Ppt. 2 (Taxonomy)
advertisement

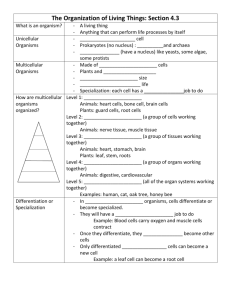
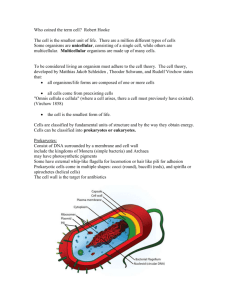
Taxonomy Biological Classification Taxonomy- the classification of an organism based on several key features. Behavior Lifecycle Genetic makeup (DNA) Nutritional needs Methods of obtaining food Taxonomy divides organisms Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species- most specific category (these organisms are grouped together based on their ability to breed and produce fertile offspring) Naming Species Carl Linnaeus Aristotle • Made current system for classifying organisms. • Binomial nomenclature- a system of naming organisms using a two-part name to label a species. • Made the first recorded attempt of classification of plants and animals. • The binomial name is written in Latin and is considered the scientific name. • He grouped everything into 2 groups: Plants and animals • Generic name (genus) specific (species) • Animals were broken into (Blooded and bloodless) Naming Example: Genus Is Capitalized And Species Is Lower Cased. The Whole Name Is Italicized Or Underlined. Canis lupus Genus Species The Six Kingdoms Super Kingdom Kingdom Basic Characteristic Example Bacteria Eubacteria Found everywhere Cyanobacteria Archaea Archaea Lives without oxygen, gets energy in inorganic matter or light, is found in many habitats Halophiles Eukaryote Protista One-celled or multicellular, has true nucleus Amoeba Fungi Multicellular feeds on dead organism, cannot move Mushroom Plantae Multicellular, cannot move, makes own food, has cell walls Tree Animalia Multicellular, moves about, depends on others for food horse Three Types of Domains 1.Eukarya- multicellular organisms 2.Eubacteria- true bacteria 3.Archaea- ancient (harsh) bacteria Protista Contains a diverse group of unicellular and multicellular organisms Plant-like protists -algae Have chlorophyll-containing chloroplasts Autotrophs- Make their own food Animal-Like protist (Protozoa)- one celled organisms Heterotrophs- cannot make their own food Parasites living in water, on soil, and on living or dead organisms Move using a flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia Flagella Cilia Pseudopodia Fungi Heterotrophic organisms that secrete enzymes, allowing them to digest their food. Unicellular or multicellular organisms Contains a cell wall (made of chitin) Live in an aquatic or moist environment Decomposers- live in or on the matter that they break down as they us it for food Ex: Bread (mold), Blue cheese, Foot fungus Reproduce sexually (spores) or asexually (mitosis) Plantae Multicellular Organisms That Have Eukaryotic (With Nucleus) cells. Contains a cell wall (made of cellulose) Use photosynthesis to obtain food and are producers Structures of plants Nonvascular Plants- lack tissues used to transport substances like water and sugars. • Vascular plants-contain specialized structures for conducting substances and as a result can live in drier environments than the nonvascular plants. Xylem-transports water Phloem- transports sugar Vascular Tissues Animalia Multicellular Organisms Made Of Eukaryotic Cells Bodies are organized into one of 4 distinct body plans: radial, segmented, bilateral, or asymmetrical Animals are heterotrophic Most reproduce sexually but some reproduce asexually All animals are capable of movement at some stage in their lives Some provide parental care, but most do not Radial Symmetry Bilateral Symmetry Segmented Symmetry Asymmetrical Animals Invertebrates Animals without a backbone. Most abundant group of animals Multicellular and most form tissues, organs and organ systems Reproduce sexually and asexually VertebratesAnimals that have a backbone. Shared characteristics: 1.notochord- a firm flexible rod that provides support and stability. 2. Pharyngeal pouches- tissues (in fish these tissue for gills) Ex: ear and jaw structures 3. Endoskeleton-internal skeleton composed of bones, cartilage or both Archaea Bacteria Prokaryotic (no nucleus) bacteria that thrive in many habitats Considered consumers or decomposers Structured cell wall, cell membrane and ribosomal RNA. Archaea are anaerobic, which means they cannot tolerate Oxygen Reproduce asexual reproduction through budding or binary fission Microbes Archaea Habitats Methanogens- Produce Methane Gas And Live In Places As The Soil And In The Intestines Of Herbivores Halophiles- live in extremely salty environments like the Dead Sea Thermoacidophiles-live in areas like the acidic sulfur springs of Yellowstone National Park and under sea vents Important to agriculture, waste water treatments and biotechnology Eubacteria-true bacteria Prokaryotic-one celled Do not have a nucleus They have a cell wall, cell membrane and circular membrane called plasmid Cause toxins Types of bacteria: cocci, bacilli, spirilla Eubacteria classified Heterotrophs-found Nearly Everywhere, Need Organic Molecules As An Every Source And Feed On Living Organisms, Dead Organisms, Or Organic Waste. Considered consumers or decomposers Autotrophs- photosynthetic bacteria that are found in ponds, lakes, streams and most areas of land Ex. Cyanobacteria (blue- Algae) Chemotrophs- obtain energy from the breakdown of inorganic or nonliving substances such as nitrogen and sulfur compounds Cyanobacteria Bacteria- types Name of disease Symptoms Syphilis Painless, skin rash, heart problems, mental problems, blindness or even death Leprosy Skin lesions and sometimes stuffy nose Tetanus Muscle spams in the jaw, spams of skeletal muscles, difficulty swallowing and muscle stiffness Tuberculosis Fever, ongoing cough that bring up thick, cloudy and sometimes bloody mucous, fatigue, weight loss, night sweats, and rapid heartbeat Peptic Ulcers Burning pain in stomach, vomiting and black stools Viruses A Small Particle That Contains Proteins And Hereditary Material (DNA Or RNA) but IS NOT ALIVE Contain a protein coat or capsid Must have a host cell DiseasesSmall Pox Flu Influenza Polio Influenza virus