Immunity
advertisement

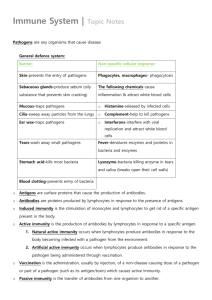
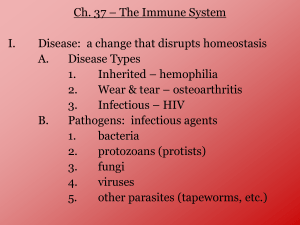
Immunity Name of the system: Immune System What is Immunity? • Immunity: ability to resist certain pathogens • Pathogen- an “agent of disease.” It is the disease causer • EX of pathogen: HIV, Flu, or common cold How do we get Pathogens? • Pathogens are transmitted by: • Airborne (i.e. Influenza) • Contaminated drinking water • Vector- an organism that carries a disease (i.e. tick) • Fluids (ex: HIV) Does anyone know what cells fight infections? •White blood cells fight infections •They are also called lymphoctyes Kinds of Lymphocytes B-Cells 1. Antibodies 2. Memory B T- Cells 1. Helper T 2. Cytotoxic T 3. Memory T T- Cells Helper T Assist Antibodies Cytotoxic T Killer T’s “Cell Police” Remember previous pathogens Memory T help produce specific antibodies Specific Defense • Pathogen have antigens on them • Antigens- trigger the immune response • Antigens have a protein, carbohydrate, or lipid on their surface An Antigen These are proteins, carbs, or lipids on the surface They are often called surface “proteins” ANTIBODIES • Shaped like a Y • Shape is Y so the antigen has 2 places to bind • EX: Virus attaches to antigens, clumps them, & attracts WBC’s Antibody Shape ANTIGEN BINDED Steps to an Infection • 1) Pathogen Invades • 2) Antigens are recognized by a body’s B’cells • 3) B cell’s produce specific antibodies and are released into the blood • 4) Memory B & T cells are made to remember Vocabulary • Immunity • Memory T Cell • Pathogen • Cytotoxic T cell • Vector • Lymphocyte • Antibody • Antigen • Helper T cell STOP Homeostasis Disrupted • Homeostasis is disrupted in 4 MAJOR ways: • 1)HIV/AIDS • 2) Organ Transplant • 3) Cancer • 4) Allergies HIV/AIDS • HIV= Human Immunodeficiency Virus • AIDS = Auto Immune Deficiency Syndrome • HIV is the virus you are infected with. • HIV attaches to T-Helper cells, and decreases immunity • This is why people with HIV/AIDS are susceptible to many different kinds of infections Cancer • Not always recognized as foreign, because cancer is made by your own cells • Cytotoxic T-cells are constantly surveilling for cancer • Causes of cancer: viral, genetic, or chemical (radiation) Allergies • Antigens from allergens (i.e. pet dander) bind to Mast cells • Mast cells release Histamine • Mast cells are another type of immune cells, common in nasal passages • Histamine is what causes the actual reaction • *ADD allergens are harmless is general, but their antigen is recognized as foreign Organ Transplant • Cytotoxic T-cells ATTACK the new organ • The new organ is seen as foreign • Patients are put on immunosuppresants for life STOP 2 kinds of Immunity Active Immunity Natural Passive Immunity Natural Acquired(Maternal) Acquired Active Immunity: the body makes its OWN antibodies in response to an antigen • Active Natural: • Active Acquired: • an antigen enters your body and YOU make antibodies to fight it • A Vaccine • EX: Chicken Pox Vaccine • A vaccine is weakened or mild form of a pathogen • This weakened form stimulates an immune response to produce specific antibodies to this particular pathogen Passive Immunity: lasts a LIMITED amount of time • Acquired Passive: • Natural Passive: • When a • You are mother INJECTED with breastfeeds antibodies her child she • EX: Rabies gives the child Shots/anti-venom antibodies STOP • HIV Immune Video