Ch 11 Drugs as Medicines
advertisement

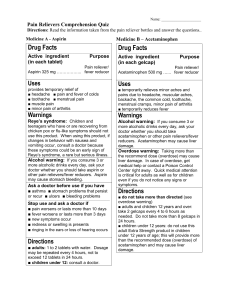
Medicines don’t cure the diseases, the body does Medicines benefit people this way: •Prevent: vaccine •Cure: penicillin •Make less severe: arthritis medication •Relieve symptom: aspirin •Bring desired effect: hair growth Aspirin: blocks actions of chemicals in the body Reduce fever, blood clots, inflammation 2 tablets double the bleeding time, lasts 4-7 days Reye’s Syndrome- damage liver & brain from to much aspirin in children Side effect- effect of a drug other than the desired effect. Example: cold medicine- drowsiness Factors that change medicine’s effects: Nature of the drug-substance Form it’s taken- liquid, tablet, capsule Route- mouth, injection, transdermal, “IV” When taken- with a meal Strongest factor- “if it is taken with other drugs” Tolerance- body gets used to it Addiction- craving for more Drug synergy- combined action of 2 or more drugs, produce stronger effect! Antagonist- one drug prevents the action of another FDA: Food and Drug Administration Safe- It won’t hurt you Effective- ingredient will do what the maker claims it will do Antibiotics- stop living cells from dividing Bacteria only (they divide faster) Anesthetic- drugs that kill pain, may or may not cause loss of conciousness Lethal dose- one that causes death Sold freely Relatively Safe Used without guidance Easy Instructions Can be overused: to many, too often Label: Active & Inactive ingredients, uses, side effects, directions Active vs Inactive ingredients Generic: small letters, chemical name, saves money same active ingredients Brand name: name given by drug company, capital letters Relapse- illness returns after being almost cured. Prescription Medicines Obtained only if ordered by a physician Dangerous, easily misused Doses adjusted to body weight, age, gender… Require guidance and adjustment Don’t use someone else’s prescription True miracles of our time!