Cold War Timeline
advertisement

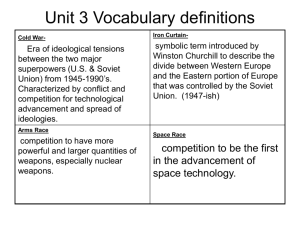
Timeline of events in the Cold War From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia 1940’s 1945 February 8: The Yalta Conference occurs, deciding the post-war status of Germany. The Allies of World War II (the USA, the USSR, Great Britain and France) divide Germany into four occupation zones. The Allied nations agree that free elections are to be held in all countries occupied by Nazi Germany. In addition, the new United Nations are to replace the failed League of Nations. April 12: US Franklin D. Roosevelt suffers a stroke and dies while on vacation in Warm Springs, GA. April 23: US President Harry S. Truman gives a tongue-lashing to Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov indicating that he was determined to take a "tougher" stance with the Soviets than his predecessor had. July 24: US President Harry S. Truman informs Soviet Union leader Joseph Stalin that the United States has nuclear weapons. August 2: The Potsdam Conference ends with the Potsdam Agreement that organizes the division and reconstruction of Europe after World War II. New boundaries of Poland are agreed. Before the agreement to divide Germany into four zones (Yalta Conference), the four nations also decide to split Germany's capital, Berlin, into four zones as well. The Allied powers also agree to start legal trials at Nuremberg of Nazi war criminals. August 6: US President Truman gives permission for the world's first military use of an atomic weapon against the Japanese city of Hiroshima in an attempt to bring the only remaining theatre of war from the Second World War in the Pacific to a swift closure. August 8: The USSR honors its agreement to declare war on Japan within three months of the victory in Europe, and invades Manchuria. In accordance with the Yalta Conference agreements, the Soviet Union also invades Japanese Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands. August 9: US President Truman gives permission for the world's second and last military use of an atomic weapon against the Japanese city of Nagasaki in order to try to secure a swift Japanese unconditional surrender in the end of the Second World War. September 2: The Japanese surrender unconditionally to the US on board the USS Missouri to representative General Douglas MacArthur. September 5: Igor Gouzenko, a clerk working in the Soviet embassy in Ottawa, Canada, defects and provides proof to the Royal Canadian Mounted Police of a Soviet spy ring operating in Canada and other western countries. The Gouzenko affair helps change perceptions of the Soviet Union from an ally to a foe. 1946 January: Chinese Civil War resumed between Communist and Nationalist forces. January 7: The Republic of Austria is reconstituted, with its 1937 borders, but divided into four zones of control: American, British, French, and Soviet. January 11: Enver Hoxha declares the People's Republic of Albania, with himself as Prime Minister. February 9: Joseph Stalin makes his Election Speech, in which he states that capitalism and imperialism make future wars inevitable.[1] 22: George F. Kennan writes his Long Telegram, describing his interpretation of the objectives and intentions of the Soviet leadership.[2] March: The Greek Civil War reignites between communists and the conservative Greek government. March 2: British soldiers withdraw from their zone of occupation in southern Iran. Soviet soldiers remain in their northern sector. March 5: Winston Churchill warns of the descent of an Iron Curtain across Europe. April 5: Soviet forces evacuate Iran after a crisis. July 4: The Philippines gains independence from the United States, and begins fighting communist Huk rebels (Hukbalahap Rebellion). September 6: In a speech known as the Restatement of Policy on Germany in Stuttgart, James F. Byrnes, United States Secretary of State repudiates the Morgenthau Plan. He states the US intention to keep troops in Europe indefinitely and expresses US approval of the territorial annexation of 29% of pre-war Germany, but does not condone further claims. September 8: In a referendum, Bulgaria votes for the establishment of a People's Republic, deposing King Simeon II. Western countries dismiss the vote as fundamentally flawed. September 24: Truman is presented with the Clifford-Elsey Report, a document which listed Soviet violations of agreements with the United States. September 27:Nikolai Vasilevich Novikov writes a response to Kennan's Long Telegram, known as the 'Novikov Telegram', in which he states that the United States are "striving for world supremacy".[3] December 19: French landings in Indochina begin the First Indochina War. They are resisted by the Viet Minh communists who want national independence. 1947 January 1: The American and British zones of control in Germany are united to form the Bizone also known as Bizonia. March 12: President Harry Truman announces the Truman Doctrine starting with the giving of aid to Greece and Turkey in order to prevent them from falling into the Soviet sphere April 16: Bernard Baruch, in a speech given during the unveiling of his portrait in the South Carolina House of Representatives, coins the term "Cold War" to describe relations between the United States and the Soviet Union. May 22: US extends $400 million of military aid to Greece and Turkey, signalling its intent to contain communism in the Mediterranean. June 5: Secretary of State George Marshall outlines plans for a comprehensive program of economic assistance for the war-ravaged countries of Western Europe. It would become known throughout the world as the Marshall Plan. July 11: The US announces new occupation policies in Germany. The occupation directive JCS 1067, whose economic section had prohibited "steps looking toward the economic rehabilitation of Germany [or] designed to maintain or strengthen the German economy", is replaced by the new US occupation directive JCS 1779 which instead notes that "An orderly, prosperous Europe requires the economic contributions of a stable and productive Germany." August 14: India and Pakistan are granted independence by the United Kingdom. November 14: The United Nations passes a resolution calling for the withdrawal of foreign soldiers from Korea, free elections in each of the two administrations, and the creation of a UN commission dedicated to the unification of the peninsula. December 30: In Romania, King Michael I of Romania is forced to abdicate by Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej, the monarchy is abolished and the Popular Republic of Romania is instituted instead. The Communist Party will rule the country until December 1989. 1948 February 25: The Communist Party takes control in Czechoslovakia, after President Edvard Beneš accepts the resignation of all non-communist ministers. March 10: Czechoslovakian Foreign Minister Jan Masaryk is reported having committed suicide. April 3: Truman signs the Marshall Plan into effect. By the end of the programs, the United States has given $12.4 billion in economic assistance to European countries. May 10: A parliamentary vote in southern Korea sees the confirmation of Syngman Rhee as President of the Republic of Korea, after a left-wing boycott. June 18: A communist insurgency in Malaya begins against British and Commonwealth forces. June 21: In Germany, the Bizone and the French zone launch a common currency, the Deutsche Mark. June 24: Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin orders the blockade of all land routes from West Germany to Berlin, in an attempt to starve out the French, British, and American forces from the city. In response, the three Western powers launch the Berlin Airlift to supply the citizens of Berlin by air. June 28: The Soviet Union expels Yugoslavia from the Communist Information Bureau (COMINFORM) for the latter's position on the Greek civil war. June 28 to May 11, 1949: The Berlin Airlift defeats Russia's attempt to starve West Berlin. July 17: The constitution of the Republic of Korea is effected. September 9: The Soviet Union declares the Democratic People's Republic of Korea to be the legitimate government of all of Korea, with Kim Il-sung as Prime Minister. November 20: The American consul and his staff in Mukden, China, are made virtual hostages by communist forces in China. The crisis did not end until a year later, by which time U.S. relations with the new communist government in China had been seriously damaged. 1949 April 4: The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is founded by Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States, in order to resist Communist expansion. May 11: The Soviet blockade of Berlin ends with the re-opening of access routes to Berlin. The airlift continues until September, in case the Soviets re-establish the blockade. May 23: In Germany, the Bizone merges with the French zone of control to form the Federal Republic of Germany, with Bonn as its capital. June 8: The Red Scare reaches its peak, with the naming of numerous American celebrities as members of the Communist Party. August 29: The Soviet Union tests its first atomic bomb. The test, known to Americans as Joe 1, succeeds, as the Soviet Union becomes the world's second nuclear power. September 13: The USSR vetoes the United Nations membership of Ceylon, Finland, Iceland, Italy, Jordan, and Portugal. September 15: Konrad Adenauer becomes the first Chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany. October 1: Mao Zedong declares the foundation of the People's Republic of China adding a quarter of the world's population to the communist camp. October 7: The Soviets declare their zone of Germany to be the German Democratic Republic, with its capital at East Berlin. October 16: Nikos Zachariadis, leader of the Communist Party of Greece, declares an end to the armed uprising. The declaration brings to a close the Greek Civil War, and the first successful containment of communism. December 27: Sovereignty is handed over to United States of Indonesia from the Netherlands through the Dutch-Indonesian Round Table Conference with Sukarno as the first president of the newly formed federation. 1950s 1950 January 5: The United Kingdom recognizes the People's Republic of China. The Republic of China severs diplomatic relations with the United Kingdom. January 19: China officially diplomatically recognizes Vietnam as independent from France. January 21: The last Kuomintang soldiers surrender on continental China. February 16: The Soviet Union and the People's Republic of China sign a pact of mutual defense. March 11: Kuomintang leader Chiang Kai-shek moves his capital to Taipei, Taiwan, establishing a stand-off with the People's Republic of China. April 17: United States State Department Director of Policy Planning Paul Nitze issues NSC-68, a classified brief, arguing for the adoption of containment as the cornerstone of United States foreign policy. It would dictate US policy for the next twenty years. May 11: Robert Schuman describes his ambition of a united Europe. Known as the Schuman Declaration, it marks the beginning of the creation of the European Community. June 25: North Korea invades South Korea, beginning the Korean War. June 28: Seoul, the capital of South Korea, falls to North Korean forces. June 30: The United Nations votes to send forces to Korea to aid South Korea. The Soviet Union cannot veto, as it is boycotting the Security Council over the admission of People's Republic of China. Eventually, the number of countries operating under the UN aegis increases to 16: Australia, Belgium, Canada, Colombia, Ethiopia, France, Greece, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, New Zealand, the Philippines, South Africa, Thailand, Turkey, the United Kingdom, and the United States. July 4: United Nations forces engage North Korean forces for the first time, in Osan. They fail to halt the North Korean advance, and fall southwards, towards what would become the Pusan Perimeter. September 30: United Nations forces land at Inchon. Defeating the North Korean forces, they press inland and re-capture Seoul. October 2: United Nations forces cross the 38th parallel, into North Korea. October 5: Forces from the People's Republic of China mobilize along the Yalu River. October 22: Pyongyang, the capital of North Korea, falls to United Nations forces. October 22: China intervenes in Korea with 300,000 soldiers, catching the United Nations by surprise. However, they withdraw after initial engagements. November 15: United Nations forces approach the Yalu River. In response, China intervenes in Korea again, but with a 500,000 strong army. This offensive forces the United Nations back towards South Korea. 1951 January 4: Chinese soldiers capture Seoul. March 14: United Nations forces recapture Seoul during Operation Ripper. By the end of March, they have reached the 38th Parallel, and formed a defensive line across the Korean peninsula March 29: Julius and Ethel Rosenberg are convicted of espionage for their role in passing atomic secrets to the Soviets during and after World War II. April 11: US President Harry S. Truman fires Douglas MacArthur from command of US forces in Korea. April 23: American journalist William N. Oatis is arrested in Czechoslovakia for alleged espionage. April 18: The European Coal and Steel Community is formed by the Treaty of Paris. July 4: American journalist William N. Oatis receives a ten-year sentence in Czechoslovakia on an espionage charge. September 1: Australia, New Zealand, and the United States sign the ANZUS Treaty. This compels the three countries to cooperate on matters of defense and security in the Pacific. October 10: President Harry S. Truman signs the Mutual Security Act, announcing to the world, and its communist powers in particular, that the U.S. was prepared to provide military aid to "free peoples." November 14: President Harry Truman asks Congress for U.S. military and economic aid for the communist nation of Yugoslavia. December 12: The International Authority for the Ruhr lifted part of the remaining restrictions on German industrial production and on production capacity. 1952 April 28: Japan signs the Treaty of San Francisco and the Treaty of Taipei, formally ending its period of occupation and isolation, and becoming a sovereign state. February 18: Greece and Turkey join NATO. June: Strategic Air Command begins Reflex Alert deployments of Convair B-36 and B47 Stratojet long-range nuclear bombers to overseas bases like purpose-built Nouasseur Air Base in French Morocco, placing them within unrefueled striking range of Moscow. June 14: The United States lays the keel for the world's first nuclear-powered submarine, USS Nautilus. June 30: The Marshall Plan ends, with European industrial output now well above that of 1938. July 23: Gamal Abdel Nasser heads a coup against King Farouk of Egypt. October 2: The United Kingdom successfully tests its atomic bomb in Operation Hurricane. The test makes the UK the world's third nuclear power. November 1: The United States tests their first thermonuclear bomb, Ivy Mike. 1953 January 20: Dwight D. Eisenhower becomes President of the United States. March 5: Joseph Stalin dies, setting off a power struggle to succeed him. May 16: American journalist William N. Oatis is released from prison in Czechoslovakia after serving 22 months of a ten-year sentence for espionage. July 27: An armistice agreement ends fighting in the Korean War.[4] August 19: The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) assists a royalist coup that ousts Iranian Prime Minister Mohammed Mosaddeq (Operation Ajax). The coup was organized because of Iranian nationalization of the oil industry and fears of Iran joining the Soviet camp. September 7: Nikita Khrushchev becomes leader of the Soviet Communist Party. His main rival, Lavrentiy Beria, is executed in December. December 4–8: Eisenhower meets with Churchill and Joseph Laniel of France in Bermuda. 1954 January 21: The United States launches the world's first nuclear submarine, USS Nautilus. The nuclear submarine would become the ultimate nuclear deterrent. May 7: The Viet Minh defeat the French at Dien Bien Phu. France withdraws from Indochina, leaving four independent states: Cambodia, Laos, and what became North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The Geneva Accords calls for free elections to unite Vietnam, but none of the major Western powers wish this to occur in the likely case that the Viet Minh (nationalist Communists) would win. May: The Huk revolt in the Philippines is defeated. June 2: Senator Joseph McCarthy charges that communists have infiltrated the CIA and the atomic weapons industry. June 18: The elected leftist Guatemalan government is overthrown in a CIA-backed coup. An unstable rightist regime installs itself. Opposition leads to a guerrilla war with Marxist rebels in which major human rights abuses are committed on all sides. Nevertheless, the regime survives until the end of the Cold War. July 8: Col. Carlos Castillo Armas is elected president of the junta that overthrew the administration of Guatemalan President Jacobo Arbenz Guzman. August 11: The Taiwan Strait Crisis begins with the Chinese Communist shelling of Taiwanese islands. The US backs Taiwan, and the crisis resolves itself as both sides decline to take action. September 8: Foundation of the South East Asian Treaty Organization (SEATO) by Australia, France, New Zealand, Pakistan, Thailand, the Philippines, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Like NATO, it is founded to resist Communist expansion, this time in the Philippines and Indochina. 1955 February 24: The Baghdad Pact is founded by Iran, Iraq, Pakistan, Turkey, and the United Kingdom. It is committed to resisting Communist expansion in the Middle East. March: Soviet aid to Syria begins. The Syrians will remain allies of the Soviets until the end of the Cold War. April: The Non-Aligned Movement is pioneered by Jawaharlal Nehru of India, Sukarno of Indonesia, Tito of Yugoslavia, Gamal Abdel Nasser of Egypt and Kwame Nkrumah of Ghana. This movement was designed to be a bulwark against the 'dangerous polarization' of the world at that time and to restore balance of power with smaller nations. It was an international organization of states considering themselves not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. May 9: West Germany joins NATO and begins rearmament. May 14: The Warsaw Pact is founded in Eastern Europe and includes East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Poland, Hungary, Romania, Albania, Bulgaria, and the Soviet Union. It acts as the Communist military counterpart to NATO. May 15: Austria is neutralized and allied occupation ends. July 18: President Dwight D. Eisenhower of the United States, Prime Minister Anthony Eden of the United Kingdom, Premier Nikolai A. Bulganin of the Soviet Union, and Prime Minister Edgar Faure of France, known as the 'Big Four', attend the Geneva Summit. Also in attendance was Nikita Khrushchev of the Soviet Union. 1956 February 25 : Nikita Khrushchev delivers the speech "On the Personality Cult and its Consequences" at the closed session of the Twentieth Party Congress of the CPSU. The speech marks the beginning of the De-Stalinization. June 28: in Poznań, Poland, anti-communist protests lead to violence. July 26: Nasser nationalizes the Suez Canal. October 23: Hungarian Revolution of 1956: Hungarians revolt against the Soviet dominated government. They are crushed by the Soviet military, which reinstates a Communist government. October 29: Suez Crisis: France, Israel, and the United Kingdom attack Egypt with the goal of removing Nasser from power. International diplomatic pressures force the attackers to withdraw. Canadian Lester B. Pearson encourages the United Nations to send a Peacekeeping force, the first of its kind, to the disputed territory. Lester B. Pearson wins a Nobel Peace Prize for his actions, and soon after becomes Canadian Prime Minister. December: Communist insurgency begins in South Vietnam, sponsored by North Vietnam. 1957 January 5: The Eisenhower doctrine commits the US to defending Iran, Pakistan, and Afghanistan from Communist influence. January 22: Israeli forces withdraw from the Sinai, which they had occupied the previous year. May 2: Senator Joseph McCarthy succumbs to illness exacerbated by alcoholism and dies. October 1: The Strategic Air Command initiates 24/7 nuclear alert (continuous until termination in 1991) in anticipation of a Soviet ICBM surprise attack capability. October 4: Sputnik satellite launched. November 3: Sputnik 2 was launched, with the first living being on board, Laika. November 7: The final report from a special committee called by President Dwight D. Eisenhower to review the nation's defense readiness indicates that the United States is falling far behind the Soviets in missile capabilities, and urges a vigorous campaign to build fallout shelters to protect American citizens. November 15: Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev claims that the Soviet Union has missile superiority over the United States and challenges America to a missile "shooting match" to prove his assertion. 1958 July 14: A coup in Iraq, the 14 July Revolution, removes the pro-British monarch. Iraq begins to receive support from the Soviets. Iraq will maintain close ties with the Soviets throughout the Cold War. August 23: Second Taiwan Strait Crisis begins when China begins to bomb Quemoy. August: Thor IRBM deployed to the UK, within striking distance of Moscow. September: A US reconnaissance C-130 airplane is shot down over Armenia by Mig-17s, with 17 casualties.[5] November: Start of the second Berlin crisis, Nikita Khrushchev asks the West to leave Berlin. October 4: The National Aeronautics and Space Administration, or NASA is formed. 1959 January 1: Cuban Revolution. Fidel Castro becomes the leader of Cuba although refrains from declaring the country Communist. Cuban-inspired guerrilla movements spring up across Latin America. March 24: New Republic government of Iraq leaves Central Treaty Organization May 24: Former U.S. Secretary of State John Foster Dulles dies from cancer. July 24: During the opening of the American National Exhibition in Moscow US Vice President Richard Nixon and Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev openly debate the capacities of each Superpower. This conversation is known as the Kitchen Debate. August 7: Explorer 6 is launched into orbit to photograph the Earth. September: Khrushchev visits U.S. for 13 days, and is denied access to Disneyland. Instead, he visits SeaWorld.[6] December: Formation of the FNL (pejoratively called Viet Cong) in North Vietnam. It is a Communist insurgent movement that vows to overthrow the anti-communist South Vietnamese dictatorship. It is supplied extensively by North Vietnam and the USSR eventually. 1960s 1960 February 16: France successfully tests its first atomic bomb, Gerboise Bleue, in the middle of the Algerian Sahara Desert. April: Jupiter IRBM deployment to Italy begins, placing nuclear missiles within striking range of Moscow (as with the Thor IRBMs deployed in the UK). May 1: American pilot Francis Gary Powers is shot down in his U-2 spy plane while flying at high altitude over the Soviet Union, resulting in the U-2 Incident, an embarrassment for President Eisenhower. June: Sino-Soviet split: The Chinese leadership, angered at being treated as the "junior partner" to the Soviet Union, declares its version of Communism superior and begin to compete with the Soviets for influence, thus adding a third dimension to the Cold War. July 31: Communist insurgents in Malaya are defeated. August 9: The Pathet Lao (communist) revolt in Laos begins. 1961 January 3: Dwight D. Eisenhower closes the U.S. embassy in Havana and severs diplomatic relations with Cuba. January 20: John F. Kennedy becomes President of the United States. February 4: Angolan nationalists, including communists, begin an insurgency against Portuguese rule. April 12: Yuri Gagarin becomes the first human in space and first to orbit the Earth when the Soviet Union successfully launches Vostok 1. April 17–19: Bay of Pigs Invasion: A CIA-backed invasion of Cuba by counterrevolutionaries ends in failure. May 25: John F. Kennedy announces the US intention to put a man on the moon kickstarting the Apollo program June 4: Kennedy meets with Khrushchev in Vienna. June: Jupiter IRBM deployment to Turkey begins, joining the Jupiters deployed to Italy as well as the Thor IRBMs deployed to the UK as nuclear missiles placed within striking distance of Moscow. August 13: The Berlin Wall is built by the Soviets following the breakdown in talks to decide the future of Germany. August 17: Alliance for Progress aid to Latin America from the United States begins. October 17: 22nd Soviet Party Congress held in USSR October 27: Beginning of Checkpoint Charlie standoff between US and Soviet tanks October 31: The Soviet Union detonates the Tsar Bomba, the most powerful thermonuclear weapon ever tested, with an explosive yield of some 50 megatons. September 1: The Soviet Union resumed testing of nuclear weapons in the atmosphere. December 2: Fidel Castro openly describes himself as a Marxist-Leninist. 1962 February 10: American pilot Francis Gary Powers is exchanged for senior KGB spy Colonel Rudolf Abel. July 20: Neutralization of Laos is established by international agreement, but North Vietnam refuses to withdraw its personnel. [1] September 8: Himalayan War: Chinese forces attack India, making claims on numerous border areas. October 16: Cuban Missile Crisis: The Soviets have secretly been installing military bases, including nuclear weapons, on Cuba, some 90 miles from the US mainland. Kennedy orders a "quarantine" (a naval blockade) of the island that intensifies the crisis and brings the US and the USSR to the brink of nuclear war. In the end, both sides reach a compromise. The Soviets back down and agree to withdraw their nuclear missiles from Cuba, in exchange for a secret agreement by Kennedy pledging to withdraw similar American missiles from Turkey, and guaranteeing that the US will not move against the Castro regime. November 21: End of the Himalayan War. China occupies a small strip of Indian land. 1963 June 20: The United States agrees to set up a hotline with the USSR, thus making direct communication possible. June 21: France announces that it is withdrawing its navy from the North Atlantic fleet of NATO. July 25: The Partial Test Ban Treaty is signed by the US, UK and USSR, prohibiting the testing of nuclear weapons anywhere except underground. November 2: South Vietnamese Prime Minister Diem is assassinated in coup, suspected CIA involvement November 22: John F. Kennedy is shot and killed in Dallas by Lee Harvey Oswald. There has been some speculation over whether communist countries or even CIA were involved in the assassination, but those theories remain controversial. Kennedy's vicepresident Lyndon B. Johnson becomes President of the United States. 1964 unknown date: 1964 decision of the Soviet Politburo to increase spending on terrorism by one thousand percent[5] March 30 / April 1: A military-led coup d'état overthrows democratically elected president João Goulart in Brazil. Goulart's proposals, such as land reform and bigger control of the state in the economy, were seen as "communist", though he was from the labour party. April 20: US President Lyndon Johnson in New York, and Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev in Moscow, announce simultaneously plans to cut back production of materials for making nuclear weapons. May 27: Jawaharlal Nehru dies. August 4: US President Lyndon B. Johnson claims that North Vietnamese naval vessels had fired on two American destroyers in the Gulf of Tonkin. Although there was a first attack, it was later proven that American vessels had entered North Vietnamese territory, and the second attack is proved unfounded. The Gulf of Tonkin Incident leads to the open involvement of the United States in the Vietnam War, after the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution. October 14: Leonid Brezhnev succeeds Khrushchev to become General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union October 16: China tests its first atomic bomb. The test makes China the world's fifth nuclear power. 1965 March 8: US military build up to defend South Vietnam. North Vietnam has also committed its forces in the war. US begins sustained bombing of North Vietnam. April 28: US forces invade the Dominican Republic to prevent a communist takeover like the one that occurred in Cuba. August 15: Second Indo-Pakistani War. September 23: The Second Indian-Pakistani War ends in a cease-fire. September 30: Six Indonesian generals murdered as part of the 30 September Movement. November 11: Rhodesian colonial government under Ian Douglas Smith declares UDI. November 14: Battle of Ia Drang, the first major engagement between US Troops and regular Vietnamese forces. 1966 March 10: France withdraws from NATO command structure. May 8: Communist China detonates a third nuclear device August 26: South African Border War begins 1967 April 25: 33 Latin American and Caribbean countries sign the Treaty of Tlatelolco in Mexico City, which seek the prohibition of nuclear weapons in Latin America and the Caribbean. March 12: General Suharto successfully overthrows Sukarno as president of Indonesia. May 23: Egypt blocks the Straits of Tiran, then expels UN peacekeepers and moves its army into the Sinai Peninsula in preparation for possible attack on Israel. May 25: Uprising in Naxalbari, India marking the expansion of Maoism as a violent, antiUS and anti-Soviet, revolutionary movement across a number of developing countries. June 5: In response to Egypt's aggression, Israel invades the Sinai Peninsula, beginning the Six-Day War. June 23: U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson meets with Soviet Premier Alexei Kosygin in Glassboro, New Jersey for a three-day summit. August 8: Bangkok Declaration is established to quell the communist threat in Southeast Asia. November 29: Robert McNamara announces that he will resign as U.S. Secretary of Defense to become President of the World Bank. 1968 January 30: Tet Offensive in South Vietnam begins. March 31: Johnson suspends bombings over North Vietnam and announces he is not running for reelection. June 8: Tet Offensive ends; while an American military victory, it raises questions over America's military chances in Vietnam July 1: The Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) is opened for signature. August 20: Prague Spring Reforms in Communist Czechoslovakia result in Warsaw Pact intervention to crush them. December 23: The captain and crew of the USS Pueblo are released by North Korea. 1969 January 20: Richard Nixon becomes President of the United States. March 2: Border clashes between the Soviet Union and China March 17: The U.S begins bombing Communist sanctuaries in Cambodia. July 20: The U.S. accomplishes the first manned moon landing, Apollo 11. Manned by Neil Armstrong, "Buzz" Aldrin, and Michael Collins. July 25: "Vietnamization" begins with U.S. troop withdrawals from Vietnam and the burden of combat being placed on the South Vietnamese. September 1: Muammar al-Gaddafi overthrows the Libyan monarchy and expels British and American personnel. Libya aligns itself with the Soviet Union. 1970s 1970 March 5: Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, ratified by the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union and the United States, among others, enters into force. March 18: Lon Nol takes power in Cambodia. Khmer Rouge and Vietnamese Communists attack the new regime, which wants to end North Vietnamese presence in Cambodia. October 24: Salvador Allende becomes president of Chile after being confirmed by the Chilean congress. November 18: United States' aid to Cambodia to support the Lon Nol regime begins. 1971 February 8: South Vietnamese forces enter Laos to briefly cut the Ho Chi Minh trail. March 25: Third Indo-Pakistani War, Bangladesh gains independence from Pakistan. September 3: Four-Power Agreement on Berlin is signed by the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, France, and the United States. September 11: Nikita Khrushchev dies. October 25 : The United Nations General Assembly passes Resolution 2758, recognizing the People's Republic of China as the sole legitimate government of China. December 16 : Bangladesh and Indian joint forces defeat Pakistan in the Bangladesh Liberation War. Bangladesh is officially recognized by the eastern bloc. 1972 February 21: Nixon visits China, the first visit by a U.S. President since the establishment of the People's Republic of China. March 30: FNL goes to the offensive in South Vietnam, only to be repulsed by the South Vietnamese regime with major American air support. May 26: Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT I) agreement signals the beginning of détente between the U.S. and USSR. September 1: Bobby Fischer defeats Russian Boris Spassky in a chess match in Reykjavík, Iceland, becoming the first official American chess champion (see Match of the Century). September 2–28: The Summit Series, an ice hockey tournament between Canada and Soviet Union. December 18: Richard Nixon announces the beginning of a massive bombing campaign in North Vietnam 1973 January 27: The Paris Peace Accords end American involvement in the Vietnam War. Congress cuts off funds for the continued bombing of Indochina. September 11: Chilean coup d'état — The democratically-elected Marxist president of Chile, Salvador Allende, is deposed and commits suicides during a military coup led by General Augusto Pinochet, supported by the US. October 6: Yom Kippur War — Israel is attacked by Egypt and Syria, the war ends with a ceasefire. October 22: Egypt defects to the American camp by accepting a U.S. cease-fire proposal during the October 1973 war. November 11: The Soviet Union announces that, because of its opposition to the recent overthrow of the government of Chilean President Salvador Allende, it will not play a World Cup Soccer match against the Chilean team if the match is held in Santiago. 1974 September 12: The pro-Western monarch of Ethiopia, Haile Selassie, is ousted by a Marxist military junta known as the Derg. June: SEATO formally ends after France leaves the organization. August 9: Gerald Ford becomes President of the United States upon the resignation of Nixon. 1975 April 17: The communist Khmer Rouge take power in Cambodia; genocide ensues, later referred to as "The Killing Fields". April 30: North Vietnam wins the war in South Vietnam. The South Vietnam regime falls with the surrender of Saigon and the two countries are united under a Communist government. November 29: Pathet Lao takes power in Laos. May 12: Mayagüez incident: The Khmer Rouge seize an American naval ship, prompting American intervention to recapture the ship and its crew. In the end, the crew is released from captivity. June 25: Portugal withdraws from Angola and Mozambique, where Marxist governments are installed, the former with backing from Cuban troops. The Civil war engulfs both nations and involves Angolans, Mozambicans, South Africans, and Cubans, with the superpowers supporting their respective ideologies. July: The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project takes place. It is the first joint flight of the US and Soviet space programs. The mission is seen as a symbol of détente and an end to the "space race". August 1: Helsinki Final Act of the Conference on Security and Co-operation in Europe signed by the United States, Canada, the Soviet Union and Europe 1976 January 8: Chinese Premier Zhou Enlai dies of cancer. March 24: Coup d'état in Argentina. A Civil war against Argentine-based guerrilla warfare starts. July 20: U.S. Military personnel withdraw from Thailand. September 1: Inception of Safari Club. September 9: Death of Mao Zedong. 1977 January 1: Charter 77 is signed by Czechoslovakian intellectuals, including Václav Havel. January 20: Jimmy Carter becomes President of the United States. June 6: U.S. Secretary of State Cyrus Vance assures skeptics that the Carter administration will hold the Soviet Union accountable for its recent crackdowns on human rights activists. July 23: The Ogaden War begins when Somalia attacks Ethiopia. 1978 March 15: The Ogaden War ends with a cease-fire. April 27: President of Afghanistan Sardar Mohammed Daoud's government is overthrown when he is murdered in a coup led by pro-communist rebels. December 25: A Communist regime is installed in Afghanistan. 1979 January 7: Vietnam deposes the Khmer Rouge and installs a pro-Vietnam, pro-Soviet government. February 17: Sino-Vietnamese War, China launches a punitive attack on North Vietnam to punish it for invading Cambodia. January 16: The Iranian Revolution ousts the pro-Western Shah, Mohammed Reza Pahlavi and installs a theocracy under Ayatollah Khomeini. CENTO dissolves as a result. May 9: War breaks out in El Salvador between Marxist-led insurgents and the U.S.backed government. June 2: Pope John Paul II begins his first pastoral visit to his native Poland. June 18: U.S. President Jimmy Carter and Soviet leader, Leonid Brezhnev, sign the SALT II agreement, outlining limitations and guidelines for nuclear weapons. July 3: President Carter signs the first directive for financial aid to opponents of the proSoviet regime in Kabul, Afghanistan.[7] July 17: Marxist-led Sandinista revolutionaries overthrow the U.S.-backed Somoza dictatorship in Nicaragua. The Contra insurgency begins shortly thereafter. September: Nur Mohammed Taraki, The Marxist president of Afghanistan, is deposed and murdered. The post of president is taken up by Prime Minister Hafizullah Amin. November 4: Islamist Iranian students take over the American embassy in support of the Iranian Revolution. The Iran hostage crisis lasts until January 20, 1981. December 12: NATO Double-Track Decision, the alliance decides to deploy LRTNF and to negotiate arms control on the same systems. December 24: The Soviet Union invades Afghanistan to oust Hafizullah Amin, resulting in the end of Détente. 1980s 1980 March 21: The United States and its allies boycott the 1980 Summer Olympics (July 19August 3) in Moscow. May 4: Josip Broz Tito, communist leader of Yugoslavia since 1945, dies at the age of 88 in Belgrade. August 31: In Poland the Gdańsk Agreement is signed after a wave of strikes which began at the Lenin Shipyards in Gdańsk. The agreement allows greater civil rights, such as the establishment of a trade union independent of communist party control. 1981 January 20: Ronald Reagan inaugurated 40th President of the United States. Reagan is elected on a platform opposed to the concessions of détente. January 20: Iran hostage crisis ends. August 19: Gulf of Sidra Incident: Libyan planes attack U.S. jets in the Gulf of Sidra, which Libya has illegally annexed. Two Libyan jets are shot down; no American losses are suffered. October 27: A Soviet submarine, the U137, runs aground not far from the Swedish naval base at Karlskrona. November 23: The U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) begins to support antiSandinista Contras. December 13: Communist Gen. Jaruzelski introduces martial law in Poland, which drastically restricts normal life, in an attempt to crush the Solidarity trade union and the political opposition against communist rule. 1982 February 24: President Ronald Reagan announces the "Caribbean Basin Initiative" to prevent the overthrow of governments in the region by the forces of communism. March 22: President Ronald Reagan signs P.L. 97-157 denouncing the government of the Soviet Union should cease its abuses of the basic human rights of its citizens.[8][9] April 2: Argentina invades the Falkland Islands, starting the Falklands War. May 30: Spain joins NATO. June 6: Israel invades Lebanon to end raids and clashes with Syrian troops based there. June 14: Falkland Islands liberated by British task force. End of the Falklands War. November 10: Death and state funeral of Leonid Brezhnev November 14: Yuri Andropov becomes General Secretary of the Soviet Union. 1983 January: Soviet spy Dieter Gerhardt is arrested in New York. March 8: In speech to the National Association of Evangelicals, Reagan labels the Soviet Union an "evil empire". March 23: Ronald Reagan proposes the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI, or "Star Wars"). September 1: Civilian Korean Air Lines Flight 007, with 269 passengers, including U.S. Congressman Larry McDonald, is shot down by Soviet interceptor aircraft. October 25: U.S. forces invade the Caribbean island of Grenada in an attempt to overthrow the Marxist military government, expel Cuban troops, and abort the construction of a Soviet-funded airstrip. November 2: Exercise Able Archer 83 — Soviet anti-aircraft misinterpret a test of NATO's nuclear warfare procedures as a fake cover for an actual NATO attack; in response, Soviet nuclear forces are put on high alert. 1984 January: US President Ronald Reagan outlines foreign policy which reinforces his previous statements. February 13: Konstantin Chernenko is named General Secretary of the Soviet Communist Party. July 28: Various allies of the Soviet Union boycott the 1984 Summer Olympics (July 28 August 12) in Los Angeles. October 31: Indira Gandhi assassinated. December 16: Margaret Thatcher and the UK government, in a plan to open new channels of dialog with Soviet leadership candidates, meet with Mikhail Gorbachev at Chequers. 1985 March 11: Mikhail Gorbachev becomes leader of the Soviet Union. August 6: Coinciding with the 40th anniversary of the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the Soviet Union begins what it has announced is a 5-month unilateral moratorium on the testing of nuclear weapons. The Reagan administration dismisses the dramatic move as nothing more than propaganda and refuses to follow suit. Gorbachev declares several extensions, but the United States fails to reciprocate, and the moratorium comes to an end on February 5, 1987. November 21: Reagan and Gorbachev meet for the first time at a summit in Geneva, Switzerland, where they agree to two (later three) more summits. 1986 February 13: France launches Operation Epervier (Sparrowhawk) in an effort to repulse the Libyan invasion of Chad. February 25: The People Power Revolution takes place in the Philippines, overthrowing Ferdinand Marcos, dictator since 1965. First female president, Corazon Aquino April 15: U.S. planes bomb Libya in Operation El Dorado Canyon. April 26: Chernobyl disaster: A Soviet nuclear power plant in the Ukraine explodes, resulting in the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. October 11–12: Reykjavik Summit: A breakthrough in nuclear arms control. October 17: Ronald Reagan signs into law an act of Congress approving $100 million of military and "humanitarian" aid for the Contras. November 3: Iran-Contra affair: The Reagan administration publicly announces that it has been selling arms to Iran in exchange for hostages and illegally transferring the profits to the Contra rebels in Nicaragua. 1987 January 16: Natives within the Party who oppose his policies of economic redevelopment (Perestroika). It is Gorbachev's hope that through initiatives of openness, debate and participation, that the Soviet people will support Perestroika. June 12: During a visit to Berlin, Germany, U.S. President Ronald Reagan famously challenges Soviet Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in a speech: "Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!" (The Berlin Wall). September 10: The Battle of Cuito Cuanavale, Angola begins and further intensifies the South African Border War. November 18: After nearly a year of hearings into the Iran-Contra scandal, the Joint Congressional Investigating Committee issues its final report. It concludes that the scandal, involving a complicated plan whereby some of the funds from secret weapons sales to Iran were used to finance the Contra war against the Sandinista government in Nicaragua, was one in which the administration of Ronald Reagan exhibited "secrecy, deception, and disdain for the law." December 8: The Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty is signed in Washington, D.C. by U.S. President Ronald Reagan and Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev. Some later claim this was the official end of the Cold War. Gorbachev agrees to START I treaty. 1988 May 11: Kim Philby (Harold Adrian Russell Philby), the high-ranking U.K. intelligence officer who defected to the Soviet Union, dies in Moscow. May 15: The Soviets begin withdrawing from Afghanistan. May 29-June 1: Reagan and Gorbachev meet in Moscow. INF Treaty ratified. When asked if he still believes that the Soviet Union is still an evil empire, Reagan replies he was talking about "another time, another era." December 22: South Africa withdraws from South West Africa (Namibia). February 22: Incident: U.S.S. Yorktown (CG-48) and U.S.S. Caron (DD-970) are rammed off the Crimean Peninsula after entering Soviet territorial waters. November 6: Soviet scientist and well-known human rights activist Andrei Sakharov begins a two-week visit to the United States. December 7: Gorbachev announces in a speech to the United Nations General Assembly that the Soviet Union will no longer militarily interfere with Eastern Europe. 1989 January 4: Gulf of Sidra incident between America and Libya, similar to the 1981 Gulf of Sidra incident. January 20: George H. W. Bush is inaugurated as 41st President of the United States. February 2: Soviet troops withdraw from Afghanistan. June 4: Tiananmen Square Massacre: Beijing protests are crushed by the communist Chinese government, resulting in an unknown number of deaths. June 4: Semi-free elections in Poland show complete lack of backing for the Communist Party; Solidarity trade union wins all available seats in the Parliament and 99% in the Senate. August: Parliament in Poland elects Tadeusz Mazowiecki as leader of the first noncommunist government in the Eastern Bloc. October 18: The Hungarian constitution is amended to allow a multi-party political system and free elections. The nearly 20-year rule of communist leader Erich Honecker comes to an end in East Germany. November 9: Revolutions of Eastern Europe: Soviet reforms and their state of bankruptcy have allowed Eastern Europe to rise up against the Communist governments there. The Berlin Wall is breached when Politburo spokesman, Günter Schabowski, not fully informed of the technicalities or procedures of the newly agreed lifting of travel restrictions, mistakenly announces at a news conference in East Berlin that the borders have been opened. December 3: At the end of the Malta Summit, Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev and US President George H. W. Bush declare that a long-lasting era of peace has begun. Many observers regard this summit as the official beginning of the end of the Cold War. December 14: Democracy is restored in Chile. December 16–25: Romanian Revolution: Rioters overthrow the Communist regime of Nicolae Ceauşescu, executing him and his wife, Elena. Romania was the only Eastern Bloc country to violently overthrow its Communist regime or to execute its leaders December 29: Václav Havel becomes President of the now free Czechoslovakia 1990s 1990 January 31: The first McDonald's in Moscow, Russia opens. March 11: Lithuania becomes independent. May 29: Boris Yeltsin elected as president of Russia. August 2: Iraq invades Kuwait, beginning Gulf War. October 3: Germany is reunified. 1991 February 28: Gulf War ends. July: Warsaw Pact is formally dissolved. August 19: Soviet coup attempt of 1991. The August coup occurs in response to a new union treaty to be signed on August 20. December 25: US President George H. W. Bush, after receiving a phone call from Boris Yeltsin, delivers a Christmas Day speech acknowledging the end of the Cold War. December 25: Mikhail Gorbachev resigns as President of the USSR. The hammer and sickle is lowered for the last time over the Kremlin. December 26: The Council of Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR recognizes the dissolution of the Soviet Union and decides to dissolve itself. December 31: All Soviet institutions cease operations.