ATP-ADP Cycle - Effingham County Schools
advertisement

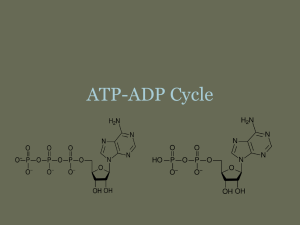
ATP-ADP Cycle But first….. Autotrophs Make their own food • with light – phototrophs • with chemicals -- chemotrophs Heterotrophs Can NOT make own food… they get their energy by the foods they eat Adenosine triphosphate P + P P ribose - adenine Adenosine diphosphate + P P ribose - adenine + + Releasing energy Storing energy - - P Releasing energy P Storing energy P P P ribose ribose adenine adenine ATP-ADP Cycle • ATP – ADP Cycle phosphate removed Transformation of Energy – Energy is the ability to do work. – Thermodynamics is the study of the flow and transformation of energy in the universe. Laws of Thermodynamics – First law - Energy can be converted from one form to another, but it cannot be created nor destroyed. – Second law - Energy cannot be converted without the loss of usable energy. HEAT • Carbohydrates – most commonly broken down to make ATP. – not stored in large amounts – up to 36 ATP from one glucose molecule • Lipids – store the most energy. – 80% of energy in your body – About 146 ATP from a triglyceride • Proteins – least likely to be broken down to make ATP. – amino acids not usually needed for energy – about the same amount of energy as a carb. ATP-ADP Cycle Using Biochemical Energy 1) Movement in cell 2) Protein synthesis 3) Active Transport (Low to high concentration across membrane)