Organelle info - Carroll County Schools
advertisement

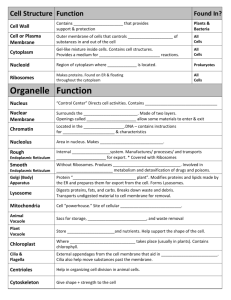
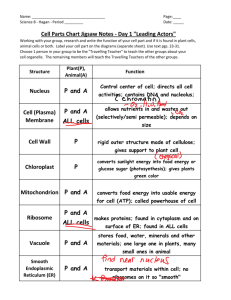
Biology 3.2 Organelle notes Cytoskeleton Function: supports and shapes the cell Shape: long threads, or fibers, made of protein 3 main types of fibers: Microtubules- long hollow tubes that act as “tracks” for movement of organelles; gives cell its shape Intermediate filaments – smaller than microtubules; gives cell strength Microfilaments – smallest fiber; enable cells to move and divide Cytoplasm Function: organizes organelles and gives cell strength Shape/location: jelly-like substance that fills space btwn the nucleus and cell membrane Other info: fluid portion is called cytosol (mainly water); cytoplasm contains the organelles Vacuole Function: storage Shape/location: fluid filled sac Other info: central vacuole in plant cells takes up most of cell space; aids in support of cell Golgi apparatus Function: modifies, packages, and transports proteins Shape/location: close to ER; closely layered stacks of membrane enclosed spaces Other info: proteins move from the ER to this organelle Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Function: aids in production of proteins and lipids Shape/location: interconnected network of folded membranes; takes up a large part of the Cytoplasm. Lumen is the interior of the ER. Rough ER: covered with ribosomes; as proteins are made by ribosomes they enter the lumen and may be modified. Smooth ER: not covered with ribosomes; makes lipids Ribosomes Function: link amino acids together to form proteins; site of protein synthesis Shape/location: very small; found on Rough ER and suspended in cytoplasm Other info: made in nucleolus; made of proteins and RNA Nucleus Function: store and protect DNA Shape/location: large, sphere shaped organelle. Has double membrane called the nuclear envelope Nucleolus Function: assembles ribosomes Shape/location: found inside the nucleus Vesicles Function: isolate and transport specific molecules Shape/location: small, membrane bound sacs; short lived Other info: After a protein is made, part of the ER forms a vesicle around the protein to protect it on its way to the golgi apparatus. Mitochondria Function: generate energy for the cell Shape/location: bean shaped; have an inner and outer membrane Other info: have their own ribosomes and DNA which suggests that they were originally free living prokaryotes. Lysosomes Function: digest and recycle foreign materials or worn-out parts Shape/location: membrane bound; contains enzymes Other info: found in animal cells; presence in plant cells is still questioned Defends cells from invading bacteria and viruses Centrosome Small region of cytoplasm that produces microtubules (including spindle fibers present during cell division. Centrioles Function: help divide DNA during cell division; also organize microtubules to form Cilia (hairs) and flagella (tail) Shape/location: cylinder shaped; made of short microtubules arranged in a circle Found in animal cells Cell Wall Function: shape and support of cell and organism Shape/location: found in plants, algae, fungi and bacteria. Surrounds cell membrane Other info: plant and algae cell walls are made of cellulose Chloroplast Function: carry out photosynthesis (convert solar energy into chemical energy) Shape/location: have an outer and inner membrane. Inside chloroplast are stacks of Thylakoids, disc shaped sacs, that contain the green pigment chlorophyll. Other info: have their own ribosomes and DNA which suggests that they were originally free living prokaryotes. Plants have chloroplasts and mitochondria