Protozoans
advertisement

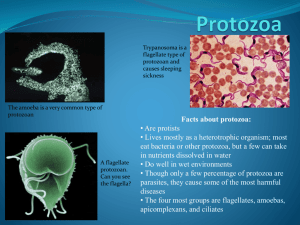
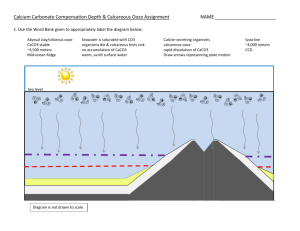
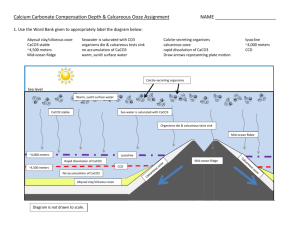
Protozoans Caroline Fowle, John Ligtenberg Rhizopoda • Pseudopodia • Amoeba – Many Nuclei – Contractile vacuole • Radiolarians – Thin, tall pseudopodia – Central capsule • Heliozoans – Simpler scales and spines http://youtube.com/watch?v=7pR7TNzJ_pA Differences • Heliozoans: – Microtubule projections smaller – Axopods • Radiolarians: – Have central capsule • Amoeba – Multiple Nuclei – Contractile vacuoles Foraminiferans • • • • Cytosol extends out Calcium shells Decompose to calcareous ooze Alternation of generations – Gamont: single nucleus – Schizont: multiple nuclei Uses of Forams • • • • Act as bioindicators Are used to locate oil Relative dating of rocks Reconstructing ocean currents Calcareous Ooze • • • • Calcium based Not in deep sea Decomposed organisms Covers 1/3 of earth’s suface Paramecium Unique structures: Cilia 2 types of nuclei Contractile vacuole Terms: Syngamy Micro/macronuclei Conjugation Soccer Game Questions 1. Calcareous ooze is formed by what? 2. Which type of protozoa has two types of nuclei? 3. What are 3 uses for foraminiferans? 4. Foraminiferans have shells composed of what element? 5. What is the fusion of 2 haploid micronuclei to create a diploid? 6. Because of its freshwater environment what organelle is used? 7. How does (answer to number 6) function? 8. Which microtubule is used by paramecium? 9. What is this: 10. A? 11. B? (Same picture as 10) 12 and 13: describe the step A 12 B 13 Soccer Game Questions 14. What is the diploid stage of a foraminifera called? 15. What do foraminiferans become after they die? 16. Name a difference between heliozoans and radiolarians. 17. What is the haploid stage of a forminifera called? 18. What are the “spokes” coming off heliozoans called? 19. How do radiolarians stay bouyant? 20. Which rhizopod has a contractile vacoule? 21. Name a use of calcareous ooze. 22. What do Rhizopds use to move? 23. What is the rhizopod in picture A? 24. What are the objects in picture B? 25. What is the principal compositions of calcareous ooze? B A