Positive Vs. Normative Econ.
advertisement

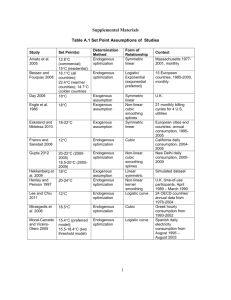
Social Sciences Vs. Natural Sciences • (A) Can economics be studied in a controlled laboratory setting? • (B) Positive Vs. Normative Economics 1 Positive Vs. Normative Econ. • Positive Economics Statements of fact & logical deductions Ex: If it rains the football field will get wet. • Normative Economics Statements about what should be (value judgments) Example: The football field is better when it is wet. 2 • Economic Variable An economic variable is an economic item of interest that can be defined and measured and takes on different possible values Examples: Price, Population 3 Endogenous Vs. Exogenous Variables Endogenous Variables An endogenous variable is a variable that is explained by the theory. It is also called a dependent or response variable. Exogenous Variable An exogenous variable influences endogenous variables but is itself determined by factors outside the theory. It is also called an independent or causal 4 variable. Own Price $ Sales # of cans (Independent (Dependent variable) variable) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Price 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 Plotting Pepsi Sales 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Sales 5 Own Price Competitors Price Relative Advertising Pepsi Sales 6 Y2 - Y1 Slope = X2 - X1 Price Intercept: y-intercept y value when x=0 Plotting Pepsi Sales 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 x-intercept: x-value when y =0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Sales 7 Equation of a straight line Plotting Pepsi Sales y= Vertical variable x= Horizontal Variable m = Slope c= y-intercept Price y = m x+c 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Sales 8 Relationships between Endogenous & Exogenous Variables Positive or Direct Relationship The relationship between an Endogenous variable and an Exogenous variable is said to be positive or direct when an increase (or decrease) in the value of the exogenous variable leads to an increase (or decrease) in the value of the endogenous variable. 9 Relationships between Endogenous & Exogenous Variables Negative or Inverse Relationship The relationship between an Endogenous variable and an Exogenous variable is said to be negative or inverse when an increase (or decrease) in the value of the exogenous variable leads to a decrease (or an increase) in the value of the endogenous variable. 10 Relationships between Endogenous & Exogenous Variables Unrelated Variables Two variables are said to be unrelated when a change in the value of one variable does not affect the level of the other variable. 11 Movements along Vs. a Shift of the line • A change in the exogenous variable represented on one of the axes results in a movement along the line. • A change in an exogenous variable not represented on one of the axes results in a shift of the curve. 12 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 Sales # of Sales # of cans cans (Dependent (Dependent variable) variable) AD = A2 AD = A1 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 Price Own Price $ (Independent variable) Movement ALong Vs. Shift of Line 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Sales (A2) Sales (A1) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Sales 13 9