Connective Tissues Powerpoint
advertisement

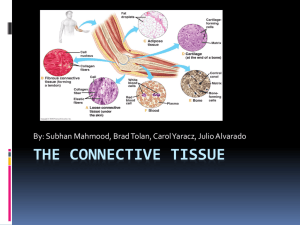
Connective Tissues What do all connective tissues have in common? • Made up of 3 components: 1) Specialized cells 2) Protein fibers 3) A fluid known as ground substance • Protein fibers and ground substance= Matrix • The matrix makes up most of the volume of connective tissues 3 Major Types of Connective Tissue: •1) Connective Tissue Proper •2) Fluid Connective Tissue •3) Supporting Connective Tissue Cells of Connective Tissue Proper • Fibroblasts: most abundant type; produce fibers and ground substance. • Macrophages: these cells “eat” or phagocytize damaged cells or pathogens. Release chemicals that mobilize the immune system. • Fat cells or adipocytes: contain large droplets of lipids (fat) • Mast Cells: found near blood vessels; have vesicles filled with chemicals released to defend the body after injury/infection. Connective Tissue Fibers: • Collagen fibers: Most common type; long, straight, unbranched- Strong and flexible. • Elastic fibers: contain protein Elastin. They are branched, wavy,and stretchy. • Reticular fibers: least common type; thin, branched and interwoven like a web. Ground Substance • Fills the spaces between cells and surrounds the connective tissue fibers. • Clear, colorless and has a maple-syrup consistency ( slows down pathogens) Types of Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective Tissue Dense Connective Tissue Loose Connective Tissue or “Areolar Tissue” • “packing material of the body” • Fill spaces between organs, provide cushioning, and support epithelia, anchor blood vessels and nerves, store lipids. Adipose Tissue ( Fat) • Loose connective tissue is called Adipose tissue if dominated by fat cells (adipocytes). Dense Connective Tissues: • Consists mostly of collagen fibers. • Types: 1) Tendons: attach skeletal muscles to bones 2) Ligaments: connect bones to each other. Have some elastic fibers ( a little more stretchy than tendons). Fluid Connective Tissues • 2 Types: Blood and Lymph • Contain cells in a watery matrix. • Unlike other connective tissues, the proteins are dissolved in the matrix and do not form insoluble fibers. Blood- A fluid Connective Tissue Consists of: Red blood cells: transport Oxygen(O2) White blood cells: fight infection Platelets: clot blood Lymph- A fluid Connective Tissue • Lymph: forms as interstitial fluid ( fluid within the body’s tissue) enters small passageways , or Lymphatic vessels that eventually return it to the cardiovascular system. Supporting Connective Tissues: • Includes: Cartilage and Bone • Provide a strong framework that supports the body Cartilage • The matrix is a firm gel containing embedded fibers. • Contains Chondrocytes: cartilage cells found within the matrix that live in small pockets called lacunae • Is avascular • Separated from surrounding tissues by perichondrium. • 3 major types: Hyaline, Elastic, Fibrous Hyaline Cartilage • Most common type • Matrix contains closely packed collagen fibers • Tough but flexible. Found: between joints, connecting ribs to sternum, supporting the larynx and trachea. Elastic Cartilage • Matrix contains numerous elastic fibers • Resilient and flexible • Found: external flap of ear (auricle), the epiglottis, and airway to the middle ear. Fibrous Cartilage or Fibrocartilage • Matrix contains little ground substance and is dominated by collagen fibers that are densely interwoven. • Tough and durable • Found: pads between vertebrae, between pubic bones of pelvis. Bone ( Osseus tissue) • Matrix consists of little ground substance containing collagen fibers . It is calcified with calcium compounds • Strong and resistant to shattering. • Contain osteocytes( bone cells) found in lacunae • Lacunae are found surrounding blood vessels . • Cytoplasmic extensions from osteocytes reach blood vessels- form a network called the canaliculi Bone • Contain osteocytes( bone cells) found in lacunae • Lacunae are found surrounding blood vessels . • Cytoplasmic extensions from osteocytes reach blood vessels- form a network called the canaliculi (little canals) • Outer layer of bone surrounded by a fibrous covering called periosteum