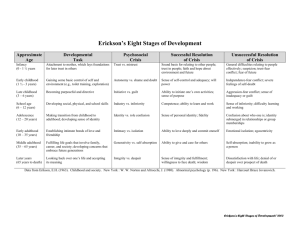
Chapter 10 - Gordon State College
advertisement

LIFESPAN PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT FELDMAN: MODULE 3-1 NORMAL GROWTH Growth occurs in a cephalocaudal (head to tail) pattern The head takes up one-fourth of total body length at birth, but only one-fifth at age 2. Growth occurs in a proximodistal (near to far) pattern. The head, chest and trunk precede the limbs and extremities. BODY GROWTH IN INFANCY Average North American newborn weight 7 ½ pounds and is 20 inches long. Birth weight triples in one year and quadruples by the end of two years. By the second year, the child is at 1/5 of its adult weight (30 lbs.) and ½ its adult height (30 + inches). Muscle tissue increases very slowly. FACTS ABOUT PHYSICAL GROWTH EARLY CHILDHOOD 2-3 inches per year 5 pounds per year Baby fat declines Posture and balance improve due to lower center of gravity. MIDDLE CHILDHOOD 2-3 inches per year 5 pounds per year Bones harden (skeletal age), lengthen and broaden ligaments are not yet firmly attached. Improved strength and muscle tone. Primary teeth are replaced with permanent teeth BODY GROWTH AND GENDER Girls are shorter and lighter and have a higher ratio of body fat to muscle than boys. Children differ in the rate of physical growth. Skeletal age is the best way to estimate the child’s physical maturity. African Americans mature faster than Caucasians and girls mature faster than boys. MOTOR DEVELOPMENT .Gross motor development involves large muscle groups and activities that generally have to do with locomotion Fine motor development involves smaller muscle groups and activities such as reaching and grasping PERSPECTIVES ON MOTOR DEVELOPMENT Nature-focused view: Developmental maturation Nurture-focused view: Dynamic systems theory: the child develops new motor skills by adapting and adding to old ones to meet his/her goals DYNAMIC SYSTEMS THEORY OF MOTOR DEVELOPMENT Mastery of motor skills involves acquiring increasingly complex systems of action. Each new skill is a joint product of: 1) Central nervous system development 2) movement capacities of the body 3) goals of the child 4) environmental supports for the skill NEWBORN REFLEXES blinking grasping rooting sucking Babinski Moro stepping swimming GROSS MOTOR DEVELOPMENT Gross motor development follows a generally universal sequence. Cephalocaudal and proximodistal trends are evident. There is no fixed maturational timetable. AGE NORMS (IN MONTHS) FOR GROSS MOTOR SKILLS* CULTURAL VARIATIONS IN MOTOR DEVELOPMENT Iranian orphans are not encouraged to move Indians in Southern Mexico are discouraged from walking Kipsigi parents in Kenya encourage motor skills and children walk early GROSS MOTOR - PRESCHOOL Age 3 – hop, jump, run for the fun of it Ages 4 and 5 – more adventurous, climb USING COMMON SENSE For adequate motor development, preschoolers need places and opportunities to play There is no evidence that formal lessons facilitate development Pushing the child may undermine self confidence GROSS MOTOR – SCHOOL CHILDREN Skipping rope, swimming, bike-riding, skating 10-11 year olds can learn from sports Gain greater control over muscles Boys outperform girls Need opportunities for physical play ORGANIZED SPORTS IN CHILDHOOD POSITIVES Opportunities for exercise Learning to compete Opportunities for peer, friendship relationships Reduces tendency for obesity ORGANIZED SPORTS IN CHILDHOOD NEGATIVES Negatives Too much pressure to perform Physical injuries Distraction from academic work Unrealistic expectations as an athlete Wrong values Possible exploitation GROSS MOTOR - ADULTHOOD Gross motor skills improve in adolescence They peak in the 20’s They decline through the remainder of adulthood FINE MOTOR SKILLS INFANCY - SEQUENCE OF REACHING BEHAVIOR Newborns pre-reach (drops out about 7 weeks) Voluntary reaching appears at about 3 months By 4-6 months an infant can grasp an object in a darkened room. By 7 months they can use one arm SEQUENCE OF GRASPING BEHAVIOR Newborn grasping reflex palmar grasp – can be varied 4-5 months, transfer objects from hand to hand 1 year – pincer grasp (Trying to push infants beyond their readiness may backfire.) FINE MOTOR SKILLS INFANCY Reaching affects cognitive development because it opens up new ways of exploring the environment. Infants use proprioceptive cues to reach as early as 4 months REACHING & GRASPING IN INFANCY Perceptual-motor coupling is used sense of touch sense of vision by 8 months Experience plays a role in development Pincer grasp goes with crawling & children pick up things from floor. FINE MOTOR – EARLY CHILDHOOD Fine motor progress is apparent in Children’s care of their own bodies Drawing and painting SELF-HELP SKILLS 2-3 years zips, puts on clothes 3-4 years button (large buttons) 5-6 years ties shoes 2-3 years 3-4 years 4-5 years 5-6 years uses spoon serves self food uses fork uses knife DRAWING AND PAINTING 3-4 years copies vertical line/circle Draws a “tadpole” person 4-5 years Cuts with scissors Copies triangle, cross, some letters 5-6 years Draws person with 6 parts Copies some numbers, simple words FINE MOTOR – MIDDLE CHILDHOOD Increased myelination of CNS 6-year-olds can hammer, paste, tie shoes, fasten clothes 7 years – use pencil & print smaller 8-10 years – write cursive & use hands independently 12 years – approach adult skill levels Girls outperform boys FINE MOTOR – OLDER ADULTHOOD Slower motor behavior Neural noise – irregular neural activity in the CNS Strategy – may have to slow to perform accurately Can learn new motor tasks, but more practice required INFLUENCES ON PHYSICAL GROWTH & HEALTH Genetics Infectious disease Childhood injuries Hormones Emotional well-being Nutrition CHILDREN’S HEALTH - PREVENTION Immunization Meningitis, measles, rubella, mumps, chicken pox, polio Accidents Poisonings, falls, drowning, choking Poverty Good medical care, nutrition, living conditions INFLUENCES ON PHYSICAL GROWTH & HEALTH - IMMUNIZATION Immunization has caused a dramatic decline in childhood diseases in the industrialized world 24% of American preschoolers lack essential immunizations (40% in poverty) Availability of care Misconceptions (MMR & autism) INFLUENCES ON PHYSICAL GROWTH & HEALTH – PITUITARY GROWTH HORMONES Growth hormone (GH) needed for development of all body tissues except CNS & genitals Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) causes the thyroid gland to release thyroxin, needed for normal nerve cell development and for GH to have a full impact on body size INFLUENCES ON PHYSICAL GROWTH & HEALTH – EMOTIONAL WELL BEING Psychosocial dwarfism Caused by extreme emotional deprivation Appears between 2 & 15 years of age Can interfere with the production of GH Very short stature Immature skeletal age Severe adjustment problems Can be treated ADOLESCENCE DEFINITION OF ADOLESCENCE Transition between childhood and adulthood Physically begins with puberty Culturally defined; ends gradually with assumption of adult responsibilities. Lasts nearly a decade (or more) in the U.S.; culturally exaggerated due to education THE GROWTH SPURT OF PUBERTY Most rapid growth since infancy Average of age 9 for girls; 11 for boys Girls grow 3.5 inches/year; boys 4 inches 50% of body weight gained in adolescence Also changes in leg length and facial structure WHY DOES PUBERTY HAPPEN EARLIER THAN IT USED TO? Nutrition ? – Better than in earlier times Hormones ? – Found in food supply Stress ? Fat ? STRESS THEORY OF EARLY PUBERTY Hypothalamus pituitary sex glands produce gonadotrophins Androgens (testosterone) Estrogens (estradiol) Pituitary thyroid gland produces growth hormone Cortisol (stress hormone) may trigger early onset (pituitary activity) FAT THEORY OF EARLY PUBERTY Weight affects the timing of menarche (106 +/- 3 pounds) Athletes and anorexics become amenorrheic Fat and leptin may also be influential ADULTHOOD NORMAL PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT: EARLY & MIDDLE ADULTHOOD Early Adulthood, peak muscle tone & joint function Senescence Middle Adulthood – gradual changes, lose height, gain weight, in 40s & 50s skin sags, wrinkles, age spots, hair thins, thicker finger- and toenails, yellow teeth CHANGES IN MIDDLE ADULTHOOD (CONT’D) Sarcopenia – age-related loss of muscle mass & strength Lose 1-2% per year starting at age 50 Exercise can help to reduce this loss Also lose bone from the late 30’s; this accelerates in the 50’s CHANGES IN MIDDLE ADULTHOOD Cholesterol increases LDL – leads to atherosclerosis Blood Pressure increases; sharply for women at menopause Metabolic disorder – hypertension, obesity, insulin resistance, high cholesterol, low HDL, weight gain (Part of normal aging?); weight loss & exercise help Lungs become less elastic ADULT HEALTH - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The 20’s are ideal for reproduction. Risks of miscarriage and chromosomal disorders are reduced. First births to women in their 30’s have increased in the past two decades Dramatic rise in fertility problems in the mid-thirties (14 to 26%) CHANGES IN MIDDLE ADULTHOOD - SEXUALITY Climacteric – loss of fertility Menopause – ceasing of menstrual cycles (average age 52) Drop in estrogen, hot flashes, nausea, fatigue, rapid heartbeat Gradual decline for men (no andropause) ADULT HEALTH IMMUNE SYSTEM Capacity declines after age 20, partially due to thymus and inability to produce mature T cells Stress and depression can also weaken the immune system ADULT HEALTH - STATES OF MIND Western stereotype: deterioration is inevitable In one study, people with positive self-perceptions of aging live 7 ½ years longer More optimistic elders are about capacity to cope with physical challenge, better they are at overcoming threats to health Low SES elders are less likely to believe they can control their health, to seek medical treatment, or to follow doctors’ orders. BIOLOGICAL THEORIES OF AGING Cellular clock (Hayflick) 70-80 cell divisions, based on telomeres 120-year lifespan Free-radical Calorie restriction antioxidants Mitochondrial Cellular energy producers Linked to free radical theory Hormonal Stress hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis Stress & decline in immune function FELDMAN: MODULES 4-1 & 4-2 Injury and Illness through the Lifespan CHILDREN’S HEALTH - PREVENTION Immunization Meningitis, measles, rubella, mumps, chicken pox, polio Accidents Poisonings, falls, drowning, choking Poverty Good medical care, nutrition, living conditions INFLUENCES ON PHYSICAL GROWTH & HEALTH - IMMUNIZATION Immunization has caused a dramatic decline in childhood diseases in the industrialized world 24% of American preschoolers lack essential immunizations (40% in poverty) Availability of care Misconceptions (MMR & autism) INFLUENCES ON PHYSICAL GROWTH & HEALTH – INFECTIOUS DISEASES 70% of deaths in children under age 5 are due to infectious diseases 99% are in developing countries and are related to malnutrition Most death due to diarrhea can be prevented by oral rehydration therapy (ORH) INFLUENCES ON PHYSICAL GROWTH & HEALTH – OTITIS MEDIA 70+% of American children have had at least one bout by age 3 Xylitol may be a preventative Tubes remain controversial Child-care settings should control infection May cause problems in language development due to hearing problems HEALTH - MIDDLE TO LATE CHILDHOOD This is generally a healthy time Otitis media becomes less prevalent. 19% of N.A. children have chronic diseases and conditions Asthma accounts for 1/3 of chronic illness and is the most common reason fro school absence Incidence has increased dramatically, 8% of U.S. children—boys, low SES, parents smoke, born underweight most at risk INJURIES IN EARLY CHILDHOOD Leading cause of childhood mortality in industrialized countries. Motor vehicle collisions are the most frequent source of injury at all ages & the leading cause of death among children over 1 year old Auto accidents, drownings and burns are the most common accidents of early childhood INJURIES IN MIDDLES TO LATE CHILDHOOD The rate of injury fatalities increases into adolescence with rates for boys rising considerably above those for girls. MV accidents are still the leading cause of death, with bicycle accidents next. Parents often overestimate children’s safety knowledge and behavior OBESITY: U. S. & WESTERN NATIONS There has been a marked rise in obesity in the U.S. and other Western nations. Percentage doubled since 1980; quadrupled since 1965 U.S. may have 2nd highest rate 15% of U.S. children 6-11 overweight CAUSES OF OBESITY Genetics SES (diet); high fat, low-cost foods Family stress (comfort food) Pastimes (TV, videogames) and lack of exercise Fast-food and busy schedules Learned food preferences (school cafeterias) NUTRITION – OBESITY IN ADULTHOOD Adult obesity correlated with increased risk of hypertension, diabetes, & cardiovascular disease May be a genetic propensity for obesity. It tends to run in families. (May also be learned eating patterns.) MIDDLE ADULTHOOD: ILLNESS & DISABILITY Cancer & cardiovascular disease are the leading causes of death. Cancer alone among women. Motor vehicle collisions decline, falls resulting in fractures & death nearly double. Personality traits that magnify stress, especially hostility and anger, are serious threats to health. CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE First detected factors may be high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and atherosclerosis (a buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries). Heart attack: blockage of blood supply to an area of the heart (50% die before reaching the hospital, 15% during treatment) Other conditions include arrhythmias and angina pectoris CANCER – MIDDLE ADULTHOOD The death rate multiplies tenfold from early to middle adulthood. Lung cancer has dropped in men (fewer smoke) and increased in women. Cancer occurs when a cell‘s genetic program is disrupted, leading to uncontrolled growth. Damage to the p53 gene is involved in 60% of cancers. This gene stops defective DNA from multiplying. Having the BRCA1 or BRCA2 tumor-suppressing gene is protection against breast cancer. CANCER 40% of people with cancer are cured. Breast cancer is most prevalent for women, prostate cancer for men. Lung cancer is next, followed by colon/rectal cancer. ADULT-ONSET DIABETES Causes abnormally high levels of blood glucose Incidence doubles from middle to late adulthood Effects 10% of the elderly Inactivity and abdominal fat deposits greatly increase risks Treated with controlled diet, exercise, and weight loss ARTHRITIS Effects 45% of American men and 52% of women over 65. Rises to 70% in women at age 85. Osteoarthritis: most common and involves deteriorating cartilage on the ends of bones of frequently used joints Rheumatoid arthritis: an autoimmune response leading to inflammation of connective tissue, especially the membranes that line the joints HEALTH & DISEASE IN OLDER ADULTHOOD Generally a continuation and intensification of problems that began in middle adulthood. PHYSICAL DISABILITIES Cardiovascular illness and cancer increase dramatically and remain the leading causes of death Respiratory diseases also rise sharply Emphysema, mostly from smoking Pneumonia, 50 types Stroke is the 4th most common killer Hemorrhage or blockage of blood flow in the brain CHRONIC CONDITIONS - OLDER ADULT Arthritis Hypertension Hearing and vision impairment Heart disease Diabetes Asthma Osteoporosis OSTEOPOROSIS Major age-related bone loss 12 to 20 % of patients die within a year of a major break such as a hip Patients are advised to: Take calcium and vitamin D Engage in weight-bearing exercise Take HRT/ERT Take bone-strengthening medications UNINTENTIONAL INJURY At age 65 and older, the death rate from unintentional injuries is at an all-time high Due to MV accidents and falls Older adults have higher rates of traffic violations, accidents, and fatalities per mile driven than any other age group 30% of people over 65 and 40% of those over 80 have experienced a fall in the last year Declines in vision, hearing and mobility make it harder to avoid hazards and keep one‘s balance