The Female Reproduction System
advertisement
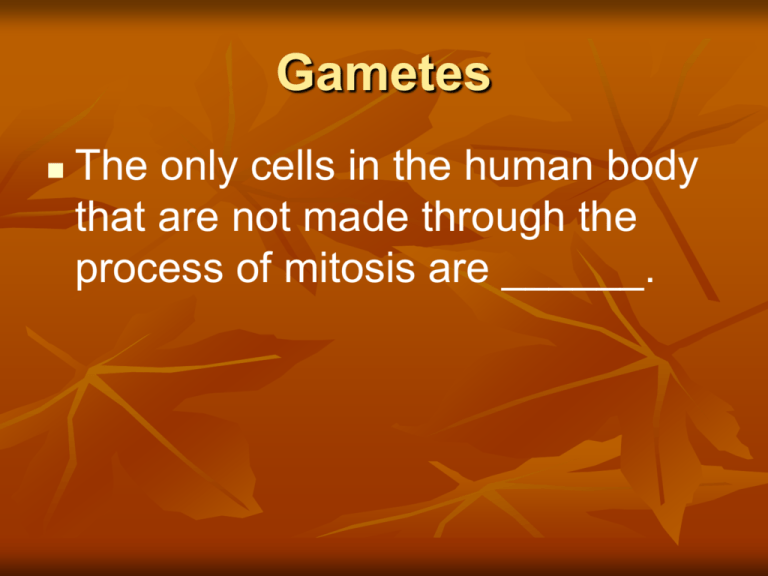
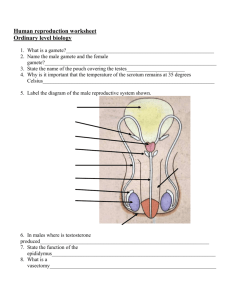
Gametes The only cells in the human body that are not made through the process of mitosis are ______. Sperm & Ovum In sexually reproducing organisms, some cells are able to divide by another method called meiosis. This type of cell division results in the production of gametes (eggs or sperm). Meiosis is much more complex than mitosis. Whereas mitosis involves the duplication and subsequent division of chromosomes, meiosis involves two divisions of genetic material. Vocabulary zy·gote - the cell produced by the union of two gametes, before it undergoes cleavage. gam·ete - a mature sexual reproductive cell, as a sperm or egg, that unites with another cell to form a new organism. cleav·age - the act of cleaving or splitting. blas·to·cyst - the blastula of the mammalian embryo, consisting of an inner cell mass, a cavity, and an outer layer, the trophoblast. troph·o·blast - the layer of extra embryonic ectoderm that chiefly nourishes the embryo or develops into fetal membranes with nutritive functions. The Female Reproduction System Female Functions Produce an ovum (egg cell) When united with sperm produces a fertilized ovum External Reproductive Organs Called the vulva Clitoris, mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, and vaginal opening External Mons pubis – rounded fatty pad of tissue, covered with pubic hair, located in front on top of the pubic bone Labia majora – outer fold of tissue on either side of the vaginal opening, also cover with pubic hair Labia minora – inner folds of skin, this forms a hood like covering over the clitoris The labia serve as a line protection against pathogens and also have a function in sexual arousal Vaginal Opening Hymen – thin membrane that stretches across the vaginal opening Clitoris – small knob of tissue in the front of the vaginal opening, important in producing sexual arousal. Internal Female Reproduction Organs Vagina – elastic, tube like passageway. Birth canal Cervix – neck of the uterus, during childbirth the cervix dilates to allow the passage of the baby Uterus – strong, elastic muscle about the size of a fist, Main Function – hold and nourish the developing embryo and fetus Fallopian Tubes – tubes on each side of the uterus Ovaries – female sex gland situated on both sides of the uterus at the end of the fallopian tubes, House the ova and produce the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. Ovulation The process of releasing one mature ovum each month into that ovary’s fallopian tube is called ovulation The ovum can live for two days in the fallopian tubes At this time one sperm will enter the ovum and fertilize the egg Menstruation If an ovum is not fertilized, or if the fertilized ovum does not attach to the uterine wall, the uterine lining is not needed The muscle of the uterine contact, causing the lining to gradually break down The lining passes through the cervix into the vagina and out of the vagina opening The process of shedding the lining of the uterus 4 to 7 days ( 3 or 9 days ) Varies from female to female Menstrual Period Abdominal cramps 2-3 tablespoons of blood The rest is other tissues that make up the lining The cycle repeats itself 10-15 years of age Menopause – the ceasing of menstruation, 4550 Methods of Predicting Ovulation Calendar or Rhythm Method Basel Body Temperature Method Sympto-thermal Method Ovulation Method Ovulation Predictor Kits Menstrual Cycle Rhonda December 25th first day of menstrual flow December 31st last day of menstrual flow January 11th mid point of woman’s cycle (January 9th-13th possible ovulation) January 30th first day of new cycle Concerns about the Female Reproductive System PMS – Premenstrual Syndrome, two weeks before or just several days Symptoms – nervous tension, anxiety, irritability, bloating, weight gain, depression, mood swings, and fatigue Concerns Dysmenorrhea – painful contractions, lasting for days, avoid aspirin Amenorrhea – lack of a menstrual cycle, a 16 year old female who has never had a period or one that is discontinued for over three months Toxic Shock Syndrome – caused by a bacterial infection, most cases have been traced to the use of a super-absorbent tampons which provide an oxygen rich environment for the bacteria Vaginitis – vaginal infection which is common, yeast infection is one example Concerns Sterility – Blockage of fallopian tubes Female does not ovulate Endometriosis – endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus areas of the pelvic cavity Untreated STD’s (Gonorrhea or Chlamydia) Concerns Breast Cancer – Most common form of cancer in women Cervical Cancer – Pap smear to detect, but a pap smear will not detect STD’s Ovarian Cancer – Lining of the ovary In the egg-making cells in the ovary Only known risk is a family history of ovarian cancer, two or more close relatives should seek professional guidance