The Lymphatic System
advertisement

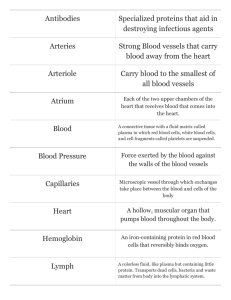
The Lymphatic System HONORS ANATOMY CHAPTER 20 Lymphatic System Parts Functions returns fluids that have leaked out of blood vessels blood vessels 2. provides structural basis of Immune System 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. lymphatic vessels Lymph: fluid in those vessels Lymph Nodes: structures that cleanse the lymph that flows through them Spleen Thymus Lymphatic Vessels 1-way network lymph flows: LYMPHATIC CAPILLARIES COLLECTING VESSELS TRUNKS & DUCTS LARGE BLOOD VEINS HEART Lymphatic Capillaries very permeable pick up fluids, proteins, particulate matter from interstitial spaces edges of adjacent cells overlap on entry point essentially acts a valve (or swinging door) so fluid flow only goes in from capillaries lymph flows through progressively larger vessels Lacteals special set of lymphatic capillaries in small intestines transport fat from villi blood Collecting Lymphatic Vessels travel with superficial veins deep arteries same 3 tunics as veins but have: thinner walls more internal valves anastomose more(junctions with other collecting vessels) Lymphatic Trunks union of larger collecting vessels major lymphatic trunks (all paired but #5) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. lumbar bronchomediastinal subclavian jugular intestinal Lymphatic Ducts receive lymph from the lymphatic trunks *right lymphatic duct right upper limb right side of head & thorax *left lymphatic duct *aka thoracic duct drains everything else Cisterna chyli: beginning portion, an enlarged sac anterior to L1 – L2 Lymph Transport no pump to transport lymph veins flow slow, maintained by 1. 2. 3. contraction of skeletal muscle pressure changes in thorax contractions of lymphatic vessels Lymphoid Cells 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Lymphocytes Plasma cells Macrophages Dendritic cells Reticular cells: form framework of lymph nodes, spleen Lymphoid Tissue reticular CT houses macrophages, lymphocytes, dendritic cells appears: diffuse 2. Follicles: densely packed may have germinal centers: B cell proliferating 1. Lymph Nodes clustered along lymphatic vessels Function: 1. filter lymph 2. involved in activation of immune system Sentinel Node 1st node that receives lymph drainage from a body area suspected of being cancerous gives best indication of metastasis thru lymphatics Spleen Functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. site for lymphocyte proliferation destroys aged or defective RBCs & bloodborne pathogens stores & releases breakdown products of Hgb stores plts fetal site of hematopoiesis Splenomegaly enlargement of the spleen due to accumulation of infectious microorganisms Causes: 1. Septicemia 2. Mononucleosis 3. Malaria 4. Leukemia Thymus T lymphocyte maturation & development of immunocompetence most active during youth MALT Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Function: prevent pathogens from penetrating mucous membranes includes: 1. Peyer’s patches in intestinal wall 2. Tonsils 3. lymphoid follicles in appendix, genitourinary tract, respiratory tract