ATP
advertisement

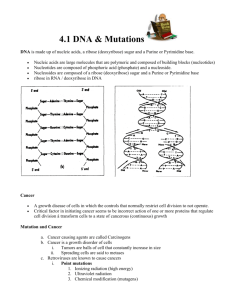
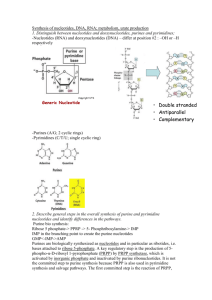
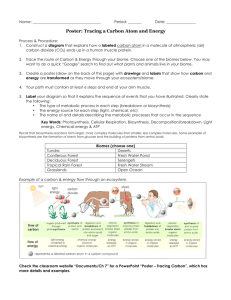
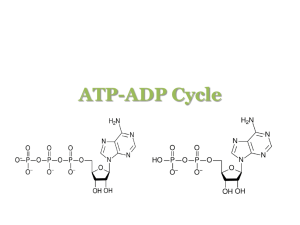
Isoleucine Aldol cleavage The a and b subunits of tryptophan synthase have different enzymatic activities, substrate channeling occurs in this enzyme. Dehydration of Ser Substrate channeling Enzymes involved in Trp synthesis may exist as multi-enzyme complexes (metabolons). Amino acids are mainly derived from intermediates of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the pentose phosphate pathway. Pyruvate The rate of these biosynthetic pathways are often regulated via allosteric feedback inhibition. The first case of allosteric feedback inhibition was discovered in studying the biosynthesis of Ile in E. coli. Umbarger, H. E. (1956) “Evidence for a negativefeedback mechanism in the biosynthesis of isoleucine”, Science 123, 848. Allosteric feedback inhibition for Ile biosynthesis The first catalytic enzyme Ile inhibits this enzyme in a minute-to-minute response. End product Concerted inhibition Three aspartokinase isozymes Enzyme multiplicity Sequential feedback inhibition Goal of regulation: provide a balanced supply of all amino acids! Interlocking regulatory mechanisms in the biosynthesis of Lys, Met, Thr, and Ile from Asp. Amino acids are precursors of many specialized biomolecules Glutathione Melatonin Catecholamine neurotransmitters like dopa, dopamine, norpinephrine, and eipnephrine are derived from Tyr. Nucleotide biosynthesis The eight nucleotides found in DNA and RNA Issues: Sources of carbon and nitrogen; assembly order; balanced synthesis of all the nucleotides; cofactors. Deoxyribonucleotides are derived from ribonucleotides, dTMP is derived from dUMP, supporting the “RNA world” hypothesis of evolution. Ribonucleotides, unlike deoxyribonucleotides, have multiple metabolic roles. Nucleotides are synthesized via either the de novo or salvage pathways. Radioisotope tracer experiments (using 14C and 15N-labeled precursors) in birds revealed the origins, not the assembly pathway, of the atoms in the purine and pyrimidine rings (Buchanan and Greenberg, 1950s). Assembled onto a ribose 5-P. Origins of the ring atoms of purines Could the assembly occur without enzyme catalysis (when enzymes were not yet available)? The ring (as orotate) is assembled first before attaching to a ribose 5-P. Gln amide HCO3The atoms of the pyrimidine rings were mostly derived from amino acids. De novo purine nucleotide synthesis: the base assembles on the ribose phosphate; IMP is the first nucleotide synthesized. Stepwise assembly of the purine ring occurs on ribose phosphate Ribose 5-P Committing step (Unstable) Nonsequential steps 1, 3, 5 are catalyzed by one multifunctional protein in eukaryotes! 1st ring closure (remnant of ATP released during His biosynthesis) Steps 10 and 11 are catalyzed by one protein. 2nd ring closure Asp donates an amino group in a similar fashion as it does in the urea cycle. Nucleotide biosynthesis occurs via either the de novo or salvage pathways • For the de novo pathway, amino acids (Asp, Gln, Gly), ribose 5-phosphate, CO2, One-carbon units (carried by H4 folate) are the precursors. • The free bases are not intermediates for the de novo pathways. • The purine ring is assembled on ribose 5-P,but the pyrimidine ring is assembled first before attached to ribose 5-P. • Cellular pools of nucleotides are quite small (continuous biosynthesis is needed). • Preformed bases are recovered and reconnected to a ribose unit in the salvage pathways. GTP as an energy source! Balanced synthesis of AMP and GMP: AMP formation requires GTP & GMP formation requires ATP! Biosynthesis of AMP & GMP from IMP. The biosynthesis of AMP and GMP is regulated mainly by sequential feedback inhibition (no covalent regulation) AMP and GMP act synergistically. Syntheses of AMP & GMP are balanced via feedback inhibition. GTP The committing step + + ATP The de novo biosynthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides: the base ring (as orotate) is first assembled before being attached to the phosphoribosyl group to form orotidylate. Gln A substrate channel is found in carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II NH4+ HCO3- ( ATP) ADP Pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis in bacteria is regulated at the aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase): feedback inhibition by CTP. CTP CTP CTP Inhibited state ATP ATP Active state CTP Feedback inhibition of CTP ATP ATP Bacterial ATCase, one of the earliest & best studied allosteric enzymes, contains separate catalytic & regulatory subunits. Base specific NMP kinases together with a nonspecific NDP kinase converts NMPs to NTPs • Each base-specific nucleoside monophosphate (NMP) kinase converts the corresponding NMP/dNMPs to NDP/dNDPs using ATP. • The nonspecific (ubiquitous) nucleoside diphosphate (NDP) kinase converts all NDP/dNDPs to NTP/dNTPs using ATP or other NTPs Metal ions (Mg2+ or Mn2+) are found to be essential for these enzymes to be active. ATP induced conformational changes prevents hydrolysis All dNDPs are derived from NDPs via the catalysis of a common ribonucleotide reductase likely via a 3`ribonucleotide radical intermediate. This is consistent with the notion that RNA preceded DNA in the course of evolution! Ribonucleotide reductase contains two types of subunits. Shown is the E. coli enzyme, based on determined structure of the R1 dimer and R2 dimer (not as a whole!) A unique feature of this enzyme The action mechanism of this enzyme is far from clear. Radical at 3`-C No activation at C-2’! Reverse of step 1 Proposed catalytic mechanism for ribonucleotide reductase. Loss of water from C’-2 Radical cation dTMP is synthesized by the methylation of dUMP. donors of one-carbon units & electrons Thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase reside in one protein in plants. dUMP is derived from dUTP, which is in turn derived from dCTP or dUDP. The reactions catalyzed by ribonucleotide reductase and thymidylate synthase are probably key for the transition from an RNA world to one in which DNA stores genetic information. Purine and pyrimidine bases can be reconverted to nucleotides via the salvage pathway. Salvage pathway of nucleotide biosynthesis Defect of HGPRT causes Lysch-Nyhan syndrome. Adenine or hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferases Uric acid is the excreted end product of purine nucleotide catabolism in humans and many other animals. AMP deminase nucleotidase Nucleotide Oxidation of GMP and AMP to produce uric acid nucleotidase Overproduction of uric acid, which will accumulate in the joints, was revealed to cause gout (痛风). Nucleoside Adenosine Deaminase ADA) purine nucleoside phosphorylase Base Nucleoside guanine deaminase purine nucleoside phosphorylase The deficiency of ADA will cause severe combined Base immunodefficiency (SCID) in human. Xanthine oxidase Xanthine oxidase Allopurinol was designed to be a suicide inhibitor of xanthine oxidase to treat gout (Elion and Hitchings shared the Nobel Prize in 1988 for their discoveries of important principles for such drug design). Uric acid is further degraded in many animals. Amidotransferases, thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase are target enzymes for cancer chemotherapeutic drugs (to inhibit the synthesis of dTMP) Analogs of Gln inhibit synthesis of nucleotides and some amino acids Suicide inhibitor of thymidylate synthase Competitive inhibitor of DHFR Summary • Atmospheric N2 is reduced to ammonia by the the nitrogenase complex (containing a key Fe-Mo cofactor) present only in certain bacteria. • Ammonia enters organic molecules via Gln and Glu. • Glutamine amidotransferases catalyzes the transferring of the amide amino group of Gln to many acceptor molecules. • The carbon skeletons of amino acids are mainly derived from intermediates of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the pentose phosphate pathway. • Amino acid biosynthesis is regulated by various forms of feedback inhibition (including enzyme multiplicity, concerted inhibition and sequential feedback inhibition). • Many other biomolecules are derived from amino acids. • Purine nucleotides are synthesized from PRPP, Gln, Gly, N10-formyl H4 folate, HCO3-, Asp through the de novo pathway. • Pyrimidine nucleotides are synthesized using HCO3-, Gln, Asp, and PRPP. • De novo synthesis of nucleotides are regulated via feedback inhibition. • Deoxyribonucleotides are derived from ribonucleotides at the NDP level, with the catalysis of ribonucleotide reductase, which contains a chain of electron carriers, uses free radicals, and be regulated for both substrate specificity and overall enzymatic activities. • The dTMP molecule is derived from dUMP by thymidylate synthase, an enzyme using N5, N10-methylenetetrahydrofolate as the donor of both one-carbon unit and electrons. • Degradation of purines and pyrimidines produces uric acid and citric acid cycle intermediate/fatty acid synthesis precursor, respectively. • Purine and pyrimidine bases can be reused via the salvage pathway. • Many cancer chemotherapeutic drugs (e.g., azaserine, acivicin, fluorouracil, and methotrexate) inhibits enzymes in the nucleotide biosynthetic pathways.