Bromine (Br)
advertisement

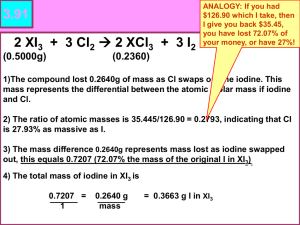
Fluorine (F) Highly toxic, refrigerants gas Basic Information Name: Fluorine Symbol: F Atomic Number: 9 Atomic Mass: 18.998 amu Electron Configuration: 2,7 Boiling Point: -188.14 ۫C Melting Point: -219.62 ۫C Diatomic element Facts Derived from the Latin word “fleure”, which means flow Discovery: In 1886, by Henri Moissan Obtained from: Mineral fluorite Description Greenish pale yellow acidic gas Most reactive of the non-metal → combined with most other elements 13th most common element in the crust Uses Helps other materials to burn → Rocket fuels Alone it is poisonous → used in fluorine compound → nuclear industry Toothpaste → Average human body contains hundredth of ounce of fluorine Damage ozone layer Bromine (Br) volatile, mobile, dangerous reddishbrown liquid Basic Information Name: Bromine Symbol: Br Atomic Number: 35 Atomic Mass: 79.904 amu Electron Configuration: 2,8,18,7 Boiling Point: 58.78 ۫C Melting Point: -7.2 ۫C Diatomic element Facts Derived from the Greek word “bromos”, which means stench Discovery: In 1826, by Antoine J. Balard from SALT WATER Poisonous Obtained from: SEA WATER Description A reddish-brown liquid The only non-metal that is a liquid at normal room conditions. Causes painful burns Uses Very poisonous → Pesticides Photographic film Malfunctioning of nervous system → Disturbances in genetic materials Organic Bromine can cause damage to organs → Can even cause cancer !!!! Iodine (I) bluish-black, lustrous solid Basic Information Name: Iodine Symbol: I Atomic number: 53 Atomic mass: 126.90 amu Electron configuration: 2,8,18,18,7 Boiling Point:183 ۫C Melting Point: 113.7 ۫C Diatomic element Facts Derived from the Greek word iôdes, which means “violet” Discovery: In 1811, by Bernald Courtois from SULFURIC ACID Required in humans Obtained from: sodium and potassium compounds Description When solid: looks metallic, grayish-black or violet-dark gray color. As a gas: violet color, with a harsh, unpleasant odor. Sublimation → Never exists as a liquid Uses → First Aid Iodine for body function A naturally occurring mineral for your body to function normally. Iodine Body Functions: Heat and Energy production Metabolism of fat Physical and Mental development Production of Thyroid hormone Iodine Deficiency Iodine Deficiency Disorders For FOOD SOURCES high in IODINE try: - Seafood - Kelp - Iodized Salt Bibliography http://www.chemicalelements.com/elements/br.ht ml http://www.carondelet.pvt.k12.ca.us/Family/Scie nce/Halogens/bromine.htm www.webelements.com/webelements/ elements/text/I/key.html http://www.lm.liverpool.k12.ny.us/HyperChart/ch emicalprops/bromine.html