Right Brain/Left Brain
advertisement
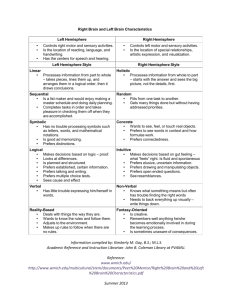
Right Brain/Left Brain What does it mean? An important factor to understanding learning styles is understanding brain functioning. Both sides of the brain can reason, but by different strategies, and one side may be dominant over the other. What does it mean? (cont.) A left brain (successive processor) prefers to learn in a step-by-step sequential format, beginning with details leading to a conceptual understanding of a skill. A right brain (simultaneous processor) prefers to learn beginning with the general concept and then going on to specifics. What does it mean? (cont.) A middle brain person shares those of both left brain and right brain characteristics. Middle brain often vacillate between the two hemispheres when making decisions. Who Am I? There are several ways to find out if your are left brain or right brain. Several online test are available to test your preferences and the way you approach problem solving. In HERE, Deb Holst’s Human Relations Class, is another location to obtain a brief understanding of what you are. Left Brain Brian Dominance Linear Symbolic Sequential Left Brain, Here You Are! Left brain individuals process information in a linear manner. They take pieces to the puzzle, line them up, and arrange them in logical order. From this drawing their conclusion to the puzzle. Left brain persons are list makers. They enjoy making a master schedule and doing daily planning. Left Brain, Here You Are! People of left brain are usually good spellers because spelling involves sequence. Left brains also work in the linear and sequential processing of math and following directions. They have no trouble processing symbols, memorizing vocabulary words and math formulas. Left Brain Characteristics Rational Respond to verbal instructions Controlled, systematic experiments Problem solves logically and sequentially looking at the parts of things Makes objective judgments Looks at differences Is planned and structured Prefers established, certain information. Left Brain Characteristics Analytic reader Primary reliance on language in thinking and remembering Prefers talking and writing Prefers multiple choice test Controls feelings Prefers hierarchical authority structures Talks, and talks, and talks Sees cause and effect Draws on previously accumulated, organized information. Right Brain Brain Dominance Holistic Concrete Random Right Brain, Here You Are! While left brain people think in logical order, right brain process from a whole to a part, holistically. Right brain have difficulty in following a lecture unless they are given the big picture first. It is important for a right brained person to read a chapter prior to lecture to better understand what is being discussed. Right Brain, Here You Are! The approach of a right brained person is random. Because of the random nature of a right brain, they should make list and schedules to help them stay on track. Right brain people are color sensitive. Try using colors to establish sequences. Right Brain, Here You Are! Right brain people are concrete. They want to see, feel, or touch the real object. Right brain individuals may have trouble learning to read using phonics. They prefer to see words in context and to see how formulas work. Create opportunities for hands on activities to use your right brain. Right Brain, Here You Are! When processing being a right brain, they use intuition. They may know the right answer to a problem, but are not sure how they got it. On a quiz, they have a gut feeling as to which answers are correct, and they are usually right. The right side of the brain pays attention to coherence and meaning, tells you if it “feels” right. Right Brain, Here You Are! Right brained people may know what they mean but often have trouble finding the right words. Right brain individuals need to back up everything visually. When giving directions, they use their hands and give names of places along the way verses hard north, south, east, west. Right Brain Characteristics Intuitive Responds to demonstrated instructions Open-ended, random experiments Problem solves with hunches, looking for patterns Makes subjective judgments Looks at similarities Is fluid and spontaneous Prefers elusive, uncertain information Bibliography “Right Brain/Left Brain, Learning Styles” www.mathpower.com/brain “Left vs. Right. Which Side Are You On?” www.mtsu.edu “Left Brain/Right Brain” http://content.scholastic.com Human Relations 1010 Nancy Conrad and Jackie