Human Reproductive System
advertisement

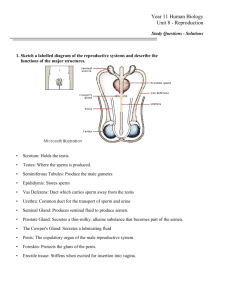
Human Reproductive System Mr. Erick Santizo Vocabulary puberty Estrogen Hormone Projesteron sex organs Menstruation Testosterone Ovulation growing pains, Nocturnal Puberty The period of life when a person’s sexual organs mature and he or she becomes able to have children Am I Normal? 1. Females start to develop ______________________ (7) 2. While going though puberty your emotions can fluctuate. At times you can be depressed or ______________________ (5) 3. Boys and girls develop ______________________ (5) hair. 4. Male genitalia increase in size. This includes the testes, scrotum and _________________ (5) 5. The release of an egg from the ovaries is called ______________________ (9) 6. Slang name for menstruation is ______________________ (6) 7. Estrogen for females and testosterone for males are two ______________________ (8) responsible for many of the obvious sexual changes during puberty. 8. A „wet dream‟ is the slang term used for a ______________________ (9) emission. 9. In boys especially, the voice becomes deeper and ______________________ (5) Create a table for puberty between Males females Genitals increase in size Develop breasts Develop pubic hair Develop pubic hair Broaden shoulders Hips widen Deepening of voice Increase in muscle size Males Females Female Reproductive system Ovary: where the eggs are produced Uterus: the womb Endometrium: inner mucous membrane of the female Cervix: the narrow end at the opening of a woman’s uterus Fallopian tube: pair of tubes that carry the egg from the ovary to the uterus Vagina: a canal that leads from the uterus to the external part Ovaries: The ovaries are small, ovalshaped glands that are located on either side of the uterus Female Reproductive System Side view Female reproductive system Video Quiz #1 1. when a boy or a girl undergoes changes _________? 2. when an ova is released from the ovary.. 3. slang name for menstruation 4. pathway for the ova from the ovary to the uterus 5. name a difference on puberty in girls and boys. 6. Oily skin only occurs in boys : True or false 7. slang name for Nocturnal Emission. 8. The muscle that keeps anything from entering the uterus EXCEPT Sperm cells. 9. name a similarity on puberty between girls and boys. BONUS: How many ovas females are born with Male Reproductive System Side view The purpose of the organs of the male reproductive system is to perform the following functions: To produce, maintain, and transport sperm (the male reproductive cells) and protective fluid (semen) To discharge sperm within the female reproductive tract during sex To produce and secrete male sex hormones responsible for maintaining the male reproductive system Male Reproductive organ Parts and functions Erectile tissue: fills with blood for arousal for penetration in sexual intercourse Epididymis: holds sperm during maturation. Testis: sperm is produced Vas deferens: sperm duct; pathway for sperm Urethra: passage way for urine and semen Seminal vesicle: gives sugar and protein fluid to make semen Prostate gland: produces the liquid texture for semen Sperm cell Sperm cell Acrosome: enzyme found at the tip of the head of the sperm cell which helps in breaking down the jelly coat of the egg cell to fertilize the egg. Menstruation Why do you have a period? What is really going on? When will you get your period? How long will it last? Menstrual cycle Menstruation if fertilization doesn’t occur, the lining (endometrium) is then discharged with blood and mucus through the vagina. Menstrual Calendar Video Quiz #2 1. What Hormone is released from the hypothalamus that stimulates secretion of follicle stimulating hormone in the pituitary gland? 2. What is the function of FSH in ovulation? 3. What does LH mean? 4. What is the Function of LH and where is it released? 5. When the Graafian follicle is expelled during ovulation what is the scar tissue formed? 6. What hormone does the scar tissue or “yellow body” release and why? 7. What days is the bleeding stage? 8. At what stage will progesterone levels be high? Differentiate ova and sperm cell. Sexual intercourse Copulation: sexual intercourse: when a man becomes sexually excited, the penis becomes erect and stiff. This is due to an increase in blood pressure in the erectile tissue spaces surrounding the urethra. The penis is inserted into the vagina of the woman and movement causes Ejaculation of semen into the vagina. Ejaculation: is brought about by contraction of the muscle surrounding the urethra. This expels semen through the urethra into the vagina. Fertilization Fertilization: The Fusion of sperm nucleus with the nucleus of the ovum/ova which occurs within the oviduct. Implantation Implantation: When the fertlize egg (zygote) divides into a ball of cells called a blastocyst and sinks into the wall of the uterus and develops into an embryo. pregnancy Fetus Uterus wall: muscular for contraction at birth, protects fetus Amnion: membrane enclosing fluid, protecting fetus from shock and allowing movement. Umbilical cord: carries nutrients in vein and waste in artery. Placenta: contains villi, formed from fetus and mother, act as a barrier for blood , bacteria Villi: large surface Birth Birth stages stage1: contraction of muscles of the uterus. Labour starts; to push out the baby. This is possible because of a hormone called oxytocin which starts contractions. Stage2: increasing contractions of the uterine muscle push the baby through the cervix and then the vagina. Stage 3: finally the baby is expelled head first. After birth: the umbilical cord is cut and tied so that the remains from the navel on the abdomen. The placenta and membranes are shed from the mother and are called afterbirth. Child birth: Kris caliz Ceaserian (C-section) Contraceptives Ways or devices that are used to prevent a women from becoming pregnant. Family planning More time and care and education It is less expensive Parents career Old parents: no kids, birth defects Types Natural Abstinence Withdrawal of penis Rhythm method Artificial Spermicidal cream only Condom Diaphragm with spermicide IUD (inter Uterine Device) Contraceptive pill Injection Sterilization (tubal ligation and Vasectomy) Withdrawal of the penis Remove penis from vagina before ejaculation Very unreliable because of sperm leakage Can get infections: STDS Rhythm method Use of SAFE PERIOD. Unreliable because of cycle variations Can get infections Ovulation may be later or Early Spermicidal Cream Unreliable Best used with other methods: condoms, diaphragm infections Condom Very reliable Prevents : STDs Can break Diaphragm with spermicide Very reliable Doesn’t prevent infections May move Inter Uterine Device Very reliable Prevents implantation Doesn’t prevent infection Can be moved Inserted only by a doctor Daily Birth control pill Reliable Tricks body into being pregnant Should be taken daily Help regulate menstraul cycle Reduce menstraul cramps Decrease risk of anemia Improve acne Weight gain Costly Heart conditions Morning after pill Can be taken three days after sexual intercourse Available in pharmacies Emergency pill Side effects: nausea, vomiting and cramps Levonorgesterol: should not be for allergic persons Depo-Provera injection A shot in the arm that prevents pregnancySafe, effective, and convenient Easy to get with a prescription Lasts for three months Costs $35–$100 per injection, Sterilization First type: Females AKA Tubal ligation Tubal ligation: different ways for tubal ligation; cauterization, Sterilization (males): Vasectomy Quiz#4 1. Prevents women from becoming pregnant 2. Two types of ways in “tricking the body into being pregnant” 3. Also know as the emergency pill. 4. Two types of sterilization methods 5. name two natural methods? 6. Covers the cervix 7. The best method of preventing pregnancy? Bonus: What is Ejaculation?