Year 7 Reproduction
advertisement

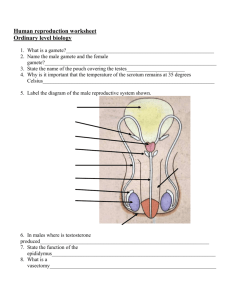
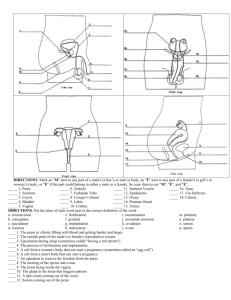
Year 7B Reproduction © Tony P. Thould September 2000 REPRODUCTON In order for a plant or animal species to survive they must reproduce. Most plants and animals reproduce by sexual reproduction which involves a male sex cell joining with a female sex cell. This is called fertilisation. 1. Why do some animals/ plants produce only a few young whilst others produce hundreds or thousands? 2. What is an endangered species? 3. What is the difference between Internal and External Fertilisation? 4. In what ways can Man help Plants / Animals to survive? Minimum you must answer is Questions 1,2 and 3. AN OVUM CELL Nucleus Contains the female set of chromosomes. Allows only one sperm inside before blocking any other ones from getting in Cell Membrane A SPERM CELL Tail for swimming Acrosome to make a hole in the ovum wall for the sperm to get into the ovum Mitochondrion to make energy to move the tail Nucleus with male chromosomes Its job is to fertilize the ovum ( egg ) cell Test The Sperm cell uses its tail to swim to the Ovum The Acrosome dissolves a hole in the Ovum wall and one Sperm enters Fertilisation FERTILIZATION Pollen Carries the Male Chromoso mes in its Nucleus + Ovule Contains the Female Chromoso mes in its Nucleus These are each a HALF SET of Chromosomes so that when they join together they form a WHOLE SET in the seed. = Seed A Fully Fertilized Ovule FERTILIZATION Sperm Carries the Male Chromoso mes in its Nucleus + Ovum Contains the Female Chromoso mes in its Nucleus These are each a HALF SET of Chromosomes so that when they join together they form a WHOLE SET in the seed. = Foetus A baby with a full set of Chromosom es FERTILIZATION There are two types of fertilisation :EXTERNAL INTERNAL This takes place outside the female body e.g. Frogs, where the female lays her eggs in water and the male sheds his sperm over them This takes place inside the female body e.g. Man, where the sperm are placed inside the females body and they swim to the Ovum. EXTERNAL FERTILISATION Fertilisation takes place outside the females body Male releases his sperm into the water nearby The female lays her eggs in a shallow hollow in the sea bed GERMINATION Once the seeds have been dispersed they need the right conditions to start growing into a new plant - Germination. These conditions are:•Warmth •Moist •Air •Light/Dark THESE ORGANS HELP WITH REPRODUCTION The male sex organs are made up from the Penis, Testes and Scrotum. The Testes make Sperm which contain the male genes. The Penis places the sperm as near as it can to the female’s egg ( Ovum ) The female sex organs are made up from the Ovaries, Vagina, Uterus and Oviduct. The ovaries make the Ovum which contains the female genes. The Uterus ( womb ) holds the developing baby. THE MALE SEX ORGANS Pubic Bone Erectile Tissue Bladder Seminal Glands Sperm Duct Penis Testicle THE FEMALE SEX ORGANS Oviduct Ovum released from the ovary into the Oviduct Ovary Uterus or Womb Cervix Vagina In a flowchart draw and label the path taken by a Sperm Cell from leaving the Testicle to fertilising the Ovum Cell THE MAIN PARTS OF A FLOWER Petal Stigma Anther Style Stamen Carpel Filament Ovary Sepal Ovule Test THE FUNCTIONS OF THE MALE PARTS Anther Stamen Makes pollen which has the male genes in it Filament Different plants have different numbers, shape and sizes of Stamens Holds the Anther up in the air so that visiting insects brush against it Test THE FUNCTIONS OF THE FEMALE PARTS Stigma Style Carpel Ovary Test Ovule A sticky surface where pollen stays when visiting insects brush against it. Guides the pollen tube down to the Ovary. Makes the Ovules which contain the female genes. Forms the fruit. THE FUNCTIONS OF THE MALE PARTS Stamen Different plants have different numbers, shape and sizes of Stamens THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Every month once puberty has been reached, an egg or Ovum is released from one of the ovaries in the female. This is called Ovulation. If the Ovum is not fertilised then it leaves the body through the Vagina along with the lining of the Uterus which had become thicker and richly supplied with blood. This happens every month and is known as a Period or Menstrual Cycle. Day 28 Day 7 THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Day 21 Day 14 THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Oviduct Week One An Ovum is made in the Ovary ready to be released into the funnel of the Oviduct. Ovary Uterus Vagina THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Week Two The Ovary releases the Ovum into the funnel of the Oviduct. This is Ovulation. The Uterus wall thickens ready for the fertilised Ovum THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Week Three The Ovary travels down the Oviduct towards the Uterus. The wall of the Uterus is well supplied with blood. THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Week Four As the Ovum was not fertilised, the Uterus wall is shed with the Ovum the Period. THE MENSTUAL CYCLE Once the period has finished the whole cycle begins again and continues each month as long as the Ovum is not fertilised. To prevent the fertilisation of the Ovum many couples take precautions which stops the Sperm reaching the Ovum - Contraception EARLY PREGNANCY The Embryo ( baby ) is held in the wall of the Uterus and is joined to the Placenta by the Umbilical Cord. The baby gets food and oxygen from the mothers blood through the Placenta. It also gets rid of waste into the mothers blood through the Placenta THE PLACENTA The Placenta forms a barrier between the blood of the mother and the baby but allows substances to pass between them. Placenta THE PLACENTA Oxygen, sugar, protein, vitamins, minerals, water, antibodies all pass from the mothers’ blood, along the Umbilical Vein in the umbilical cord to the baby. Placenta THE PLACENTA Placenta Waste products such as Carbon Dioxide, Urea and excess salts pass from the baby along the Umbilical Artery in the unbiblical cord to the Placenta and into the mothers blood so that her body can get rid of it. THE PLACENTA The Umbilical Cord carries food and Oxygen to the baby and waste away. Food and Oxygen in the mothers blood Placenta Waste food and Carbon Dioxide THE PLACENTA Unfortunately, some harmful substances can pass from the mothers blood into the baby e.g. Alcohol, Drugs, Nicotine and AIDS Placenta THE AMNION This is a bag that surrounds the baby and is filled with a fluid which protects the baby from bumps and bangs. Placenta The Amnion NINE MONTHS LATER Placenta or Afterbirth Cervix The baby is ready to be born. The head is engaged - in the right position for birth, at the mouth of the Uterus, the Cervix. Adolescence When children reach their teens many physical and emotional changes take place which some of them find difficult to come to terms with. PRIMARY SEXUAL CHARACTERISTICS Males Females Secondary Sexual Characteristics These are changes in the bodies of boys and girls when they are changing from a boy to man and girl to woman Physical Changes Puberty is the period when certain physical changes take place in the male and female body usually in early teens. Males Females • Pubic facial and armpit hair grows • Pubic and armpit hair grows •Voice breaks and deepens •Breasts develop and body more curved •More muscular body •Menstrual cycle begins giving her monthly periods •Sperm produced by testes.