force
advertisement

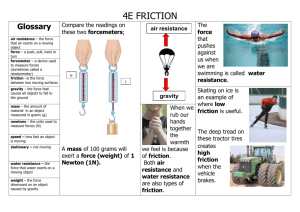
Types of Forces Gravitational Force An attractive force between all objects that have mass. On Earth gravity is a downward force, always pulling objects towards the center of Earth Weight and Mass Mass is the amount of matter in an object and does not change with location. Weight is the gravitational force on an object and changes with location. Friction Friction is a force that opposes the movement between two surfaces in contact. EXAMPLE A book pushed across a table slows down because of friction. Static Friction The force between two surfaces in contact that keeps them from sliding when a force is applied. EXAMPLE A force is applied to a heavy box, but the box doesn’t move. The forces are balanced, the force pushing the box equals the force of static friction pushing in the opposite direction. Kinetic Friction Friction force that acts on objects that are moving EXAMPLE The frictional force that acts on the sliding book is called kinetic friction. Fluid Friction A force that opposes the motion of an object when an object moves through a fluid Air Resistance Fluid friction acting on an object moving through the air Elastic Forces An elastic force occurs when a material is stretched or compressed. EXAMPLE A diving board exerts an upward elastic force on the diver when it is bent downward. Elastic Force: Tension A pulling force exerted by an object when it is stretched, such as a rubber band. Elastic Force: Compression A pushing force exerted by a material when it is squeezed or compressed. The size of the compression force exerted by a material is equal to the size of the force that compresses the material. Normal Force The force exerted by an object that is perpendicular to the surface of the object. Weight acts in a direction opposite of a normal force The support force exerted upon an object that is in contact with another stable object EXAMPLE The cup is exerting a downward force on the table, caused by gravity. The table is exerting an upward normal force on the cup, caused by compression. Normal Force Gravity Forces in the Vertical Direction Upward normal force balances the downward force of gravity on an object that is not moving vertically. Centripetal Force A force that makes an object follow a curved path As an object moves in a circle, it is constantly changing its direction. Because of this direction change, you can be certain that an object undergoing circular motion is accelerating (even if it is moving at constant speed) Without a centripetal force, an object in motion continues along a straight-line path. Force Diagrams Normal Force Friction Applied PUSHING Force Gravity 20 N 5N 15 N 3N You try With your group, create a situation in which normal force, gravity, and friction affect the overall motion of an object. Draw a force diagram that represents the situation. Be ready to present the situation to the class. EXAMPLE A person is trying to move their book across the table. Gravity causes a downward force on the book, normal force acts in an upward direction, a force is applied in one direction and friction acts in the opposite direction of the applied force. YOU MAY NOT USE THIS EXAMPLE!!! Force Diagram WKSHcomplete it Addressing Misconceptions Sustained Forces Objects do NOT require a sustained force to stay in motion. FRICTION causes objects to slow down. EXAMPLE: A car’s engine propels it forward. Friction between the tires and the road, and between the body of the car and surrounding air, cause the car to slow down. Newton’s First Law of Motion If there is will NO FORCE acting on an object, the object not CHANGE it’s motion. Newton’s first law: An object in motion STAYS in motion UNLESS a force acts on it? What force causes a ball rolling on the ground to slow down and eventually come to a stop?