ATP-ADP Cycle
advertisement

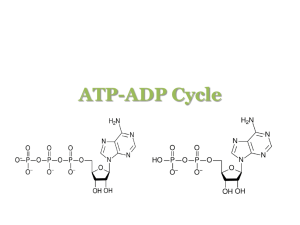
ATP-ADP Cycle ATP-ADP Cycle • Transformation of Energy – Energy is the ability to do work. – Thermodynamics is the study of the flow and transformation of energy in the universe. ATP-ADP Cycle • Laws of Thermodynamics – First law - Energy can be converted from one form to another, but it cannot be created nor destroyed. – Second law - Energy cannot be converted without the loss of usable energy. ATP-ADP Cycle • ATP – ADP Cycle – ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) transfers energy from the breakdown of food molecules to cell functions – Energy is released when a phosphate group (Pi) is removed – ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) is changed into ATP when a phosphate group (Pi) is added ATP-ADP Cycle • ATP – ADP Cycle phosphate removed ATP-ADP Cycle • Carbohydrates – Carbohydrates are the molecules most commonly broken down to make ATP. – not stored in large amounts – up to 36 ATP from one glucose molecule ATP-ADP Cycle • Lipids – Lipids store the most energy. – 80 percent of the energy in your body – About 146 ATP from a triglyceride ATP-ADP Cycle • Proteins – Proteins are least likely to be broken down to make ATP. – amino acids not usually needed for energy – about the same amount of energy as a carbohydrate ATP-ADP Cycle