Integumentary System
advertisement

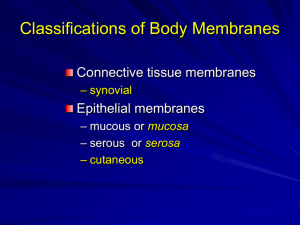
Do Now: Tuesday, Sept. 15 • Objective: Integumentary Overview • Do Now: 1. What is homeostasis and why do we need it? 2. Positive or negative feedback? a) More common? b) Change is good and want to increase it? c) Thermoregulation as an example? Integumentary System • Definition: External covering of the body, including skin, hair, nails and sweat glands. Purposes of Skin 1. Protective covering 2. Regulate body temperature 3. Prevent water loss 4. Hold sensory receptors 5. Synthesize (make) biochemicals (vitamin D) Four Types of Membranes: • • • • Serous Mucous Synovial Cutaneous Four Types of Membranes: • 1. Serous: lines cavities not open to surface (thorax (chest), abdomen) Four Types of Membranes: 2. Mucous: line cavities open to surface (nasal, oral, digestive, urinary, reproductive) Four Types of Membranes: • 3. Synovial: line joints (makes fluids that protect joints) Four Types of Membranes: • 4. Cutaneous: protection (skin) CFU: • Please identify what type of membrane I would use for each of these purposes: 1. Keep my joints from grinding into each other. 2. Protect my body from bacteria entering through the nose. 3. Keep my lungs from jamming into my ribs 4. Keep out bacteria from entering through the surface of the skin. Layers of Cutaneous Membrane • 1. Epidermis: (top) many layers of flat cells – Protection • 2. Dermis: hair, sweat glands, nails, oil glands – Largest layer • 3. Hypodermis: (bottom) largely fat – Insulation, holds major blood vessels. Layers of Cutaneous Membrane Class you need to know this GP: Types of Membranes Serous What does it do? Where is it found? Mucous Synovial Cutaneous GP: Layers Epidermis Layer: Top, Middle or Bottom? What’s it made of? Why is it important? Dermis Hypodermis Independent Practice: Whiteboards Types of Membranes Layers of Cutaneous Membrane • • • • • 1) Epidermis • 2) Dermis • 3) Hypodermis 1) Serous 2) Mucous 3) Synovial 4) Cutaneous