File
advertisement

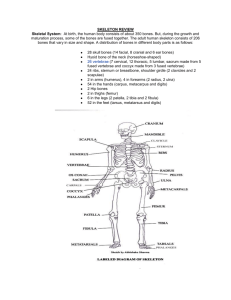
Anatomy Practical [PHL 212] Skeletal System Composed of the body’s bones and associated ligaments, tendons, and cartilages. FUNCTIONS: 1. Support The bones of the legs, pelvic girdle, and vertebral column support the weight of the erect body. The mandible (jawbone) supports the teeth. 2. Protection The bones of the skull protect the brain. Ribs and sternum (breastbone) protect the lungs and heart. Vertebrae protect the spinal cord. 3. Movement Skeletal muscles use the bones as levers to move the body. 4. Reservoir for minerals and adipose tissue 99% of the body’s calcium is stored in bone. 85% of the body’s phosphorous is stored in bone. Adipose tissue is found in the marrow of certain bones. 5. Hematopoiesis Blood cell formation (An average of 2.6 million red blood cells are produced each second by the bone marrow ). Skull Middle ears Hyoid bone Vertebral column Thoracic cage 22 bones (8 Cranial + 14 Facial) 6 1 26 (7 + 12 + 5 + 1 + 1) 25 Pectoral girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Pelvic girdle 4 60 60 2 Total bones 206 Axial Skeleton (supports and protects organs of head, neck and trunk) Skull (cranium and facial bones) Hyoid bone Vertebral Column (vertebrae and disks) Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Appendicular Skeleton Upper Limb Bones Pectoral girdle Lower Limb Bones Pelvic girdle (arms) (clavicles and scapulae) (legs) (coxal bones) Classification of Bones on the Basis of Shape Cranial Bones Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Sphenoid Ethmoid Facial Bones Mandible Maxilla Palatine Zygomatic Nasal Lacrimal Vomer Turbinate The Hyoid Bone The only bone that does not articulate with another bone Serves as a moveable base for the tongue The vertebral column consists of a series of irregularly shaped bones, called vertebrae. Each vertebrae is given a name according to its location. The vertebral column can be broken up into four sections. Neck - 7 Cervical vertebrae Thorax - 12 Thoracic vertebrae Abdomen - 5 Lumbar vertebrae Pelvis - Sacrum (5 fused vertebrae) and Coccyx (4 fused vertebrae) Vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs Vertebrae vary in size and morphology Structure of a Typical Vertebrae To protect major organs Made-up of three parts: Ribs, Sternum, Thoracic vertebrae Ribs ◦ Ribs give the chest its familiar shape. ◦ Protect the heart and lungs from injuries and shocks. ◦ Also protect parts of the stomach, spleen, and kidneys. ◦ Help you to breathe. Sternum (Manubrim, Body, Xiphoid process) Thoracic vertebrae The Appendicular Skeleton Limbs (appendages): Upper & Lower Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle The Appendicular Skeleton Arm Forearm Hand :Humerus :Radius & ulna :Carpals, metacarpals, phalanges Bones of the Upper Limb (The Arm) Bones of the Upper Limb (The Forearm) Bones of the Upper Limb (The Hand) The hand Wrist: Carpals (8) Palm: Metacarpals (5) Fingers: Phalanges (14) The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Composed of two bones Clavicle – collarbone Scapula – shoulder blade These bones allow the upper limb to have exceptionally free movement Bones of the Shoulder Girdle Femur Tibia, fibula Tarsals, metatarslas, phalanges Patella Bones of the Lower Limbs (Thigh) Bones of the Lower Limbs (Leg) Bones of the Lower Limbs (Foot) The foot (26 bones) Ankle: Tarsus (7) Sole: Metatarsals (5) Toes: Phalanges (14) Bones of the Lower Limbs (Patella) Bones of the Pelvic Girdle (Hip girdle) Coxal bones (Hip), innominate bone Composed of three pair of fused bones Ilium Ischium Pubic bone The total weight of the upper body rests on the pelvis Protects several organs Reproductive organs Urinary bladder Part of the large intestine The developing fetus in a pregnant woman The Pelvic Girdle Gender Differences of the Pelvis Joints Articulations of bones Functions of joints Hold bones together Allow for mobility Classification: Functionally Structurally 1. Immovable (synarthroses): Bones sutured together by fibrous connective tissue: e.g. Suture in the skull between skull bones 2. Slightly movable (amphiarthroses): Connected by fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage: e.g. vertebrae, rib/sternum joint, pubic symphysis 3. Freely movable (diarthrosis): Have joint cavity filled with synovial fluid ligaments- hold bones together tendons- muscle to bone lined by synovial membrane Structural Classification of Joints Fibrous joints Generally immovable Cartilaginous joints Immovable or slightly moveable Synovial joints Freely moveable Fibrous Joints [Synarthrosis or immovable] Bones joined by fibrous connective tissue Example: Suture in the skull between skull bones Cartilaginous Joints- Amphiarthrosis Bones connected by hyaline or fibro cartilage Examples: Pubic symphysis, Intervertebral joints, ribs sternum joint Synovial Joints- Diarthroses Have a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid Hyaline cartilage covers the ends of bones a. b. c. d. e. f. Gliding: Sliding and twisting. E.g. wrist and ankle joints Hinge: up and down movement in one plane. E.g. knee and elbow joints Pivot: Allow rotation around an axis. E.g. The neck and forearms. In the neck the occipital bone spins over the top of the axis. In the forearms the radius and ulna twist around each other. Condyloid: Movement in different planes but not rotations. E.g. Between metacarpals and phalanges Saddle: Allows movement back and forth and up and down, but does not allow for rotation like a ball and socket joint. E.g. Carpal and metacarpal bones of thumb Ball and socket: Allows for radial movement in almost any direction. E.g. Shoulder and hip joints Types of Synovial Joints Based on Shape Types of Synovial Joints Based on Shape Flexion: move lower leg toward upper Extension: straightening the leg Abduction: moving leg away from body Adduction: moving leg toward the body Rotation: around its axis Supination: rotation of arm to palm-up position Pronation:palm down Inversion: turning foot so sole is inward Eversion: sole is out Elevation and depression: raising body part up or down