Upper and Lower Egypt - Mr. Csage's History Classes
advertisement

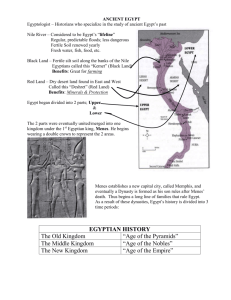
First Civilizations: Africa and Asia 3200 B.C.E.-500 B.C.E Ancient Kingdoms of the Nile Geography of the Nile Valley 1. 2. Yearly Floods Uniting the Land Two distinct regions 1. 2. Upper Egypt in the south Lower Egypt in the north Upper Egypt Stretched from the first cataract or waterfall of the Nile northward to within 100 miles of the Mediterranean. Valley of the Nile is 500 miles long, measured from the First Cataract. Until it reached the delta it is only a few miles in the valley. Flooding irrigated the land. Menes, the King of Upper Egypt, united both the upper and lower Egypt in 3100 B.C.E. Early Civilization in Ancient Egypt Farming began in the Nile Valley after 6000 B.C.E. Climate was much wetter, even farmed in the area that is now the Sahara desert. By 4,000 B.C.E, the climate was drier and the Sahara had turned to desert. Some of the farmers had returned nomadic life and others migrated to the Nile Valley. By 3,000 B.C.E, a kingdom in southern Egypt had emerged. The use of hieroglyphics as the form of writing had been developed. Hieroglyphics http://www.kingtuttreasures.com/hiero.htm Upper and Lower Egypt 6000 B.C.E. Farming begins in the Nile Valley 3300-3100 B.C.E. 3000 B.C.E The first towns develop. The hieroglypic script is invented. Upper and Lower The first pyramid Egypt united into is built for king one kingdom. Djoser at Saqqara Timeline 2630 B.C.E Early Dynastic Period A dynasty is when one ruling family passes power to another. Power of the king is derived from belief that the king was the son of the sun god Ra and was thought to be immortal. Egypt is united into one kingdom Established Memphis as the capital, placed in between the two areas. 2940-2649 B.C.E Old Kingdom 2649-2134 2490-2452 B.C.E. 2134-2040 Unknown Sphinx 2589-2566 B.C.E. Khufu’s Pyramid Built on the Giza Plateau 2558-2532 2575 B.C.E. B.C.E. Khafre’s During the fourth Dynasty, Pyramid Built on the Giza royal power Plateau increases dramatically B.C.E. Menekaures’s Pyramid Built on the Giza Plateau B.C.E. First Intermediate Period Egypt is divided into 2 kingdoms. The Old Kingdom Pharaohs were the Egyptian rulers who organized a strong, centralized state. 1. 2. 3. Pharaohs claimed divine support for their rule. Believed the pharaoh was a god Had absolute power, owning and ruling all the land in the kingdom. Pharaohs had a vizier, a chief minister who supervised the business of government. 1. 2. Supervised departments such as tax collection, farming, irrigation system. Scribes Pyramids Khafre Khafre was the son of Khufu, was also known as Rakhael or Chaphren . He ruled from 2520-2494 B.C. And is responsible for the second largest pyramid complex at Giza, which includes the Great Sphinx, a Mortuary Temple , and a valley temple. The most distinctive feature of Khafre’s Pyramid is the topmost layer of smooth stones that are the only remaining casing stones on a Giza Pyramid. Pyramid Built: 2558-2532B.C. Average weight of individual blocks of stone: 2.5 tons Height: Originally 471 feet, now 446 feet Base: 704 ft. Khufu King Khufu, who is also known by the greek name, “Cheops,” was the father of pyramid building at Giza. He ruled from 2589-2566 B.C. and was the sun of King Sneferu and Queen Hetpeheres. Giza Pyramid Built: 2589-2566 B.C. Total Blocks used: 2, 300,000 Weight: 6.5 million tons Average weight of individual blocks of stone: 2.5 tons Height: Originally 481 feet, now 449 feet Menekaure Built the smallest pyramid Son of Khafre http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/pyramid/e xplore/ Pyramids http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/pyramid/e xplore/ http://college.livetext.com/doc/64508 End of the Old Kingdom Factors that contributed to the collapse of the Old Kingdom: Power struggles Crop failures Cost of the pyramids Egypt split into two parts for over one hundred years. Middle Kingdom New pharaohs came to power who reunited the kingdoms Turbulent period Nile did not rise as frequently so farming was less abundant. Corruption and rebellions were common. On the positive side: new land was claimed when drainage projects were successful Egyptian armies invaded Nubia Trade was established around the Middle East and the Mediterranean. Middle Kingdom continued The Middle Kingdom ended with the invasion of the Hyksos in the delta area of the Nile in 1700 B.C.E They brought new technology with chariots Hyksos adopted Egyptian customs, beliefs and names. After 100 years, Egyptian leaders threw out the Hyksos which led to the New New Kingdom Probably the greatest time of growth and power as Egypt developed into a large empire. At its height of power it reached to the Euphrates River. During the period of conquest, the Empire brought more of its citizens in contact with southwestern Asia and Africa. Hatshepsut (1540 B.C.-1462) Daughter of Tutmoses I and wife of Tutmoses II Was regent when husband died Took over throne and declared herself the pharaoh. Built temples and funeral temple Wore the beard of pharaoh Reigned for 20 years Successor tried to erase all mention of Hatshepsut and her accomplishments. Hatshepsut as Pharaoh Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut Designed by Senenmut, the queen’s confident and architect Ramses II Pushed Egyptian empire to Syria Most powerful ruler of New Kingdom period Ruled for 67 years. Had over 111 sons and 51 daughters with all his wives. Built many monuments Egypt declined in power after his death. Egypt and Nubia Nubia was also known as Kush Traded with Nubia-slaves, ivory and cattle During the New Kingdom, Egypt invaded and captured Nubia. Used gold to build monuments Nubians served in army and other areas of Egyptian life. In 750 B.C. the Nubians captured Egypt Ruled for 100 years until pushed back to Nubia in 650 B.C.E Nubian rulers continued to rule for 1,000 years. Hierarchy of Egyptian Society Status of Women Enjoyed higher status and greater independence Could inherit property Enter into business deals Buy and sell goods Go to court Obtain a divorce Women’s employment Owned businesses Managed farm estates Served as doctors and priestesses Could not be a scribe Scribes Scribes had a central role Temple scribes kept records of ceremonies, taxes and gifts. Served nobles and the pharaoh Could rise in society. The evolution of the written language Hieroglyphs Ideograms Demotic Use of papyrus and reed pens Rosetta Stone After the decline of the Egyptian empire and loss of papyrus documents, the hieroglyphs could not be read. Found by Napoleon’s troops in early 1800’s Champollion unraveled the mystery of the hieroglyphs with the use of the Rosetta Stone. http://www.thebritishmuseum.ac.uk/explore/hig hlights/highlight_image.aspx?image=an16456b.j pg&retpage=22108 Advances in Medicine and Science Medicine Astronomy Mathematics Arts and Literature Statues Paintings Carvings Pharaohs depicted as larger figures. Human figures drawn in profile. Use of animal heads on people to show gods. Statues very stiff and stylized. The Gods of Egypt Religion and Ancient Egypt The Ancient Egyptians worshipped a number of gods and goddesses, each of whom have different roles or functions, as well as variety of creation myths. Amun Originally a Theban deity, the god became the primary god during the Middle Kingdom. Represented as man with a double plumed crown or with the head of a ram. Combined with other deities-with the sun god Ra, became Amun-Ra With Fertility god became Amun-Min Anubis Represented as a dog or as a man with dog’s head. Anubis is the god of the dead. Priests may have performed the rituals wearing a mask. Weighing of the heart Cult later merged with Osiris Bastet Daughter of Ra Sekhment-lioness goddess Earliest depiction was of a women with a lionness’ head By 1,000, she appeared as the cat. Hathor Bovine goddess Hathor was one of the most important deities in Ancient Egypt. Goddess of dance and music Lady of the west-received the sun And kept it safe to dawn Lady of Turquoise or of Byblos Offered protection to the dead in the afterlife. Horus Falcon god, Horus Embodiment of divine kingship Son of Osiris, avenge death of Father to become king Deity of the sky,Horus was associated With the sun and the moon: God of the sunrise Isis Cult of Isis-spread beyond Egypt Wife of Osiris Mother of Horus Divine mother of reigning Pharaoh Healing powers Protected young Cured the sun god, Ra for knowledge of his secret name. Told Horus Myth of Osiris Jealous of Osiris, who reigned over Egypt, his brother, Seth assassinated him in order to gain power. Isis searched for the body, found it in Byblos and brought it back to Egypt. Crazed with anger, Seth cut the body into pieces, which he scattered over the country. Isis took up her quest again, reassembled the body and, with the help of Anubis, mummified her husband. After turning herself into a bird, she brought Osiris back to life, magically conceiving Horus in the process. Osiris One of the most important of the gods. Associated with death, resurrection and fertility. Maat Personification of truth, justice and harmony Responsible for regulating the stars, the seasons, and the actions of both humans and god. Weighing of the heart-justice. Nephthys Sister of Isis Wife of the evil god, Seth Mother of Anubis, father was Osiris Protectress of the dead Often pictured at the head of the coffin, Isis at the feet Ptah God of craftsmen Ptah brought the world into existance by uttering the names of things. Held a scepter that symbolized stability, life and welfare. Seth Murderer of Osiris, enemy of Horus Associated with the hostile deserts of Egypt Guarded Ra in his dangerous 12 hour journey through the night. Sobek The crocodile god Associated with the strength and power of the pharaoh Also to ward off the crocodiles Thoth Depicted with the head of a baboon or an ibis God writing and wisdom Lunar deity Wrote down the results of the weighing of the heart ceremony Ra Ra was depicted as hawk-headed figure Wearing a headdress featuring a solar disk THE AFTERLIFE The AFTERLIFE Akhenaton and the Sun God Aton Son of Tiy and Amenhotep III Forced religion on subjects: worship of the sun god, Aton or Aten Pushed out other gods Moved capitol to el-Amarna Married to Nefertiti and had six daughters Was succeeded by Smenkere and Tutankhamun Tuthankhamun Minor king of the 18th dynasty Came to throne at 8 Died by the time he was 18 Probably the sun of Akhenaton and a lesser wife. Tomb found by Howard Carter City States of Ancient Sumer •First known civilization in the Fertile Crescent •Tigris and Euphrates Rivers provided irrigation, but also flooded the lands •The Epic of Gilgamesh is the story of a flood that destroyed the world. •Priests and leaders organized public works to build dikes and irrigation canals. •Built cities out of clay •Trade routes were developed to Sumer •First to use wheeled vehicles. Sumerian Civilization Rival city-states battled for control of land and water. Ruler was responsible for: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Maintaining city walls Irrigation system Led armies Enforced the laws Chief servant of the gods and lead ceremonies Employed scribes to keep records and collect taxes. Sumerian Social Hierachy Women’s Role in Society Mother goddess Wives of rulers had special powers: ruled in place of king when he was at war Supervised royal workshops Women had legal rights Wealthy women engaged in trade and owned property Sumerian Religion Polytheistic Gods had human behavior Highest duty to keep the divine beings happy and city-state safe Shrine to gods Responsible for violence and suffering Favored truth and justice Sacrifices Holy days and ceremonies Belief in afterlife of grim place with no relief Ziggurat Ziggurats Temples were originally built on platforms. During the third millennium B.C., these were made higher and bigger. Eventually it was decided to build even higher temples on platforms which were stepped. These stepped towers we call ziggurats. By 2000 B.C. mud-brick ziggurats were being constructed in many Sumerian cities. Later, ziggurats were constructed in Babylonian and Assyrian cities. No one knows for certain why ziggurats were built or how they were used. They are part of temple complexes, so they were probably connected with religion. http://www.mesopotamia.co.uk/ziggurats/home_set.html Advances in Learning Invented the earliest form of writing-cuneiform Pictographs Record: records, myths, prayers, laws, treaties, business contracts. Schooling of scribes Mathematics Developed algebra and geometry Number system of six Hour 360 degrees Astronomy Calendar Movement of stars Invaders, Traders, Empire Builders Sargon,ruler of Akkad, defeats Sumer Hammurabi, king of Babylon, defeats Mespotamia Code of Hammurabi 300 laws on stone pillar: stele Codified laws for governing a state Criminal law: “eye for an eye” Civil law: business contracts, property inheritance, taxes, marriage and divorce He improved irrigation, organized a well-trained army, repaired temples Promoted Babylonian god, Marduk, over other gods. Hittites Contributions 1400 B.C. Able to extract iron out of ore. Tools and weapons were harder Ushered in the Iron age Assyrian Warriors 1100 B.C.E-started to expand across Mesopotamia 500 years most feared warriors Well ordered society Regulated life in royal household Women secluded Veiled First library Persian Empire Babylon fell to Cyrus the Great in 539 B.C. Policy of tolerance for peoples they conquered Asia Minor to India Present day: Turkey, Iran, Egypt, Afghanistan and Pakistan Darius (522-486 B.C.) Unified Persia Divided into provinces: governor called Satrap Common set of laws Built roads Weights and measures Use of coins: went from barter system to monetary system Zoroaster Religious beliefs helped to united Persia Zoroaster lived about 600 B.C. Only one god: Ahura Mazda Wise god Battle with Ahriman-prince of lies and evil Each individual had to choose between gods Teachings in Zend-Avesta Judgment day Ideas later stressed by Christianity and Islam Phoenician Sea Traders Sailors and traders Came from cities around Mediterranean that is now Lebanon and Syria Manufacturing: glass, dye from shells, papyrus to make books Traded goods all over the Mediterranean even as far as England: established colonies Alphabet of 22 letters The Roots of Judaism Nomadic People Abraham of Ur in Mesopotamia led people to Canaan Moses-lead slaves out of Egypt Kingdom of Israel David: united tribes into one nation Solomon: wise and understanding king Revolt after death Division into two kingdoms: Israel and Judah 722 B.C. Israel fell to Assyrians 586 B.C. Babylonian armies captured Judah. Destroyed temple Exiled to Babylon-Now called Jews Jews freed by Cyrus of Persia-allowed to return to Israel Religion One God: monotheistic Covenant with Abraham Moses renewed covenant Patriarchal society Ten Commandments: keeping the Sabbath Prophets Ethics Diaspora