Disorders of Genitourinary Function
advertisement

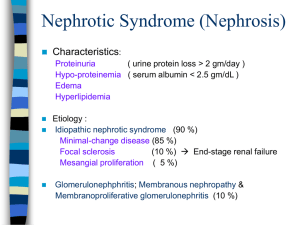
Disorders of Genitourinary Function Chapter 31 Genitourinary • Common in children • Caused by a variety of factors • Responsible for maintaining fluid & electrolyte balance within the body • May be potentially life threatening Urinary Tract Infection • May affect the upper urinary tract or lower urinary tract or both • More prevalent in females, uncircumcised males, and sexually active adolescents • Most frequently gram negatives organisms UTI • Shorter urethra in females • Urinary stasis • Congenital anomaly UTI • Signs & symptoms • May be subtle • Infants • • • • • Fever Weight loss Failure to thrive Feeding difficulties Vomiting & diarrhea • Children • • • • • Urinary frequency Pain during urination Foul smelling urine Incontinence Abdominal or flank pain • Hematuria • Vomiting Nephrotic Syndrome (Nephrosis) • Clinical state characterized by: • • • • Proteinuria Edema Hyperlipidemia Hypoproteinemia • Three forms • Idiopathic or primary – most common • Secondary • Congenitally acquired Nephrotic Syndrome • Etiology • 90% cause is unknown • Autoimmune & hypersensitivity to an antigenantibody reaction - possible causes • Proteinuria – results from glomerular damage that renders the glomerulus permeable to protein • Leads to low levels of protein in the blood • Decreases colloidal osmotic pressure in the capillaries Nephrotic Syndrome • Edema • Hypovolemia • Compensation – kidneys retain sodium & water • Level of lipids increasing – poorly understood Nephrotic Syndrome • Clinical manifestations • • • • • • • Subtle Periorbital edema Abdominal distention - ascites Anasarca Vomiting Anorexia/diarrhea Irritability Nephrotic Syndrome • Hallmark signs • Increased body weight • Decreased urine output • Marked edema Nephrotic Syndrome • Diagnostic tests • Clinical manifestations • Urine studies • Marked proteinuria • High specific gravity • May be dark & frothy • Serum protein levels reduced • Serum lipid levels elevated • Renal biopsy Nephrotic Syndrome • Medical management • Principal goal – reduce edema • Steroid therapy – adrenocortical - reduce proteinuria & then edema • Response – 7 to 21 days • Taper once asymptomatic • Bedrest – progression to ambulation • Low sodium diet • No diuretics • Relapse Nephrotic Syndrome • Nursing • Observation & monitor • I&O, body wt, abdominal girth • Skin care • VS • Nutrition – good protein intake • Steroids – risk of infection • Activity increase • Support of family Nephrotic Syndrome • Instruct parents • • • • • Test urine for albumin Admin meds Diet restrictions Side effects Assess for signs of relapse Nephrotic Syndrome • Prognosis • Good response – early detection & therapy start • Remissions – prolonged if follow instructions • Ultimate recovery - good Acute Glomerulonephritis • Inflammation of the glomeruli of the kidney • Postinfection phenomenon • APSGN – most common – early school age children APSGN • Follows a strep infection of the throat or skin • Fixed to basement membrane of glomeruli • Become edematous & infiltrated with WBCs • GFR decreases – Accumulation of Na & H2O APSGN • Circulatory congestion & edema • Proteinuria from inflammation & damage APSGN • Clinical manifestations • 10-14 days after the infection • Sudden onset – hematuria, proteinuria, oliguria • Tea or cola colored urine • Edema, abdominal pain, pallor, low grade fever, anorexia, vomiting, & h/a • HTN & hrt failure - hypovolemia APSGN • Diagnostic tests • • • • UA – proteinuria, hematuria, elevated SG Urine culture – negative Cultures of throat/skin – strep positive Antistreptolysin O - elevated APSGN • Medical management • Acute phase – 1-2 weeks • Bed rest recommended • Restricted fluid, sodium, potassium, phosphate – initially • VS, body wt, I&O • Antihypertensive & diuretics - control HTN • Antibiotic therapy APSGN • Nursing • • • • Promote rest & adequate nutrition Prevent & detect complications Support Educate parents APSGN • Prognosis • Recover completely Wilm’s Tumor (Nephroblastoma) • Most common malignant tumor of childhood • 20% of solid tumors in children • Peak age – 2 to 3 years Wilm’s • Etiology • • • • Most commonly – left kidney Both – 10% of cases Hereditary & non hereditary origins Metastasis sites – lungs, lymph nodes, liver, brain, & bone Wilm’s • Clinical manifestations • Enlarging, asymptomatic, and firm abdominal masses • Abdominal pain, hematuria, fever, HTN, wt loss, & fatigue • Metastasis – dyspnea, cough, & chest pain Wilm’s • Diagnostics • Detected by parents • Physical exam • Radiographic • CT • Hematologic & chemistry studies • Definitive – surgical biopsy • DO NOT PALPATE Wilm’s • Medical management • Surgical resection • Extent and metastasis • One affected - tumor, kidney, & adrenal gland • Both – part of kidney, total kidney on opposite side • Radiotherapy • Chemotherapy Wilm’s • Nursing • Preop • Prepare family • Postop • Bowel sounds • Renal function • Support family • Return to normal lifestyle Wilm’s • Prognosis • Excellent • Localized tumor – 90% chance • 5 year survival rate is 90-93% Structural Defects • Hypospadias • Urethral opening located along the ventral (anterior) surface of the penile shaft • Surgical correction – extending the urethra to a normal position • Normal reproductive and urinary function Structural Defects • Epispadias • Urethral opening located along the dorsal (posterior) surface of the penile shaft • Surgical correction – penile and urethral lengthening and possible bladder neck reconstruction Structural Defects • Phimosis • Narrowing or stenosis of the opening of the foreskin • Mild – manual retraction • Severe - circumcision Structural Defects • Hydrocele • Fluid in the scrotal sac • Surgical correction – if not resolved spontaneously in one year Structural Defects • Cryptorchidism • Failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum • Medical management – human chorionic gonadotropin • Surgical correction – orchiopexy • Prevent testicular damage and malignancies Structural Defects • Inguinal hernia • Protrusion of the abdominal organs through the inguinal canal and into the scrotal sac • Surgical correction - closure