traits
advertisement

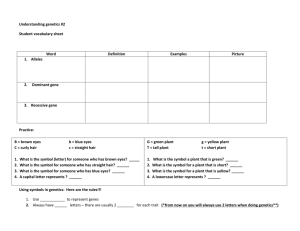
Warm ups: 1. What do I mean if I say I “INHERITED” my green eyes from my mother? 2. Give examples of some “TRAITS” that you inherited from your parents…. Word 1. Alleles Definition Two forms of a gene (one from mother, one from father) Examples: Height – short and tall Hair – straight or curly Tail – long or short Picture Word 2. Dominant Gene Definition The strong form of the gene (you ALWAYS see it) Written as: Capital Letter Picture Word 3. Recessive Gene Definition The weak form of the gene (NOT always seen) Written as a lowercase Picture DOMINANT AND RECESSIVE TRAITS Traits in the left-hand column dominate over those listed in the right-hand column. Dominant Recessive Traits Traits Eye coloring Brown eyes Gray, green, hazel Blue Grey, green, hazel,blue eyes Blue Albino (pink) Vision Farsightedne Normal vision Nearsightedness ss Night vision Normal Color blindness vision Normal sight Normal color vision Hair Dark hair Non-red hair (blonde, brunette) Curly hair Full head of hair Widow's peak hairline Blonde hair, light hair Red hair Straight hair Baldness Normal hairline Practice B = brown eyes C = curly hair b = blue eyes c = straight hair 1. What is the symbol (letter) for someone who has brown eyes? B 2. What is the symbol for someone who has straight hair? c 3. What is the symbol for someone who has blue eyes? b 4. A capital letter represents ? Dominant gene or trait Practice G = green plant T = tall plant 1. 2. 3. 4. g = yellow plant t = short plant What is the symbol a plant that is green? G What is the symbol for a plant that is short? t What is the symbol for a plant that is yellow? g A lowercase letter represents ? Recessive gene or trait Using symbols in genetics 1. Use letters to represent genes 2. Always have two letters – 2 genes for each trait Word 4. Purebred or Homozygous Definition Having the same two Always two Dominants or two recessives Picture Word 5. Hybrid – “mutt” or Heterozygous Definition Having two different alleles Always a Dominant and a recessive Picture Purebreds vs. Hybrids Practice Homozygous Heterozygous Examples: a. Two dominant tall genes --- TT b. Two recessive short genes --- tt c. One dominant and one recessive --- Tt Hybrid and Purebred Practice problems T = tall G = green t = short g = yellow 1. A plant is purebred tall. What genes does it have? TT 2. A plant is hybrid green. What genes does it have? Gg 3. A plant is purebred yellow. What genes does it have? gg Hybrid and Purebred Practice problems B = brown C = curly b = blue c = straight 1. A dog is purebred with brown eyes. What genes does it have? BB 2. A person is hybrid with curly hair. What genes does he have? Cc 3. A dog has blue eyes. What genes does it have? bb Physical vs. Actual Word 6. Genotype Definition Genes written in letter symbols that show possible traits. Picture Word Definition An organism’s 7. inherited Phenotype appearance. (What physically shows.) Picture Phenotype and Genotype Practice Problems T = tall t = short 1. What is the phenotype for a person who is tall? 2. What is the genotype for a person who is short? 3. What is the phenotype for a person who is short? 4. What is the genotype for a person who is tall? The relationship between the genotype and phenotype is a simple one ... The genotype codes for the phenotype! Sum it all up! • Traits from an organism pass from the parents to the offspring. • Gene pairs determine traits. • Organisms inherit genes in PAIRS. One from each parent. • Genes are dominant and recessive. (When the two go a walking, the capital does the talking! Hybrid) Exit slip: Five finger summary! Take out a piece of paper. Trace your hand on the paper and write genetics in your palm. List five things that you learned from today’s lesson and write them in each of your five digits.