Synovial Membranes
advertisement

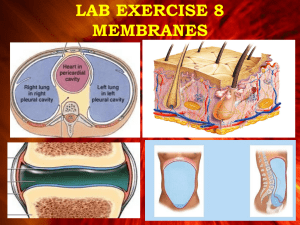
Classifications of Body Membranes Connective tissue membranes – synovial Epithelial membranes – mucous or mucosa – serous or serosa – cutaneous Synovial Membranes (Connective) Some joints are surrounded by a membrane (synovium) that produces a thick, synovial fluid. This fluid nourish the cartilage and keeps it slippery. Knee Joint Mucosa Membranes (Epithelial) Mucus-secreting membrane that lines all body cavities or passages that come in contact with the outside of the body. Membranes are involved in absorption and secretion. Lichen planus (Fungus) Serous Membranes (Epithelial) Serous membranes line body cavities that do not open directly to the outside, and they cover the organs located in those cavities. Fluid lubricates the membrane and reduces friction and abrasion when organs move against each other. Canine Reproductive Organs Serous Membranes cont…. Serous membranes occur in pairs separated by serous fluid Specific serous membranes – Peritoneum Abdominal cavity – Pleura Around the lungs – Pericardium Around the heart Cutaneous Membranes (Epithelial) Cutaneous membranes of the skin cover the surface of the body. They consist of stratified squamous epithelium and the underlying connective tissues. Cutaneous membranes are thick, relatively waterproof, and dry. Skin Cancer







![4-Membranes-functions [Compatibility Mode]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008852505_1-4ebcde23cd32c24e95becfaeb634e24e-300x300.png)