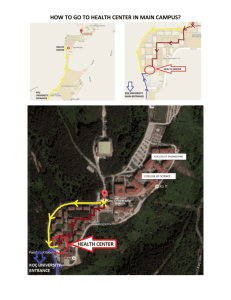
Drugs and Medicines Hand Out
advertisement

Drugs, Medicines, OTC, Drug Interactions Drugs v. Medicines Drugs Substances other than food that change the structure or function of the body or mind. Effective in treating illnesses when taken as directed by a physician or according to the instructions. Examples:______________________________________________ Medicines Drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions. A vaccine is an example of a medicine. A vaccine is a weakened or dead pathogen that causes the disease. Examples:_______________________________________________ OTC V Prescription Drugs OTC (Over-the-counter) Over the counter medicines/drugs can be obtained without a doctor’s script. Generic forms available: Walgreen’s, Safeway, Jewel Examples:__________________________________________________ Prescription Drugs Medicines/drugs that are obtained through a doc’s script. Must have an appt. before receiving a script. Examples: Amoxicillin, Z Pack, Oxycontin, Xanax, Paxil Vocabulary Analgesics: The most commonly used pain medicines otherwise known as pain relievers .Range from mild medicines such as aspirin, to strong narcotics such as opium based morphine and codeine. Examples: Ibuprofen, Aspirin, Tylenol with Codeine Antibiotics: A class of drug that destroy disease-causing microorganisms known as bacteria. Examples: Penicillin, Amoxicillin, Zithromax Drug Misuse v Drug Abuse Drug Misuse Using a medicine or drug in ways other than the intended use. Examples: Failing to follow instructions on the package, taking a medicine for a longer or shorter period than recommended. Discontinuing use of a medicine without informing your health care provider. Drug Abuse Intentionally taking medications for nonmedical reasons. Example: Taking Ritalin to study without a prescription, taking a pill to lose weight instead of changes in diet and exercise. Drug Interactions 1.Additive Interaction: Occurs when drugs work together in a positive way. Example: Ibuprofen and vicadin after having your wisdom teeth pulled. 2. Synergistic Interaction: an interaction of two or more drugs that result in a greater effect than when the meds are taken alone. Example: Mixing alcohol with another depressant type drug. 3. Antagonistic Interaction: The effect of one medicine is cancelled or reduced when taken with another one. Example: Antibiotics and birth control