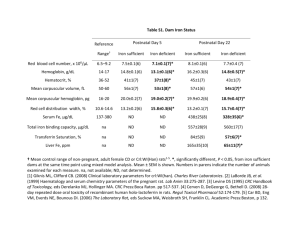
1 x 3 , enalapril(5)
advertisement

Case Discussion In Hematology Case 1 CC: PI: x 3 , เหนื่อยเพลียง่ายมา 1 สัปดาห์ underlying DM และ hypertension ได้รบั ยาเป็ น metformin(500) 1 enalapril(5) 1 x 1 มาตลอด 1 wk PTA รูส้ ึกว่ามีอาการเหนื่อยเพลีย ง่าย no orthopnea, no PND อายุ 79 ปี และสังเกตว่ามีขาบวมทั้ง 2 ข้าง ปั สสาวะอุจจาระปรกติ Physical examination BP 110/70 mmHg, RR 20 /min, PR 88 /min Investigation CBC: Hb 3.7 g%, HCT 12.7 %, WBC 18,300 /mm3, plt 557,000 /mm3 N 77 %, L 12 %, M 8 %, E 3 % MCV 73.6 fl, MCH 21.6 pg, MCHC 29.5 g/dl, RDW 25.8%) (85-95) (28-33) (32-36) Reticulocyte count: 3.91 % (12-13.6) Discussion Diagnosis Further investigation • A elderly woman with subacute anemia, and glossitis without organoomegaly • Hypochromic microcytic anemia IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA (IDA) - The most common hematological disorder in general practice - A deficit in total body iron resulting from a sustained increase in iron requirements over iron supply : DDx of microcytic hypochromic anemia 1. With decrease body iron stores : iron deficiency anemia 2. With normal or increase body iron stores 2.1 Impaired iron metabolism : ACD, Defective absorption, transport or use of iron 2.2 Disorders of globin synthesis : thalassemia. other microcytic hemoglobinopathies - Diagnosis is base on history, physical examination, and laboratory investigations - Gold Standard : BM iron staining There are 2 main categories of laboratory methods for identifying iron deficiency 1. Screening measurements that detect iron deficient erythropoiesis (IDE) : Hb, Tf sat, MCV, Percentage hypochromic erythrocytes, Reticulocyte hemoglobin content, Zinc protoporphyrin (ZPP) 2. Definitive measurements that evaluate tissue iron status : 2.1 Storage iron : serum ferritin, BM hemosiderin 2.2 tissue iron : serum transferin receptor (sTfR) - Causes of IDA I. Increased Iron requirement 1. Blood loss : GI, GU, RS, Blood donation 2. growth 3. Pregnancy and Lactation II. Inadequate iron supply 1. Dietary insufficiency of bioavailable iron 2. Impaired absorption of iron 3. Intestinal malabsorption : Gastric surgery, impaired iron transport - การส่ งตรวจเพื่อหาสาเหตุข้ ึนกับข้อบ่งชี้ทางคลินิก เช่น (+) stool occult blood stool for parasite, panendoscopy - Iron study, serum ferritin - U/A, FBS, BUN/Cr Plasma iron and Transferrin saturation - Transferrin saturation, which equal the ratio of plasma iron to total iron-binding capacity, provide a measure of current iron supply to tissues. - Tf. Sat. < 16% often is used as the criteria for iron-deficient erythropoiesis - By contrast, the plasma iron and transferrin saturation are not reliably elevated with increased iron stores within macrophages, as occurs initially with transfusional iron overload, although the transferrin saturation may increase with parenchymal iron loading - Interpretaion of transferrin saturation is complicated by the substantial circadian fluctuations in plasma iron, as well as by dayto-day variation of 30% or greater - Furthermore, the plasma iron is decreased by infection, inflammation, malignancy, and ascorbate deficiency but increased by iron ingestion, aplastic and sideroblastic anemias, ineffective erythropoiesis, and liver disease. UA: sp.gr. 1.015, pH 7.0. albumin – negative, sugar – negative, cell – 0 FBS 122 mg%, BUN 12.1 mg/dL, Cr 0.8 mg/dL Iron study SI 10 mg/dL, TIBC 247 mg/dL, Tf sat 4 % (80-180) (280-480) (27-45) Stool exam: occult blood - positive Diagnosis: iron deficiency anemia Discussion treatment response to treatment duration of treatment indication for PRC transfusion TREATMENT - The goal of therapy is to supply sufficient iron to repair the hemoglobin deficit and replenish storage of iron Oral iron therapy - should begin with a ferrous salt, taken apart from meals in three or four divided doses and supplying a daily total of 150 to 200 mg of elemental iron in adult. - Ferrous sulfate is the most widely use, well absorbed, each tablets containing 60 to 70 mg of iron for adult - Administration between meals maximizes absorption - In pts. with a Hb concentration of less than 10 g/dL, this regimen will initially provide about 40 to 60 mg of iron daily for erythropoiesis, permitting red cell production to increase to two to four time normal and the Hb concentration to rise by about 0.2 g/dL/day - An increase of Hb concentration of at least 2 g/dL after 3 wk. of therapy generally is used as the criterion for an adequate therapeutic reaponse - For milder anemia, a single daily dose of about 60 mg iron per day may be adequate - After the anemia has been fully corrected, oral iron should be continued to replace storage iron, either empirically for an additional 4 to 6 mo. or until the plasma ferritin concentration exceeds approximately 50 mg/L • Most pts. are able to tolerate oral iron therapy without difficulty • The most common side effects are gastrointestinal • Either diarrhea or constipation can be treated symtomatically,because these symtoms do not relate to the dose of iron • Upper gastrointestinal tract symptoms seem to be dose related,usually occur within approximately 1 hr.after ingestion and may be mild • Administration with food or some drugs (e.g.antacid) or decreasing the dose will diminish the amount of iron absorbed daily and therapy prolong the period of treatment • Causes of refractory to treatment with oral iron therapy 1. poor compliance 2. concurrent loss 3. poor absorption 4. comorbid diseases;infection,inflammation,CRF,CNT dis.,malignancies 5. misdiagnosis Parenteral iron therapy Parenteral iron therapy with the risk of adverse reaction,should be reserve for the exceptional pts. Who 1. Remain intolerant of oral iron therapy despite repeated modifications in dosage regimen 2. Malabsorbed iron 3. Iron needs that can be met by oral iron therapy because of chronic uncontrolled bleeding or other sources of blood loss,such as hemodialysis • A screening test for iron malabsorption is the administration to the fasting pt. of 100 mg. of elemental iron as ferrous sulfate in a liquid preparation,follow by measurements of the plasma iron 1 and 2 hr.later • In an iron-deficient pts. With an initial plasma iron of less than 50 mcg/dL,an increase of 200-300 mcg of Fe/dL is expected;an increase in plasma iron of less than 100 mcg/dL suggests malabsorption and is an indication for a small bowel biopsy • Iron dextran ( suspension of ferric oxyhydroxide and low molecular weight dextran ) contains about 50 mg of elemental iron per ml. • Route;i.m. or i.v. • Side effects:anaphylactic shock,serum sickness synd. Other treatment • RBC transfusion if indicated • IDA is a clinical syndrome,looking for the cause and correct it Treatment - PRC 2 unit (HCT - FBC 1 x 3 CBC เพิม่ เป็ น 19 ต่ อ หลังการรักษา 2 สัปดาห์ Hb 6.0 g%, HCT 19 %, %) Gastroscope: ulcerative mass at body and antrum Gastric biopsy: poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma koilonychia Esophageal web Plummer Vinson syndrome Case 2 44 ปี CC: เหนื่อยเพลียง่ายมา 1 เดือน PI: 1 เดือนก่อนมีอาการเหนื่อยเพลีย ง่ายเวลาทางาน ร่วมกับมีอาการ เวียนศีรษะเวลาลุกขึ้นเร็วๆ มี อาการใจสั ่นเป็ นบางครั้ง อาการ เป็ นมากขึ้นเรื่อยๆ ระหว่างนี้ไม่มีไข้ ไม่มีเลือดออก ผิดปรกติที่อื่น ประจาเดือนมาปรกติ ไม่มีถ่ายดา Physical examination BP 120/80 mmHg, PR 86 /min, RR 16 /min Liver was palpable, 1 FB below RCM Spleen was palpable 1 FB below LCM Investigation CBC: Hb 7.7 gm%, HCT 20 %, WBC 8,300 /mm3. Platelet 317,000 /mm3 N 54 %, L 29 %, M 8 %, E 8 %, B 1 %, NRC 1/100 MCV 120 fl, MCH 33.6 pg, MCHC 36.3 g/dL, RDW 17.5 % (85-95) (32-36) Reticulocyte 12.7 % (32-36) (12-13.6) LFT: chol 116 mg/dL, alb 4.1 g/dL, glob 3.8 g/dL, TB 4.3 mg/dL, DB 0.4 mg/dL, ALT 9 U/L, AST 38 U/L, AP 65 U/L Discussion Diagnosis Further investigation A middle - aged woman with subacute anemia,jaundice and hepatosplenomegaly PBS:microspherocytes 3+,polychromasia and NRC Reticulocytosis Indirected hyperbilirubinemia Jump to first page AIHA AIHA represents a spectrum of disorders in which antibodies against self antigens on the erythrocyte membrane cause a shorten RBC life span. The serologic properties and consequent clinical characteristics distinguish 3 types of AIHA 1. Wam autoimmune hemolytic anemia : IgG antibody 2. Cold agglutinin disease : IgM antibody 3. Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria; IgG DonathLandsteiner antibody Jump to first page Diagnosis 1. History and physical examination - exclude causes of anemia : Blood loss, under production - confirm clinical of acquired hemolytic anemia and evaluation of severity - Look for secondary AIHA 2. CBC, PBS - Anemia with normal or high MCV - Anisocytosis, microspherocyte, polychromasia, NRC, Basophilic strippling - Autoagglutination (~ 30 % of cases) - Evan’s syndrome ?, CLL ? Jump to first page 3. Reticulocytosis 4. DAT (+) VE (Anti igG, Anti IgA, Anti C3d) 5. Others : Indirect bilirubin , urine urobilinogen 6. BM study : Plt , WBC , Reticulocytopenia, suspected disorder of BM such as CLL 7. Investigations that have been associated with warm autoimmune antibodies Jump to first page Investigation ที่จาเป็ นต้องทารวมทั้งการ work up หา secondary causes of AIHA Investigations ในผูป้ ่ วย AIHA ประกอบด้วย 3 ส่ วน 1. เพื่อการวินิจฉัย : CBC, PBS, Reticulocyte count, DAT, serum bilirubin, U/A 2. เพืื่อหา secondary causes of AIHA 3. เพื่อการวางแผนในการดูแลรักษาผูป้ ่ วย : หาโรคติดเชื้อที่อาจ เป็ น precipitating cause เช่น การเพาะเชื้อ : หาโรคที่อาจจะเลว ลง หลังการรักษา เช่น FBS, CXR, stool exam Jump to first page Secondary causes of AIHA 1. Autoimmune disorders : SLE, RA, Scleroderma, UC, APS 2. Lymphoproliferative disorders : CLL, HD, NHL, AILD 3. Infections : EBV, Hepatitisc, HIV 4. Hematologic malignancies อื่น ๆ : AML, MM, WM, MMM 5. BMT 6. Pregnancy 7. Solid tumor : thymoma, Teratoma, Kaposi sarcoma, ovarian dermoid cyst carcinoma (colon, kidney, Lung, ovary) Jump to first page 8. DPT vaccine 9. Immune deficiency states : Congenital immune deficiency states, Hypogammaglobulinemia, dysglobulinemia, Acquired immune deficiency states 10. Mucocutaneous Lymph node syndrome (Kawasaki disease) 11. Misc : Thyroid disease, Pernicious anemia, GBS, Evan’s syndrome, Primary biliary cirrhosis, muliply transfused patients with hemoglobinopathies - การ work up เพื่อหา secondary causes of AIHA ขึ้นกับว่าสงสัยโรคหรื อภาวะใด Jump to first page Coombs’ test – positive 2+ UA: Sp.gr. 1.005, pH 7.0, alb – negative, sugar-negative, cell o Anti HIV –negative ANA – negative, HBs Ag – negative, anti HCV – negative Diagnosis: AIHA Discussion Treatment response to treatment duration of treatment indication for PRC transfusion การรักษา 1. เริ่ มให้การรักษาเมื่อใด (TSH Practice Guideline 2000) - ควรให้การรักษาในผูป้ ่ วยที่มีอาการแสดงของ hemolytic anemia ชัดเจน - ผูป้ ่ วยที่ไม่มีอาการ แต่ตรวจพบ DAT (+) ve ไม่ได้เป็ นโรค มีส่วนน้อยที่จะเป็ น AIHA ในภายหลังจึงไม่จาเป็ นต้องรักษา 2. การรับไว้รักษาใน รพ. (TSH Practice Guideline 2000) - โดยทัว่ ไปถือว่าผูป้ ่ วยที่มีอาการรุ นแรงหรื อมีโอกาสที่จะมี การรุ นแรงได้มาก ควรรับไว้ดูแลรักษาใน รพ. Jump to first page ลักษณะของผูป้ ่ วย AIHA ท่ี่ควรรับไว้รักษาใน รพ. (คะแนน 7-9) 1. Hct <20 vol% 2. ไข้ 3. ซีดลงเร็ ว 4. อายุมาก (60 ปี ) 5. มีอาการหอบเหนื่อย 6. สับสน, ซึมลง 7. มีปัจจัยหลายข้อร่ วมกัน Jump to first page - ลักษณะของผูป้ ่ วย AIHA ที่สามารถดูแลรักษาที่ แผนกผูป้ ่ วยนอกได้ 1. เป็ นมานาน, อาการคงที่ 2. ภาวะซีดไม่รุนแรง 3. ไม่มีอาการของ Vital organ hypoxemia 4. สามารถมาพบแพทย์ได้ง่าย หากมีอาการมากขึ้น 5. อายุไม่มาก (< 60 ปี ) Jump to first page ยาที่ใช้ ในการรักษา 1. Steroids : standard treatment : dose 1 - 1.5 mg / kg / day of prednisolone : response rate 80 - 90 % : High dose dexamethasone (40 mhlday) : report response in 7 decompensate AIHA Jump to first page 2. Transfusion : Necessary for life -threatening patients due to severe anemia : Rapid onset, Reticulocytopenia, old age, pts with underlying cvs diseases, cerebrovascular disease : The least incompatible blood : Clinician must supervise the transfusion and insist on close observation of the pts. Jump to first page : HTR is not frequent but life threatening : Overtransfusion in the presence of high-output cardiac failure can easily lead to circulatory overload 3. Splenectomy : Indicate in pts who failure to treatment with corticosteroids or intactable side effects of corticosteroids : response rate ~ 80% in idiopathic AIHA : risk of splencetomy include surgical risk, severe infection and thrombocytosis Jump to first page 4. Immunomodulatory therapy : Alkylating agents ( cyclophosphamide, chlorambucil ), thiopurines (Azathioprine, 6-MP), Cyclosporine : Indicate in pts who failure to treat with corticosteroids delayed response, steroid dependant and relapsed cases : Response rate 20 - 50 % : severe side effects such as BM suppression, teratogenic effect, hemorrhagic cystitis, leukemogenesis 5. Rituximab therapy : Well - establish favorable safety profile Jump to first page : Induce remission within 1 wk to 3 mo : massive cytokine release leads to complications (hypotension fever, respiratory distress and immune suppression in long term use) 6. Plasma exchange : therapeutic advantage is in removal of the IgG and/or IgM plasma antibodies : there are some case report in occasional dramatic response 7. Others : Ing, Danazol, Vincristine, splenic irradiation, BMT, EPO therapy Jump to first page Tapering of steroid ไม่มีการศึกษาที่บอกชัดเจนว่า จะต้องให้ steroids นานเท่าใด และจะลด dose อย่างไร TSH Practice guideline 2000 แนะนา ให้ Prednisolone ขนาดแรกเริ่ มจน Het ถึง 30% จึงลดยาลงสัปดาห์ละ 10 mg จนเหลือวันละ 30 mg และลดขนาดลงช้าขึ้น เช่น ลด 5 mg ทุก 1-2 สัปดาห์ จนเหลือขนาด 10 - 15 mg แล้วจึงลดลงช้ามากขึ้นจน ส ามารถหยุดยาได้ Jump to first page Melody J. cuningham and Leslie E,Silberstein : Hematology Bassic and principles, 4th eds, 2005 “ In the absence of contraindications, prednisone is continued at the initial dose until the Hb reaches a level of 10 g/dL or greater, by which time transfusion should no longer be necessary. Thereafter, gradual reduction in the dose can begin, usually at a rate of 5 - 10 mg/wk. During Jump to first page this second phase of treatment, the divided daily prednisone dose can be consolidated into a single daily dose IF the renission remain stable after a dose of 10 mg/day is reached, further tapering over a 3- to 4month peroid can proceed with caution taken some hematologists will continue treatment for many months, at Low dose (e.g. 10 mg every other day), but the efficacy of this practice has not been investigated. Jump to first page Treatment Day 0 Day 3 Day 14 Day 30 HCT 20 24 33 40 Rx Dexa 5 mg x 4 Pred 4 x 3 Pred 4 x 3 Pred 4 x 3 Treatment Day 45 HCT Rx 42 Pred 2 x 3 Day 60 Day 90 Day 120 40 38 40 Pred 2 x 2 Pred 2 x 2 Pred 2 x 2 Case 3 ผูป้ ่ วยหญิงอายุ 28 ปี โสด อาชีพรับจ้าง บ้านอยูห่ นองคาย CC: เลือดออกตามไรฟั นมา 3 สัปดาห์ PI: 3 สัปดาห์ก่อน มีมีเลือดออกตามไรฟั นตลอดเวลา และออกมากขึ้น เวลาแปรงฟั น สังเกตว่ามี จุดเลือดออกเหมือนจุดยุง กัดตามตัว ไม่มีไข้ ไม่มีเลือดออกที่อื่น อุจจาระและปั สสาวะปรกติ ประจาเดือนปรกติ ไม่มีโรคประจาตัว ไม่ได้กินยาอะไรเป็ นประจา Physical examination CBC: Hb 15.3 gm%, HCT 46.8 %, WBC 9,600 /mm3, Platelet 22,000 /mm3 N 75 %, L 25 % Discussion Diagnosis Further investigation Index • A young woman with bleeding per gum and superficial skin bleeding • CBC&PBS:Isolated thrombocytopenia without abnormal RBC morphology Index ITP ; Diagnosis - Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) remains a clinical diagnosis made by the exclusion of other causes of thrombocytopenia. - It is based on pts history , physical signs , CBC and examination of peripheral blood smear Index - Criteria for diagnosis 1. Isolated thrombocytopenia 2. Evidence of peripheral destruction of platelet : BM study 3. No splenomegaly 4. Exclusion of other causes of thrombocytopenia 5. PAIgG (+) ve BM study Index - ตาม ASH Practice Guideline กล่าวว่ า ไม่ มีความจาเป็ นที่จะต้ อง ตรวจไขกระดูกในผู้ป่วย ITP ทุกราย หรื อการตรวจดังกล่าวควรใช้ เป็ น การตรวจเพิม่ เติมเท่ านั้น - ตาม TSH Practice Guideline มีความเห็นว่ าควรเจาะตรวจไขกระดูก ทุกราย (Consensus score = 8.0 + 2.7) และในกลุ่มผู้เชี่ยวชาญทีไ่ ม่ เห็นด้ วยแนะนาให้ เจาะใน กรณี ดังต่ อไปนี้ (9 8.0 + Index 1. ถ้ าประวัติและอาการไม่ typical 1.8) 2. ก่อนจะให้ การรักษาด้ วย steroid ( 9 + 1.8 ) 3. ก่ อนการตัดม้ ามเพื่อการวินิจฉัยที่ถูกต้ อง ( 9 + 1.8 ) 4. ถ้ าอาการไม่ ดขี นึ้ ( 9 + 3.0 ) - BM study จะมีลกั ษณะที่สาคัญ คือ Mgk ปกติหรื อมากกว่าปกติ และอาจพบตัวอ่อนได้ รวมทั้งลักษณะ Budding ลดลง หรื อหายไป ซึ่งบ่ งชี้ Plt turnover เพิม่ ขึน้ และ granulocytic กับ erythrocytic series ปกติ - ถือเป็ นการยืนยันการวินิจฉัยที่ดที ี่สุด Index Investigation ที่จาเป็ นต้ องทา • ตาม TSH Practice guideline 2000 ได้ แนะนาการตรวจทางห้ อง ปฏิบัติการที่เหมาะสมในคนไข้ ITP ซึ่งคงแตกต่ างกันไปตาม Clinical setting ในแต่ ละราย นอกเหนือจาก CBC+ PBS 1. การตรวจทีจ่ าเป็ น (คะแนน 7.0 - 9.0) : BMA, Anti HIV, urinalysis Index 2. การตรวจทีอ่ าจจาเป็ น (คะแนน 3.01 - 6.99) : LE cell, ANA*, DAT, LA, Serum complement, coagulation study, reticulocyte count, FBS*, BUN CR*, LFT, TFT, CxR* , Abdominal CT หรื อ ultrasound 3. การตรวจทีไ่ ม่ จาเป็ น (คะแนน 1.0 - 3.0) : PAIgG, Plt antigen specific antibody, Plt survival * ใน Pt. บางรายอาจเป็ นการตรวจทีจ่ าเป็ นได้ Index - ในต่ างประเทศการวินิจฉัย ITP จะขึน้ อยู่กบั ประวัติ ตรวจร่ างกาย ร่ วมกับดู CBC และ peripheral blood smear ซึ่งถ้ าเข้ าได้ กบั ITP การ ตรวจไขกระดูกก็ไม่ จาเป็ น ซึ่งการตรวจไขกระดูกอาจช่ วยแยก ITP จาก MDS (Atypical finding) หรื อ จาก Amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenic purpura หรื อจาก Alcohol induced thrombocytopenia หลังจากนั้นจึงมาแยก secondary forms ของ immune thrombocytopenia ออกจาก idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura Index - Secondary forms of immune thrombocytopenic purpura 1. Infections : HIV, Hepatitis C, H.pylori infection, infectious mononucleosis, 2. Collagen V ascular disorder : SLE, RA, Scleroderma, MCTD 3. Lymphoproliferative disorder : CLL, Lymphoma, Hodgkin’s disease, LGL leukemia Index 4. Drugs or toxic substance : heparin 5. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome 6. Autoimmune thyroid disease : Grave’s disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis 7. Others : IBD, primary biliary cirrhosis, sarcoidosis, posttransplantation BMA: normal cellularity, increase megakaryocyte, normal erythroid and myeloid series UA: sp.gr. 1.015, pH 7.5, protein– negative , sugar-negative, cell 0 ANA – negative, Anti HIV – negative HBsAg – negative, anti HCV-negative CXR –normal Stool exam – occult blood – negative, no parasite Diagnosis: ITP Discussion Treatment response to treatment duration of treatment other treatments Index - ตาม TSH Practice Guideline 2000 ได้ กาหนดแนวทางการรักษา ไว้ ดังนี้ 1. การรับผู้ป่วยไว้ รักษา ในโรงพยาบาล ผู้ป่วยที่ควรรับไว้ รักาาใน ร.พ ได้ แก่ 1.1 มีภาวะเลือดออกที่รุนแรงหรื อ เลือดออกในอวัยวะที่สาคัญอัน อาจเป็ นอันตรายต่ อชีวติ ไม่ ว่าระดับของเกร็ดเลือดจะเท่ าใดก็ตาม 1.2 มีระดับของเกร็ดเลือด < 20,000 ร่ วมกับมีเลือดออกตาม เยื่อบุ ต่างๆ 1.3 มีปัญหาว่ าอาจจะไม่ รับประทานยาตามที่แพทย์ สั่ง หรือมีความยากลาบากในการเดินทาง Index Emergency Rx • Emergency in cases of life-threatening bleeding e.g.ICH,GIH,Pulmonary hemorrhage,Gross hematuria etc.,usually related with plt. Count < 20,000/ml • Treatment modalities included high dose glucocorticoids(pulse methylprednisolone) ,IVIG+/methylprednisolone,high dose dexamethasone( 40 mg/day )with emergency splenectomy Index Rx at first Dx • • Depend on clinical severity and number of plt.count. Modalities of Rx 1. Observation 2. Corticosteroids 3. IVIG 4. Anti-(Rh)D 5. Splenectomy 6. Other การรักษาเริ่มต้ นที่เหมาะสมสาหรับผู้ป่วย ITP ผู้ใหญ่ (TSH Practice Guideline 2000) อาการทางคลินิก 1. ไม่มีอาการ 2. จ้ำเลือดเล็กน้อย 3. เลือดออกเยื่อบุ และช่องคลอด 4. เลือดออก อันตรายต่อชีวิต Index จานวนเกร็ดเลือด / การรักษาที่เหมาะสม (คะแนน 7 – 9 ) < 20,000 20,000-30,000 30,000-50,000 > 50,000 prednisolone prednisolone prednisolone สังเกตอาการ prednisolone prednisolone prednisolone Prednisolone prednisolone, prednisolone, prednisolone, Prednisolone Dexathethasone Dexathethasone Dexathethasone Dexamethasone / methylprednisolone / splenectomy / IVIG Index * Prednisolone 1 - 2 mg/ kg/ day , Dexamethasone 5 - 10 mg ทุก 6 hr, Methylprednisolone 1 gm / day x 3 days , IVIG 2 gm / kg ( แบ่ งให้ 2 - 5 วัน ) ** Anti-D (50 - 75 mg/kg) Alternative treatment - จากการประชุ ม ASH 2004 (Robert B Mcmillan) “Pts. With platelet counts <25 - 30,000/mL should be treated with the aim of obtaining a stable, safe platelet count (>30,000/ mL) on no treatment” Index Refractory ITP • After initial treatment with prednisolone,responding will occurred within 1-4 wk. • About 25%-50% of pts.show no response to treatment with corticosteroids and splenectomy • ASH 2004 (Robert B. McMillan) 1. All refractory pts.should be evaluated for an accessory spleen 2. Rx must be individualized,depend on the pt s level of activity and other clinical situations 3. The presence of significant clinical bleeding will require periodic emergency therapy Index Refractory ITP • TSH Practice Guideline 2000 • เฉพาะผู้ป่วยที่มอี าการ ควรได้ รับการรักษา โดยเฉพาะเมื่อมี มีระดับเกร็ดเลือด < 10,000 ส่ วนผู้ป่วยที่ไม่ มอี าการเลือดออก อาจพิจารณาให้ vinca alkaloid หรื อ dandzol ถ้ าระดับเกร็ด เลือด < 10,000 การรักษาที่ควรเลือกใช้ ได้ แก่ immunosuppressive drugs หรื อ IVIG ถ้ ามีอาการรุนแรง Index Refractory ITP • Refractory ITP 3 groups 1.Asymptomatic pts.(usually plt.count >30,000) 2.Pts. With occasionally bleeding (risk of bleeding when plt.count<30,000 likely to be responsed to occasionally high dose corticosteroids) 3.Bleeding pts.who have plt.count<30,000 Goal of Rx:maintain plt.count>30,000 Index “ ดัดแปลงจาก วันชัย วนะชิวนาวิน update on ITP เอกสารประกอบการ ประชุมวิชาการ ประจาปี ครั้งที่ 23” Index Splenectomy - splenectomy is recommend if 1. Safe platelet counts cannot be maintained 2. Remission is considered unlikely 3. Drug toxicity is severe 4. The approach becomes too burdensome (frequent blood tests, office visits, Lost work time, etc) Index (ASH 2004) - splenectomy ถือเป็ น second line treatment ในผู้ป่วย ITP ที่ไม่ ได้ ผล จากการรักษาด้ วย prednisolone, ได้ ผลดีประมาณ 50 -56 % ของผู้ป่วยที่ทาการรักษาด้ วยวิธีนี้ - Factors detemine response to splenectomy 1. Splenic sequestration of rsdiolabeled platelets 2. Response to treatment with IVIG 3. Age Index - Immunization with pneumococcal, H influenzae and meningococcal vaccines is advised at least 2 wk. Prior to surgery - IVIG, anti-D or steroids are used to boost the platelet count prior surgery - Approximately 75% - 85% of patients have and initial respense ; of these, 25% - 40% relapse within 5 -10 yr. - Complications of splenectomy 1. Risk of surgery 2. Risk of postsplenectomy infection Index TSH Practice Guideline & Splenectomy • TSH แนะนาให้ ตัดม้ ามในผู้ป่วยที่ล้มเหลวจากการรักษาด้ วย steroids และไม่ มีข้อห้ ามในการผ่ าตัดได้ แก่ 1. ผู้ป่วยได้ รับการวินิจฉัยและรักษามาแล้ วอย่ างน้ อย 6 สั ปดาห์ และระดับเกร็ดเลือดตา่ กว่า 10,000 แม้ ไม่ มี ภาวะเลือดออกก็ตาม 2. ผู้ป่วยได้ รับการวินิจฉัยและรักษามาแล้ วอย่ างน้ อย 3 เดือน และมีระดับเกร็ดเลือดขึน้ บ้ าง แต่ ยงั ต่ากว่า 30,000 หรื อ ยังมีปัญหาเลือดออกอยู่ Index Immunosuppressive Drugs • I.Second line therapy 1.Cyclophosphamide -starting dose 150 mg/day po. -adjusted to maintain mild neutropenia -response occur within 8-12 wk -if the count normalizes,full dose are given for 3 additional mo. And then treatment is stopped -pts. Should drink at least 2 quarts of liquid daily to prevent hemorrhagic cystitis and blood count should be monitor each week Index • 2. Azathioprine - initial dose of 150 mg/day po - adjusted to maintain mild neutropenia - response occur slowly,over 3-6 mo - in responding pts.,therapy should be continued at full doses for 12-18 mo. And then gradually tappered and discontinued Index 3. Cyclosporine :- The dose of 1.25 – 2.5 mg/Kg BID - Adjust based on cyclosporine and creatinine levels - 30% of pts. stopped therapy due to side effects 4. Mycophenolate mofetil :- Few pts. have been studied - starting dose 500 mg BID PO and increase to 1,000 mg BID after 2 wk. - Few side effects were noted Index II. Third line therapy : should be reserved for pts.with lifethreatening symptoms or extremely low platelet counts (<10,000/mL) : Stop therapy if there is no response after 2 courses : Responding pts. should receive 3 – 6 courses 1. High dose cyclophosphamide : 1 – 1.5 g/m2 q 4 wk. 2. Combination chemotherapy Index ดัดแปลงจากแนวทางการรักษา โรคโลหิ ตวิทยาในประเทศไทย สมาคมโลหิ ตวิทยา Index ดัดแปลงจากแนวทางการรักษา โรคโลหิ ตวิทยาในประเทศไทย สมาคมโลหิ ตวิทยา Treatment Day 0 Week 4 Week 6 Week 10 Week 14 ไม่ มีเลือดออก เลื อ ดออก ไม่ มีเลือดออก ไม่ มีเลือดออก ไม่ มีเลือดออก อาการ Cushing ไรฟั น appearance platelet 22,000 Rx pred 4 x 3 66,000 pred 3 x 3 19,600 pred 4 x 3 Endoxan 1 x 1 164,000 372,000 Endoxan 1 x 1 Taper off pred in 4 wk Endoxan 1 x 1