Reading
advertisement

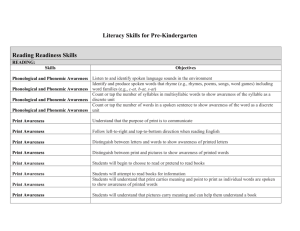
Reading EXC 7765 Teaching & Learning II Spring 2004 Standards Based Reform & Special Education IDEA 1997 Establish goals for the performance of students with disabilities that are consistent with goals & standards for all students Address and report on the performance of students with disabilities on assessments, graduation, drop-out rates Provide access for students with disabilities to the general education curriculum Research-based Best Practice “The ultimate beneficiaries of education research must be children, not the researchers themselves. Enlightened educators look to education research for well-founded evidence to help them do a better job with the children they serve” (Slavin, 2004, p. 27). Differentiation (Tomlinson, 1995, ED38914) • Variety of ways for students to explore curriculum content • Variety of sense-making activities or processes through which students can come to understand and “own” information and ideas • Variety of options through which students can demonstrate or exhibit what they have learned. Quality vs. quantity Differentiation (Tomlinson, 1999; Strieker, 2004) • Readiness: Readiness for a given skill, concept, or way of thinking (ability). Begin where students are. • Interests: Those things learners find relevant, fascinating, or worthy of their time. Engage students in instruction. • Learning Profile: Learning style, intelligence preference, processing preferences, and/or how the learner sees himself in relation to the rest of the world. Students learn in different ways Differentiated Instruction (Tomlinson, 1999) Grouping Interest Modalities Rates of instruction Level of complexity Active exploration Highly complex PLANNING PYRAMID FEW WILL LEARN Functional or Access Skills MOST WILL LEARN Next important concepts or skills ALL WILL Learn Most Important Concepts & Skills http://www.nrrf.org/synthesis_research.htm A Synthesis of Research on Reading from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development by Bonita Grossen University of Oregon November , 1997 Phonemic awareness Children who are not phonemically aware are not able to segment words and syllables into phonemes. Consequently, they do not develop the ability to decode single words accurately and fluently, an inability that is the distinguishing characteristic of persons with reading disabilities. Phonological Processing Component Skill Phonological Awareness Assessment Say cat without the /t/ sound Phonological recoding in Name objects, letters, lexical access (Rapid colors quickly naming) Phonological recoding in Repeat sentences, words, working memory or digits accurately. Key principles of effective reading instruction identified in the research 1. Begin teaching phonemic awareness directly at an early age (kindergarten). 2. Teach each sound-spelling correspondence explicitly. 3. Teach frequent, highly regular sound-spelling relationships systematically. 4. Show children exactly how to sound out words. 5. Use connected, decodable text for children to practice the sound-spelling relationships they learn. 6. The use of interesting stories to develop language comprehension. Balance, but don't mix. http://www.cornerstoneliteracy.org/ "To read, to write, to think critically, to reason, to analyze and evaluate information, to communicate effectively in a variety of forms, and to inquire systematically into any important matter." Proficient Reader Research Miller (2002) • Activating relevant, prior knowledge (schema) before, during, and after reading text (Anderson & Pearson, 1984) • Creating visual and other sensory images from text during & after reading (Pressley, 1976) • Drawing inferences from text to form conclusions, make critical judgments, and create unique interpretations (Hansen, 1981) • Asking questions of themselves, the authors, and the texts they read (Raphael, 1984) • Determining the most important ideas and themes in a text (Palinscar and Brown, 1984) • Synthesizing what they read (Brown, Day, and Jones, 1983) Stages of Reading Development • Readiness Listening comprehension Phonemic awareness • Beginning Reading Phonological processing Automaticity Reading comprehension • Functional Reading Locating information Following directions Organizing ideas • Recreational Reading Choosing appropriate reading materials Reading Comprehension Reading comprehension is viewed as the process of using one’s own prior knowledge and the writer’s cues to infer the author’s intended meaning (Johnson, 1981, p. 16). Reading comprehension requires active involvement by the reader. Strategy Use (Keene & Zimmerman, 1997) • • • • • • Uses schema (connections) Infers Asks questions Determines what is important in text Monitors comprehension Visualizes & creates mental images while reading Rand Reading Study Report (2001) http://www.rand.org/publications/MR/MR1465/index.html Reading comprehension capacity builds on successful initial reading instruction Text Activity Reader How Good Readers Process Text (Irwin, 1991) • Microprocesses – individual sentence level • Integrative processes – use of context • Elaborative processes – interaction with past • Macroprocesses – reading strategies for main ideas • Metacognitive processes – self-monitoring strategies Building Connections (Herrell, 2000) • Listening to proficient reader (teacher/parent) • Proficient reader stops to check understanding of new or key vocabulary words • Role play or act out new vocabulary words • Picture or realia to represent new vocabulary word • Repetition – reread/continue role play • Students use vocabulary in context – oral and then written • Repetition of student use in context. Crafting sessions • • • • • • Quality children’s literature Teacher model Student participation Active engagement Monitor Review Vocabulary Journals New words How I used my word Flung I told my mom, “I flung my towel over the towel rack.” Intently I asked my dad, “What are you looking at so intently?” (He was impressed.) Vocabulary Instruction • Essential vocabulary – Survival – Literacy • Reading vocabulary – Comprehension – Semantic map • Content vocabulary – Comprehension – Relationships Levels of Word Knowledge (Snyder, 2003) • Unknown No idea at all what word means • Acquainted Must deliberately think about word in order to recall its meaning • Established Recognizes word and gives meaning to it easily • In-depth Word is thoroughly understood in all or most contexts; uses word flexibly; can associate it with range of experiences Processing unknown words • Unknown word: eleemosynary • Write the word • Context sentence: The philanthropist made an eleemosynary gesture. • Synonym: gratutious • Definition : Of or relating to alms or the giving of alms; contributed as an act of charity Learning New Words (Snyder, 2003) • • • • • • • • Label known concept Receptive – expressive oral vocabulary Oral – reading vocabulary Clarification & enrichment – known words New meanings for known words Multiple meanings for known words Receptive – expressive written vocabulary New words & new concepts Balance Genres Learning to read Reading to learn Surface skills Deep structure • • • • Listening Speaking Reading Writing http://www.standards.dfee.gov.uk/literacy/ Closure Differentiated practice activity Review Explicit Instruction Dimensions of Learning (Marzano, 1992) 1. Positive attitudes and perceptions about learning 2. Thinking involved in acquiring and integrating knowledge 3. Thinking involved in extending and refining knowledge 4. Using knowledge meaningfully 5. Productive habits of mind Vocabulary Enrichment & Dimensions of Learning (Marzano, 1992) 1. Positive attitudes and perceptions about learning 2. Thinking involved in acquiring and integrating knowledge 3. Thinking involved in extending and refining knowledge 4. Using knowledge meaningfully 5. Productive habits of mind Dimension 1: Positive attitudes and perceptions about learning • Task value – Student interest – Product choice • Wait time Stahl, 1994 (ED 370885) – Processing time – Active engagement • Guidance – Cues & prompts – Feedback March Madness < 1.5 > 3 seconds Crossword, “sounds like, synonym Vocabulary Instruction & Reading Comprehension (Smith, 1197, ED412506) Vocabulary instruction should be included across all areas of curriculum Direct involvement of students in constructing meaning is more effective that memorization techniques Study of relationships is important in content area reading Beginning with current student framework facilitates learning Dimension 2: Acquiring and integrating knowledge DeclarativeKnowledge KWL Representations Patterns Graphic Organizers Memory Strategies Vocabulary Frames are a flashcard method for learning new vocabulary. Do not use Vocabulary Frames for every vocabulary word encountered. Words that introduce new concepts are best used with Vocabulary Frames. Top Right Corner: Write the word’s definition top Left Corner: Write the word’s opposite and cross it out Lower Left Corner: Write a silly sentence that uses the definition of the word Lower Right Corner: Draw a graphic to help you visualize the concept In the Center: Write the word Isolate any prefixes Isolate the root Note the meaning of the root Isolate any suffixes Label the part of speech in parenthesis http://litsite.alaska.edu/uaa/workbooks/readi ngvocabulary.html WRITING YOUR OWN DEFINITION DEFINITION WORD CHART http://www.tandl.leon.k12.fl.us/lang/Elementary/Anchorvoc.html Word Things I know about the word General category this word might belong in Examples of other related words My definition Dimension 2: Acquiring and integrating knowledge Procedural Knowledge Algorithms Strategies General rules Analogies Think Aloud Flow Charts Latin & Greek Roots • http://www.quia.com/jg/275995.html • http://english.glendale.cc.ca.us/quizr.html • http://hyper.vcsun.org/HyperNews/nherr/get /SED646/S99.1/104.html?nogifs • http://www.resourceroom.net/Comprehensio n/index.asp Dimension 3: Extending and refining knowledge • • • • • • • • Comparing Classifying Inducing Deducing Analyzing errors Constructing support Abstracting Analyzing perspective Dimension 4: Using knowledge meaningfully • Application-oriented tasks • Long-term tasks • Student-directed tasks Dimension 5: Productive habits of mind • Self-regulated thinking and learning • Critical thinking and learning • Creative thinking and learning Integrating & Weaving Vocabulary Instruction Across the Curriculum • Graphic organizers • Compare/contrast • Preview strategies Facilitating retention, understanding & independent application Elaboration Techniques • Teach new vocabulary in context (meaningful subject-matter lesson) • Select vocabulary that is: – Key to understanding – Repeated • Facilitate student discussion to promote use of new term • Build on previous knowledge • Use examples/non-examples • Use multiple formats Clarifying Table (Titanic) Term Elitism Core Idea being especially proud of belonging to a small group who thinks its superior Use it to describe Clarifiers Knowledge connections Example of: “Superior to others” belief Snobby acting movie stars “more valuable” belief Snobby acting Aristocracy, super-rich, celebrities Integrating & Weaving Vocabulary Instruction Across the Curriculum • Graphic organizers • Compare/contrast • Preview strategies Facilitating retention, understanding & independent application Elaboration Techniques • Teach new vocabulary in context (meaningful subject-matter lesson) • Select vocabulary that is: – Key to understanding – Repeated • Facilitate student discussion to promote use of new term • Build on previous knowledge • Use examples/non-examples • Use multiple formats Clarifying Table (Titanic) Term Elitism Core Idea being especially proud of belonging to a small group who thinks its superior Use it to describe Clarifiers Knowledge connections Example of: “Superior to others” belief Snobby acting movie stars “more valuable” belief Snobby acting Aristocracy, super-rich, celebrities Stages of spelling development • Readiness 20xot7 • Prephonetic TR • Phonetic tejr • Transitional teechir • Correct teacher Communication Disorders • Language - cognitive function • Form: • Phonology • Morphology • Syntax (sounds) (parts) (grammar) • Content – Semantics (vocabulary) • Use – Pragmatics (function) Language Disorders • Pragmatics – – – – – – Function or use of language What to say Who to say it to When to say it How to say it Under what circumstances Expansion of Expressive Vocabulary • • • • • • • Opportunity Model Expansion Establish Transfer Maintain Correction http://toread.com/ http://www.brainconnection.com http://www.ncrel.org/sdrs/timely/briiss.htm http://www.ncrel.org/sdrs/timely/brires.htmhttp://www.ericfac ility.net/ericdigests/ed435986.html http://www.indiana.edu/~eric_rec/ieo/digests/d144.html http://www.indiana.edu/~eric_rec/ieo/bibs/balanced.html http://www.dfes.gov.uk/index.htm