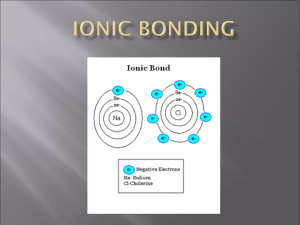
Ion – an atom or group of atoms that has
advertisement

Bonding A chemical bond is a force that holds atoms together. Two Types of Bonds 1. Ionic Bond – the attraction between two oppositely charged ions. An ionic bond is formed when atoms gain or lose electrons. Ionic bonds form compounds. Ion – an atom or group of atoms that has become electrically charged. It is a charged particle. When an atom loses an electron, it loses a negative charge and becomes a positive ion. When an atom gains an electron, it gains a negative charge and becomes a negative ion. Ionic bond Atoms that gain electrons have a negative valence. (charge) Atoms that lose electrons have a positive valence. (charge) 2. Covalent Bonding – A type of bonding in which electrons are shared. When covalent bonding occurs, molecules are formed. Covalent Bond Compound – two or more elements chemically combined by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons. Molecule – a particle made of 2 or more atoms covalently bonded together. Chemical formulas – a shorthand way to represent a compound. ( H2O) In a chemical formula, the element with the positive charge is always written first. Valence number – The number of electrons an atom needs to gain, lose, or share to become stable. (Gain electrons – negative valence) (Lose electrons – positive valence.) Subscript – the number that shows how many atoms of an element are in the compound. How to Write Formulas • 1. Write the symbol correctly for both elements. • 2. Write the valence number above each symbol. Make sure you have a positive first, and then a negative. • 3. Criss-cross valences to make a subscript. • 4. NEVER write 1 as a subscript. (It is understood to be 1 if there is no number.) • 5. Reduce to lowest terms. Examples • Sodium Chloride • Copper (I) Sulfide Aluminum Oxide Iron (III) Iodide 1. Calcium Sulfide 2. Copper (I)Iodide 3. Potassium Chloride 4. Iron(III) Bromide 5. Sodium Nitride 6. Antimony (V) Oxide Practice Problems • Aluminum Bromide • Calcium Iodide • Copper (I) Chloride • • • • • Hydrogen Oxide Magnesium Nitride Potassium Sulfide Barium Fluoride Lead Bromide Binary Compound – a compound composed of 2 elements. Polyatomic Ion- a group of positively or negatively charged covalently bonded atoms. Calcium Phosphate Tin (IV) Chromate Ammonium Oxide Magnesium Sulfate Naming compounds – change the ending of the second element to – “ide”. (Do not change the names of polyatomic ions.) Check to see if Roman numeral is needed. Ex: NaCl - Sodium Chloride Fe2O3 – Iron (III) Oxide Examples • Zn3N2 ______________________ • K2SO3 ______________________ • CuO ______________________ • Ba(C2H3O2)2 _____________________