Ming and Qing Dynasties
advertisement

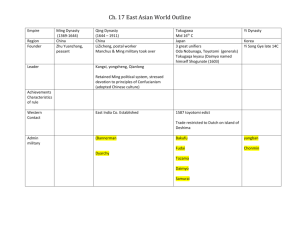
Ming and Qing Dynasties Last 3 Dynasties (Beijing) • Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368) – Mongolian – north of China proper • Ming Dynasty (1368-1644) – Han Chinese • Qing Dynasty (1644-1911) – Manchu – northeast of China proper Confucian culture • modern concept of political nation state • Chinese defined by Confucian culture • civil service exam (605-1905) – social mobility – reward diligence, discipline, and willpower, but not talent or innovation • law of avoidance • “sum of social relationships” Social hierarchy and mobility • scholar-officials, farmers, artisans, and merchants • scholar-official-landlord – learning, political power, and economic wealth • local elite (gentry) and lineage • lack of work ethic – literati’s long gown – foot-binding for women Ming Dynasty (1368 - 1644) China’s Tributary System • Traditional system for managing foreign relations • The ``Central Kingdom” worldview • Ming dynasty had the most extensive tributary system – tributes from East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and even West Asia and Africa Zheng He’s fleet (1405 - 1433) • Over 300 ships & 20,000 men • trade and commerce • Southeast Asia, South Asia, West Asia, and East Africa Zheng He’s expeditions Qing Dynasty (1644 - 1912) • Ming dynasty fell in 1644 amid peasant uprisings and Manchu invasion • Manchu and Han Chinese Ming and Qing Emperors Mandate of Heaven The 6 Bu • Ministries • 6-Bu system started in early Tang Dynasty (618 - 907) The 6 Bu (ministries) • • • • • • Ministry of Personnel Ministry of Revenue Ministry of Rites Ministry of Military Ministry of Criminal Justice Ministry of Public Works Emperor & Macartney (1793)