Female Reproductive System
advertisement

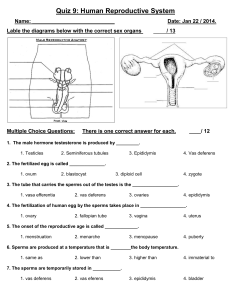
Female Reproductive System Estrogen – the principle female hormone, regulating reproductive functions and the development of secondary sex characteristics. Progesterone – a female hormone that helps regulate the menstrual cycle and sustain pregnancy Ovary – one of a pair of organs that produce ova Ovum – an egg, an oocyte Ovulation – the release of an oocyte from the ovary during the ovarian cycle Fallopian tube – one of two uterine tubes extending toward an ovary. Fertilization – occurs if sperm cells are present while the ovum is in the fallopian tube. One sperm unites with the ovum usually in the upper third of the fallopian tube. Once fertilization occurs the female is pregnant and cell division begins. Uterus – a hollow, thick walled, muscular organ held in the pelvic cavity by flexible ligaments and supported by several muscles. Also know as womb. Cervix – the end of the uterus, opening towards the vagina Vagina – a flexible muscular organ that begins between the legs and extends diagonally toward the small of the back. Hymen – a thin membrane partially covering the opening of the vagina prior to the first intercourse or other breakage Vulva – the collective term for the external female genitals Clitoris – a small knob of tissue on the front of the vaginal opening. Mons pubis – the mound of fatty tissue covering the pubic bone Labia – the labia majora is the outer fold of tissue on either side of the vaginal opening. The inner folds are called the labia minora Menstruation – the shedding of the endometrium (the inner lining of the uterine walls) during the menstrual cycle. Menstruation usually last about 3 to 5 days. During menstruation about 2 – 3 fluid ounces of blood and other tissue leave the body. Menstrual Cycle – the time from the beginning of one menstruation to the onset of the next. During this time, the uterus is readied for impanation of a fertilized ovum. Toxic Shock Syndrome – a potentially life threatening condition caused by a bacteria and linked to the use of super absorbent tampons. Vaginitis – vaginal infection – three types of vaginitis include yeast infection, nonspecific vaginitis, and trichomoniasis. Sterility – female sterility takes many forms including when the female does not ovulate and endometriosis Endometriosis – a condition in which tissue grows outside the uterus in other ares of the pelvic cavity