Unit 3: Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt, and Kush
advertisement

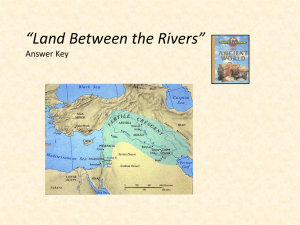
Unit 2: Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt, and Kush Chapter 3: Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 51-77 Bell Work 9-9 P. TN10 (1-5) Bell Work 9/10 Societal Changes Instructions: List features of the following societies. Leave cities blank and we will come back to it. Characteristics ____________ Hunter-Gatherer Society Characteristics Farming Societies (Small Villages) Characteristics _______________ Cities (Civilizations) ______________ Chapter 3: Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent The first civilizations grew up in river valleys in Asia and Africa. Such valleys provided water and fertile land for farming. In the region of the Tigris and Euphrates river valley, the Sumerians developed the world’s first civilization. Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent Early farming villages were not technologically advanced. As the communities grew more food, their settlements grew in size. What inventions, technology, or organizations would be needed in the community as it grows? Chapter 3: Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent Fertile Crescent Silt Irrigation Canals Surplus Division of Labor Rural Urban City-State Gilgamesh Sargon Empire Polytheism Priests Social Hierarchy Cuneiform Pictographs Scribe Epics Architectur e Ziggurat Monarch Hammurabi ’s Code Chariot Nebuchadn ezzar Alphabet Civilization A civilization is a society with cities, a central government, workers, who specialize in certain jobs leading to social classes, that has religion, writing, art, and architecture. There is no civilization without agriculture – societies need a stable food supply before they can develop. A civilization is made up of many parts. We will use the acronym G.R.A.P.E.S. to remember them! Geography – Where is the civilization? What sort of crops can they grow? What natural resources do they have? Religion – What do the people believe? How do their beliefs affect their lives? Achievements – What did they contribute to the world? What did they invent? What did they build (architecture)? Politics – What was their government like? Who made the decisions in the society? Economy - -How did the society distribute their resources? Did they trade or use money? What did they sell or trade? What did they need to get from outside of their civilization? Social Structures – What were their social class systems? Who was considered more important in their society? What were their art, music, and recreation like? Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Flooding & Silt Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia (land between the rivers) Draw a quick sketch of the Fertile Crescent with labels. Fertile Crescent (color this area green) Asia Minor Arabian Peninsula Persian Gulf Mediterranean Sea Mesopotamia Tigris and Euphrates River Africa P. 55 Farming Community Activity Part I: Sketch a small farming community in its early stages (color #1) Add irrigation to your community (color #2) Add surplus of food to your community (color #3) Surplus of food leads to a division of labor. Add division of labor (color #4) Things You Should Have Included in Your Farming Community Sketch Wood/ Mud Houses Crops Water Source Megalith Water Diverti ng From the Water Source to Crops Added Food Sources through out the commu nity People in the commun ity doing chores: making pottery, cropping, taming animals, building canals, building homes How might big construction projects like the building of canals and large buildings lead to laws and government? Farming settlements grew in size and complexity. They gradually developed into cities between 4000 and 3000 BC. Quick Review What is the acronym for characteristics of a civilization and what does each letter stands for? What region did the first civilizations choose to settle? How did Mesopotamians control the floods that destroyed crops, killed livestock, and washed away homes? What lead to the creation of laws and governments? Picture: Ziggurat at Ur p. 51 Mesopotamian temples known as ziggurats served as places of worship and were the largest, most important buildings in their cities. The photo here shows one of the most famous Mesopotamian ziggurats, the ziggurat at Ur. The ruins of the ancient Sumerian temple, believed to have been built in about 2100BC, are located near the present-day city of Nasiriyah, in southeastern Iraq. Attempts at restoring the ziggurat took place in the 1930s, but only the lower level of the temple was restored. What types of technology or knowledge were probably needed to build this temple?