The American Revolution
advertisement

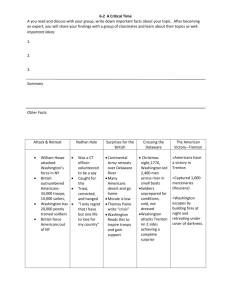
The American Revolution 1775-1783 Loyalist Strongholds Battle for the Middle States • NY & PA – 1776-1777 • Colonists suffered many defeats early on • “These are the times that try men’s souls” – Thomas Paine Battle for New York The British wanted NYC to isolate New England – By both land & sea • Summer 1776- General William Howe and Admiral Richard Howe sailed to NY Harbor Defeat in NY • Goal: humiliate Washington & end the Revolution • Washington had 23,000 soldiers and was greatly outnumbered • Howe brought 32,000 soldiers & Hessians • By late August the colonists retreated with heavy losses Defeat in NY • By the Fall: – Washington’s troops were pushed back across the Delaware River • Less than 8,000 troops left HW- pages 107-111 • What are Hessians? • What was the result of the Battle of NY? • Why did General Washington desperately need a victory prior to December 31, 1776? • Describe the Battle of Trenton. • Who won the Battle of Princeton? The Battle of Trenton American Casualties- 5 British Casualties- 107 • Washington knew he needed a victory to keep his troops • Christmas night,1776 he crossed the almost frozen Delaware River in row boats – Washington’s troops lacked shoes – The storm made muskets unfit for use & Washington ordered his men to use bayonets Battle of Trenton • 4am they marched 9 miles in sleet & snow to capture Trenton • Sneak Attack– Hessians were drunk & passed out from Christmas celebration • Washington’s troops took 1,000 Hessian prisonerswhich were all treated with great respect • This prompted many American soldiers to reenlist The Battle of Trenton The Fight for Philadelphia • Spring 1777: General Howe planned to take the capital of Philadelphia – Howe’s troops left New York by sea & landed in Philadelphia by August • The Continental Congress fled the city & Washington tried to stop the redcoats • Washington had no successful & the British celebrated with the Loyalists Victory at Saratoga September 19-October 17,1777 American Leader: Gen. Horatio Gates British Leader: Gen. John Burgoyne • General Burgoyne planned to move from Canada to Albany and eventually meet Howe & his troops in NYC – He traveled with 8,000 soldiers and 138 pieces of artillery Saratoga • Burgoyne was constantly attacked by militiamen & Continental soldiers – One of the worst was Ethan Allen and his Green Mountain Boys Saratoga Continued • Burgoyne did not realize that Howe was not going to meet him – October 17, 1777- Burgoyne was forced to surrender at Saratoga he was surrounded by General Gates and his army • From this point on the British kept their troops close to the coast & supply bases – British confidence took a heavy blow • The French looked to increase their support to the Patriots – February 1778- a treaty of cooperation signed The Surrender of General Burgoyne at Saratoga- October 17, 1777 French Aide • After victory at Saratoga, Americans had a morale boost • Since 1776: The French had secretly sent weapons & ammunition – Victory proved to the French that Americans had a real chance at beating the British – The French saw it as an opportunity to avenge the British after the French & Indian War Valley Forge Valley Forge Dec 19, 1777- June 19,1778 Valley Forge • Winter Camp 20 miles outside Philadelphia – Congress had little $$ for supplies • 10,000 soldiers battled: – Wind, snow & ice – Built makeshift housing, slept on straw – 2,000 soldiers died Financing the War • Continental Army was unable to pay the troops – When Congress ran out of hard currency, gold & silver - it borrowed money by selling bonds – Started printing paper $ or Continentals – Had no gold or silver to back up currency • Caused inflation War Financing • Americans had a hard time supplying the troops – Blockade forced Americans to smuggle goods – Corrupt government officials engaged in profiteering Civilians at War • Women stepped into men’s roles • Many women joined the war effort – Made ammunition – Followed husbands to battle • Washed, mended & cooked for troops- some even fought Abigail Adams Molly McCauley • “Molly Pitcher” • Born NJ 1754 • Battle of Monmouthstepped in for her husband John Hays after his collapse • Nursed wounded soldiers Sarah Franklin Bache • Daughter of B. Franklin • Ladies Association of Philadelphia – Supervised the making of shirts for troops during the war Betsy Ross • A seamstress acquainted with George Washington • According to legend Ross made the first flag – Stars & Stripes European Allies Shift the Balance • During the winter of 1778 Friedrich von Steuben (Prussian) volunteered to help Washington at Valley Forge – “make regular soldiers out of country bumkpins” – With his an others help the Continental Army became an effective fighting force European • 20 year old Frenchman Marquis de Lafayette • Lobbied France for reinforcements – France took time to organize its forces which meant no immediate improvement for American troops British Move South • Summer 1778 the British focused on the South & force their way north – The British wanted to use port cities to attack the French • By the spring of 1779 the British had taken over Georgia & put a royal governor in place • 1780- General Clinton replaced Howe and with the help of General Charles Cornwallis captured Charles Town – They marched 5,500 soldiers off as prisoners of war Continue South • Throughout most of 1780 the redcoats advanced & gained continued support from escaped slaves hoping to win their freedom • Within 3 months the British also took North Carolina only to be pushed back by Patriot forces into South Carolina British Reverses:1781 • Nathaniel Greene, under Washington’s orders, harassed Cornwallis as he retreated • Greene divided his forces & sent 600 of his troops under the command of General Daniel Morgan to South Carolina – Cornwallis sent Lieutenant Colonel Banastre Tarleton after Morgan • When the forces met in January 1781 at Cowpens, South Carolina the battle ended in the redcoats surrendering – Angered by defeat Cornwallis attacked Greene in North Carolina & won • Cornwallis had 93 troops killed, 413 injured, & 26 missing Victory at Yorktown • Lafayette & his 6,000 French soldiers unite with the American troops and attack Cornwallis – The French navy defeated the British & blocked the coast • The siege of Yorktown lasted almost a month where the British were attacked day & night by 17,000 French and American troops • October 17, 1781- Cornwallis forced to surrender since his troops were outnumbered • Cornwallis was expected to officially surrender on October 19th, but he sent General Charles O’Hara to surrender to Washington, French Generals, and the troops Seeking Peace • Representatives from the US, Britain, France, and Spain met in Paris 1782 to negotiate the treaty • They all had their own interests – many thought the Europeans would easily outwit the Americans • John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, and John Jay demanded full independence before they would even talk Treaty of Paris • September 1783 • US now covered the Atlantic to the Mississippi and from Canada to Florida • Treaty contained problems: – British did not protect the land interests of their Native allies – Did not specify when the British would leave America United States of America 1784 Symbol of Liberty • One of the major changes in the colonies was the rise of egalitarianism or all people being equal • Were all people truly equal? – Women – Slaves – Native Americans Equality? • African Americans were still enslaved and those that were free faced discrimination – By 1804 many New England & Middle States took steps to outlaw slavery – Some Southerners (Washington) took steps to free slaves • Native American interests were of great uncertainty – 50% population decline east of Mississippi Symbols of Liberty • “Novus Ordo Seclorum” – “a new order for the ages” was chosen to be on the reverse of the Great Seal of the United States • Now came the difficult job of creating a government for the people