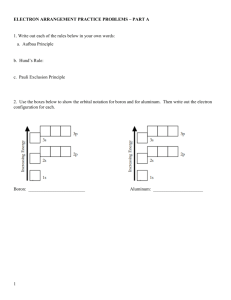
Electron Configurations
advertisement

Electron Configurations You will need: 1. Your homework from Friday (Quantum Mechanical Model in last week’s packet) 2. Your homework from last night (Electron Configuration Guided Reading in this week’s packet) Anything that you see in white, you should write down Bohr Model of Hydrogen Nucleus e e Possible electron orbits Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry 2002, page 331 Bohr Model of Hydrogen • Bohr model = epic fail for all other elements e e The Quantum Mechanical Model The Quantum Mechanical Model • 2 parts of an atoms –Nucleus –Electron cloud »Where the probability of finding an electron is high »Drawn as a fuzzy cloud »The cloud is more dense where the probability of finding the electron is high. Less likely to find an electron Electron cloud More likely to find an electron Nucleus The Quantum Mechanical Model • Atomic Orbitals –Space around the nucleus –High probability of finding an electron –Has a specific energy level –Has a specific sublevel »Sublevels have different shapes • Further describes where an electron is likely to be found The Quantum Mechanical Model Atomic orbital shapes: AKA: Angular momentum quantum number S orbital Angular momentum quantum number (l) = 0 The Quantum Mechanical Model Atomic orbital shapes: P orbitals Angular momentum quantum number (l) = 1 The Quantum Mechanical Model Atomic orbital shapes: D orbitals Angular momentum quantum number (l) = 2 The Quantum Mechanical Model Atomic orbital shapes: F orbitals Angular momentum quantum number (l) = 3 Think-Pair-Share • Turn to your neighbor and… –Explain what an orbital is –List the 4 shapes of atomic orbitals Vocabulary • Quantum numbers: tell us the properties of atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons in the orbitals • Principle quantum number – Symbol: n – The energy level that an electron occupies • Angular momentum quantum number – Symbol: l – The shape of the orbital • Spin quantum number – +1/2 or -1/2 – Spin state of an electron Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 2 3 4 s 1 2 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 3 4 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 3 4 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 s 1 2 3 4 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 s 1 2 p 3 6 3 4 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 s 1 2 p 3 6 3 d 4 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 3 4 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 3 4 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 s 1 2 3 4 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 s 1 2 p 3 6 3 4 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 3 4 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 3 4 f Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 f 7 3 4 Main energy Sublevels Number of orbitals Number of electrons level (n) (orbital shape) per sublevel per sublevel 1 s 1 2 2 s 1 2 p 3 6 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 s 1 2 p 3 6 d 5 10 f 7 14 3 4 Electron Configurations • Electron configuration: – The arrangement of electrons in an atom • The lowest-energy arrangement of the electrons for each element is called the element’s ground-state electron configuration Rules for writing electron configurations • Aufbau principle: – An electron occupies the orbital of lowestenergy first 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s 2p 3p 4p 5p 6p 3d 4d 4f 5d 5f 6d 6f Rules for writing electron configurations • Hund’s rule: – Electrons occupy equal energy orbitals one at the time – The electrons in each orbital have the same spin – School bus rule 2px 2py 2pz Rules for writing electron configurations • Pauli exclusion principle: –Electrons in the same orbital must have different spins 2px 2py 2pz Think Pair Share • Turn to your neighbor and explain the three rules for electron configurations in your own words Orbital Diagram p. 105 Box = orbital Up and down arrow = electrons with opposite spins Arrow = electron Electron Notations • Orbital notation – Lines (or boxes) represent orbitals – Arrows represent electrons He Writing Electron Configurations 1. Locate the element on the periodic table Writing Electron Configurations 1. Locate the element on the periodic table 2. Determine the number of electrons in the element Writing Electron Configurations 1. Locate the element on the periodic table 2. Determine the number of electrons in the element 3. Fill in the electrons in the orbital notation diagram starting at 1s (remember the rules) Writing Electron Configurations 1. Locate the element on the periodic table 2. Determine the number of electrons in the element 3. Fill in the electrons in the orbital notation diagram starting at 1s (remember the rules) 4. Write the electron configuration from the completed orbital notation diagram Writing Electron Configurations 1. Locate the element on the periodic table 2. Determine the number of electrons in an atom of the element 3. Fill in the electrons in the orbital notation diagram starting at 1s (remember the rules) 4. Write the electron configuration from the completed orbital notation diagram 5. Calculate the number of electrons in the electron configuration and make sure it matches what you found in step 2 Orbital Notation Li = # of electrons = 3 Aufbau principle: an electron occupies the orbital of lowestenergy first Electron Notations • Electron configurations • Written in the following order: 1. Number of energy level 2. Letter of sublevel 3. Number of electrons in each sublevel written as a superscript 2 Number of electrons 1s Energy level Sublevel Energy levels Sublevels Number of electrons 2 2 6 1s 2s 2p Electron Configurations Li =1 Aufbau principle: an electron occupies the orbital of lowestenergy first Electron Configurations Li =1s Aufbau principle: an electron occupies the orbital of lowestenergy first Electron Configurations Li =1s2 Aufbau principle: an electron occupies the orbital of lowestenergy first Electron Configurations Li =1s22 Aufbau principle: an electron occupies the orbital of lowestenergy first Electron Configurations Li =1s22s Aufbau principle: an electron occupies the orbital of lowestenergy first Electron Configurations Li =1s22s1 # of electrons = 3 Aufbau principle: an electron occupies the orbital of lowestenergy first Electron Configurations # of electrons = 6 C= Hund’s rule: electrons occupy equal energy orbitals one at the time with the same spin Electron Configurations C=1 Hund’s rule: electrons occupy equal energy orbitals one at the time with the same spin Electron Configurations C = 1s Hund’s rule: electrons occupy equal energy orbitals one at the time with the same spin Electron Configurations C = 1s2 Hund’s rule: electrons occupy equal energy orbitals one at the time with the same spin Electron Configurations C = 1s22 Hund’s rule: electrons occupy equal energy orbitals one at the time with the same spin Electron Configurations C = 1s22s Hund’s rule: electrons occupy equal energy orbitals one at the time with the same spin Electron Configurations C = 1s22s2 Hund’s rule: electrons occupy equal energy orbitals one at the time with the same spin Electron Configurations C = 1s22s22 Hund’s rule: electrons occupy equal energy orbitals one at the time with the same spin Electron Configurations C = 1s22s22p Hund’s rule: electrons occupy equal energy orbitals one at the time with the same spin Electron Configurations C # of electrons = 6 = 1s22s22p2 Hund’s rule: electrons occupy equal energy orbitals one at the time with the same spin Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = # of electrons = 20 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s2 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s2 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22p Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22p6 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22p63 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22p63s Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22p63s2 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22p63s23 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22p63s23p Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22p63s23p6 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22p63s23p64 Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22p63s23p64s Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Ca = 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 # of electrons = 20 Electron Configurations Cl = # of electrons = 17 Electron Configurations Cl = 1 Electron Configurations Cl = 1s Electron Configurations Cl = 1s2 Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22 Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22s Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22s2 Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22s22 Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22s22p Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22s22p6 Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22s22p63 Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22s22p63s Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22s22p63s2 Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22s22p63s23 Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22s22p63s23p Electron Configurations Cl = 1s22s22p63s23p5 Exit Ticket • Fill out the worksheet that is being passed out • Turn it in when you are finished • Begin working on tonight’s homework – Save #4 for tomorrow night Blocks of the Periodic Table s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 p 1s 2s f 2p 3s d (n-1) 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 5d 6p 7s 6d 7p 6 (n-2) 7 4f 5f 1s Electron Notations • Noble gas notation – The noble gas that comes before the desired element on the periodic table is written in brackets – The rest of the electron configuration is written at the end • Energy level Sodium’s noble gas notation: • Sublevel Number of electrons 1 Noble gas [Ne]3s • Number of electrons Energy level Sublevel Electron Configurations Fe = 1s Electron Configurations Fe = 1s2 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s2 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p6 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p63 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p63s Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p63s2 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p63s23 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p63s23p Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p63s23p6 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p63s23p64 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p63s23p64s Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p63s23p64s23 Electron Configurations Fe = 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d Electron Configurations Pauli exclusion principle: electrons in the same orbital must have different spins Fe = 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6