Pancreas
advertisement

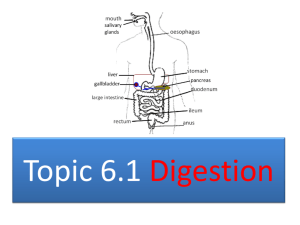
Pancreas Pancreas Anatomy Located retroperitoneal, posterior to stomach Midportion from the upper right to the left quadrant Parts Head Body Tail Pancreas Complex organ Two types of function Exocrine function Endocrine function Function of Pancreas Exocrine function Compound acinar gland – connects to small ducts – connects to larger ducts – joins the pancreatic duct – joins the common bile duct and enters the duodenum (small bowel) Function of Pancreas What are the secretions and what do they do? Hco3 Enzymes to digest protein Trypsin Chymotrypsin Carboxypeptidases Nuclease Enzyme to digest Carbohydrate Pancreatic amylase Enzymes to digest Lipids Pancreatic lipase Function of Pancreas Control of function Form Hormonal Neural Initiating factor Result Secretin Acidic chyme Large amounts of HCO3 to neutralize acid Cholecystokinin Fatty acids and amino acids Digest fatty acid and amino acids Parasympathetic stimulus food Secretion of enzymes into the gut Function of Pancreas Endocrine function Specialised cells (tissue) – secretes hormones directly into blood stream Digestion Digestion – breaking down of food to molecules Mechanical – larger to smaller Chemical – breaking of covalent bonds Digestion, Absorption and Transport Digestion Digestion – breaking down of food to molecules Carbohydrates – monosaccharides Protein – aminoacids Fats – fatty acids and glycerol Absorption Absorption – begins in the stomach Mainly alcohol,asprin but NOT the three main food products Transport Transport – move the molecules across the intestinal wall Facillitated diffusion- no need energy e.g glcose from cell to blood Cotransport – requires energy e.g glucose from intestine to cell Active transport – requires energy e.g amino acid from blood to organs Carbohydrate, Lipid Protein , Water and Mineral Carbohydrate Cellulose (plant cell- fiber not carbohydrate) Starches Complex carbohydrate (plant energy storage molecule) Glycogen ( muscle energy storage molecule) Sucrose Fructose Lactose Disacharide Carbohydrate Digestion Salivary amylase Complex carbohydrate Polysaccharides Pancreatic amylase Disacharides Polysaccharides Disacharidaseintestine Disacharide Monosaccharides Carbohydrate Digestion -Sucrose Disaccharidase -Glucose + Glucose -Fructose -Glucose + Maltose -Lactose -Glucose + Galactose Disaccharide Monosacharide Carbohydrate Intestine Absorption and Transport Intestine cell Cotransport Blood/capillary Facillitated diffusion Glucose is the end product in blood is a source of energy is stored and use by the cells and increased/decreased by the presence of insulin Lipids Triglycerides – three fatty acids and glycerol Phospholipids – required for transport and solubility of fat Steroids Cholesterol, corticosteroid, esters Lipids Digestion Emulsification by bile salts Lipid Transforms large lipid into smaller droplets Pancreatic amylase Transforms large lipid into smaller droplets Fatty acid and monoacylglyc erides Lipids Absorption and Transport Intestine Simple diffusion Within Intestine cell they are packed into Exocytosis chylomicron Carried in lacteals as chyle into liver and stored as cholesterol, LDL, HDL LDL,HDL, Triglyceride and cholesterol is the end product in blood is a source of energy is stored and use by the cells Proteins Plant protein Animal protein Proteins Digestion Pepsin Protein Polypeptides Trypsin,chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase Polypeptides Peptides Peptidases Peptides Amino acids Protein Absorption and Transport Intestine Cotransport Within Intestine cell they brokendown toActive amino acid transport Carried in blood to liver and throughout the body Amino acid is the end product in blood is a source of building block and the rest is metabolised to release energy and indirectly converted to small amounts of glycogen and the rest as fat which is stored and use by the cells. Transport is stimulated by growth hormone and insulin Water and Mineral 9 liters enters the digestive tract 2l – food 1l – salivary gland 2L – Gastric secretion 1.2L – Pancreatic secretion 0.7L – Bile 2L – Small intestine 97% absorbed in small intestine 6-7% in large intestine 1% excreted in faeces Water and Mineral Absorption and Transport Intestine Within Intestine Osmosis Blood Osmosis Na ,K, Ca, Mg, PO4, Cl- Blood Active transport Passive transport in duodenum /Active transport in ileum