics) are useful in preventing nasal discomfort caused by release of histamine in allergic disorders. 1. Sympathomimetics • The sympathomimetics stimulate 1-adrenoceptor lead to vasoconstriction in the inflamed mucous membranes • Used for symptomatic relief A. Systemically used : • Pseudoephedrine, Phenylpropanolamine Hcl • Its alpha stimulant action may raise blood pressure especially in patients given MAO inhibitors. • It has C.N.S stimulant action like amphetamine. B. Topically used: • Imidazoline derivatives: oxymetazoline • The imidazoline compounds activate alpha adrenergic and imidazoline receptors and causes vasoconstriction. • Some imidazolines are administered by topical ocular or nasal administration to produce local decongestants, while others are administered by systemic routs. Adverse reactions and precautions: Topical application: • Burning and dryness of the mucosa which interfere with the ciliary action. • Rebound phenomena and tolerance: repeated and frequent use of topical decongestants can produce chronic swelling of the nasal mucosa similar to that of chronic rhinitis. (It is reversible on stopping the drug). • Chronic use may lead to atrophic rhinitis. • Systemic reactions when absorbed especially in infants and small children (tachycardia, palpitation, hypertension, arrhythmias). Oral administration: • This route may produce systemic effects if larger doses are given, especially in infants and children or diseased patients. • Orally administered drugs may produce dangerous rise in blood pressure. 2. Antihistamine • There are three types of histamine receptors: – H1 receptors: present in different tissue mediate inflammation – H2 receptors: present in gastric parietal cells, heart and mast cells – H3 receptors: present at presynaptic sites-Nerve endings & Brain, inhibit the release of neurotransmitters. – H4 Highly expressed in bone morrow and white blood cells. Mediate mast cell chemotaxis. Pharmacological Effects: • Extravascular smooth muscles : – Histamine increases permeability of blood vessels, which results in edema. • Cardiovascular system – Histamine decreases both systolic and diastolic blood pressure – Histamine produces positive inotropic and chronotropic effects • Exocrine glands – Histamine increase the release of gastric acid. – Histamine can also stimulate pancreatic, bronchiolar, lacrimal and salivary secretions. ( H1 receptors stimulation). • Nerve endings: – H1 stimulates various nerve ending causing pain and itching Physiologic and Pathologic Roles • Gastric secretion • Allergic reactions and anaphylactic shock • Tissue repair and growth. Therapeutic Uses • Histamine and its analogs have no wellestablished therapeutic uses, however it can be used in diagnoses of pernicious anemia and to test gastric acid secretion. Antihistamine Physiological antagonists e.g. adrenaline Blockers of histamine receptors: H1 blockers (antihistamines) H2 blockers. (antiulcer) H3 blockers (still not approved for clinical use). Histamine release inhibitors (mast cell stabilizers) e.g. ketotifen and cromoglycate. Desensitization Therapy Classification of antihistamines 1st generation 2nd generation Group Example (Trade name) I- Ethanolamines Diphenhydramine Dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) Clemastine II-Ethylinediamines Antazoline III-Alkylamines Chlorpheniramine maleate IV- Phenothiazines Promethazine V- Piperazines Cyclizine Meclizine VI- Others Cyproheptadine -Loratidine Terfenadine Pharmacological Actions • The term antihistaminics still restricted to the drugs blocking H1 receptors. • Competitive block of H1 histaminic receptors and thus could prevent or reverse all effects of histamine produced by stimulation of H1 receptor at different tissues: Smooth muscle of bronchi, small blood vessels and intestine. Sensory impulses for itching. Capillary endothelium. Exocrine glands, except the stomach • CNS effects: Sedation Antiemetic effect (Decrease CRTZ). Antimotion sickness (Decrease vestibular activity). Muscarinic receptor blocking action (share in antimotion sickness activity). Competitive block of other monoamine receptors e.g. Alpha adrenergic receptors. 5-HT receptors. Block of sodium channel of excitable membrane (membrane stabilizing effect) e.g. Antazoline Additional effects of the first generation • Anticholinergic effect → dry mouth, urinary retention, tachycardia • α- blocking effect →postural hypotension, reflex tachycardia. • Antiserotonin effect → ↑appetite Therapeutic Uses • Prophylaxis and treatment of different allergic disorders • Treatment of vomiting of pregnancy e.g. cyclizine & promethazine. • Prophylaxis of motion sickness e.g. promethazine, dimenhydrinate and vertigo. • Treatment of carcinoid tumor (cyproheptadine) • Promotion of appetite (cyproheptadine) The use of first generation H1 antihistamines is contraindicated in treatment of individuals working in jobs where wakefulness is critical Differences between the old antihistaminics and the newer ones 1st generation Anticholinergic effects Present 2nd generation (non sedative group) Absent Sedative effect All of them have sedative Almost absent due to poor effect with variable degrees penetration to blood brain barrier Antiemetic effect Present Absent -blocking effect Present Absent Local anaesthetic effect Present Absent Duration of action Short Most of them have long duration of action. Side effects 1-Sedation with impaired concentration 2-Atropine-like side effects 3- Postural hypotension 4-Drug allergy is relatively common. 1-Cardiac arrhythmias (prolong QT interval) 2-Interaction with enzyme inhibitors e.g. macrolid antibiotic and ketoconazol leading to lethal ventricular arrhythmia.