Annelids: Segmented Worms Worksheet - Biology Study Guide
advertisement
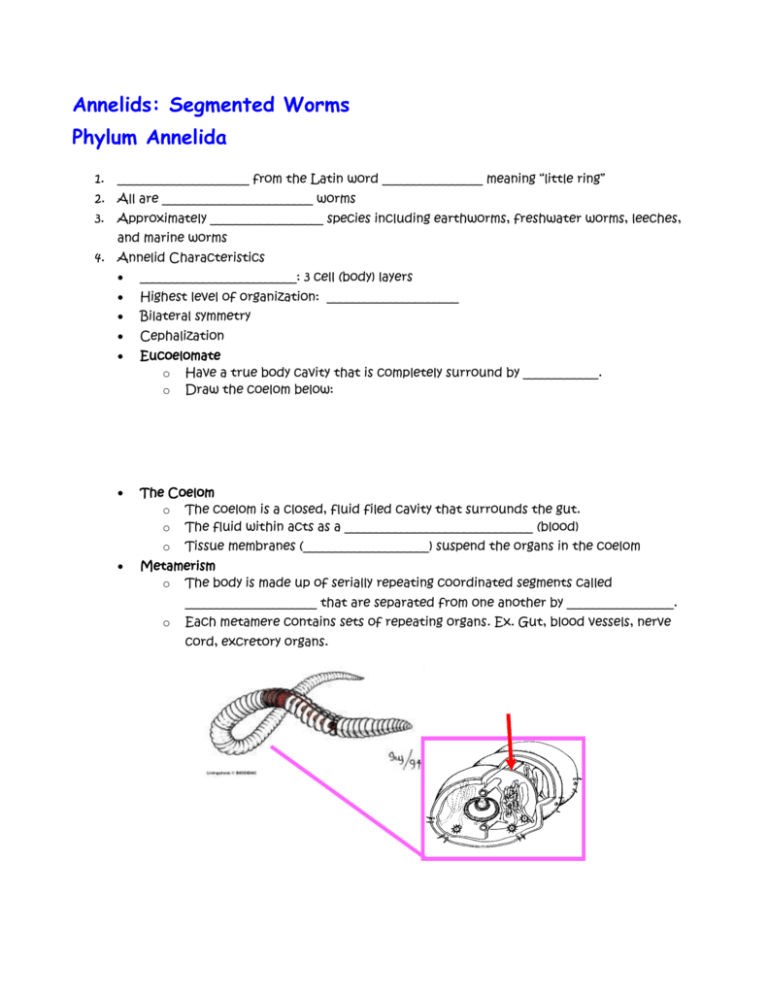
Annelids: Segmented Worms Phylum Annelida 1. _____________________ from the Latin word ________________ meaning “little ring” 2. All are ________________________ worms 3. Approximately __________________ species including earthworms, freshwater worms, leeches, and marine worms 4. Annelid Characteristics _________________________: 3 cell (body) layers Highest level of organization: _____________________ Bilateral symmetry Cephalization Eucoelomate o Have a true body cavity that is completely surround by ____________. o Draw the coelom below: The Coelom o The coelom is a closed, fluid filed cavity that surrounds the gut. o The fluid within acts as a ______________________________ (blood) o Tissue membranes (____________________) suspend the organs in the coelom Metamerism o The body is made up of serially repeating coordinated segments called _____________________ that are separated from one another by _________________. o Each metamere contains sets of repeating organs. Ex. Gut, blood vessels, nerve cord, excretory organs. Two part head consisting of: _____________________________: fleshy lobe that overhangs the mouth o _____________________________: first body segment ___________________: circular rings _________________________: the last segment where the anus is _________________________: reproductive structure Nervous System o 2 cerebral ganglia A ventral nerve cord with two ganglia per metamere In some species, sensory organs such as _____________, ____________, and __________________ have arisen. (________________ are appendages that may or may not be covered in cilia that help the worm find and pull in food) Locomotion o Both _____________________ and ________________ muscles o Most have _____________ (chitonous bristles secreted by the epidermis) that aid in locomotion and burrowing o Setae may be modified into appendages called ___________________ Skeletal System o Fluid in the coelom acts as a _______________________________ o o o PARAPODIA Gas Exchange o Mainly by ____________________ through skin o Class Polychaeta often has specialized structures for gas exchange (ex. Parapodia, gills) Digestive System o ____________________________ o 5. Regional ________________________ (digestive organs) Circulatory System o ________________ circulatory system composed of blood vessels (some of which are contractile and act as “hearts”) o Some circulation is also accomplished by the _________________ fluid Excretion o Excretion is accomplished by organs called _______________________ (singular nephridium) Reproduction o Sexual Three Classes of segmented worms _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ Class Polychaeta Characteristics • All _________________ • This class contains 2/3 of all known Annelids • Common species are _________________ , ___________________ , and _____________________ • Have a well developed head with specialized sense organs • Commonly called _____________________________ because…. o Have many ________________ (chitonous bristles secreted by the epidermis) o (Poly = many, chaeta= setae) o These setae are arranged in bundles on paddle-like appendages called ____________________ o • The parapodia function in ______________________, locomotion, and __________. _____________________ (tagmosis): the fusion and specialization of formerly metameric segments • Many are ____________________ feeders with specialized structures • Many are __________________________ with specialized structures • Many construct their own homes out of __________ (calcium carbonate), __________________, and _______________________. • Reproduction o Usually ___________________ o No permanent sex organs; gametes are shed into coelom where they stay until time for fertilization o Fertilization is usually ___________________ in water o ________________ development __________________ larvae swims around until it grows into adult for by adding segments • Ecology o o Polychaetes often have effective defense strategies: some have tubes to hide in some have vicious jaws some have modified “stinging” setae Some Polychaetes have a mutualistic relationship with their host For example, many scaleworms are found near, or in the mouth, of brittlestars, starfish, and sea urchins. The scaleworm eats its host’s leftovers and with its vicious jaws, it will attack any predator trying to eat it’s host. Class Oligochaeta Characteristics Earthworms are the most common Habitats: __________________________, freshwater, and __________________ Have few setae (“Oligo” = ________________, “chaeta” = setae Usually feed on ___________________________ (decaying organic matter) Depends on habitat, but they can feed on… o Dead leaves and plant roots o Living things such as other worms, bacteria and fungi o Decomposing remains of other animals Do earthworms eat dirt? o Yes and n. o Earthworms ________________________ dirt as they burrow, so yes they swallow it. o HOWEVER, they do not get ______________________ from dirt. Their nutrients come from decaying plant and animal remains that are in the dirt. Earthworms have a specialized digestive system to obtain the maximum amount of nutrients out of the detritus. o Example: pharynx, crop, gizzard, etc. Locomotion o Circular muscles contraction o Longitudinal muscle contraction Reproduction o Usually ________________________ o Still have to have a partner o Cross-fertilize by exchanging _______________. Ecology o Earthworms are essential soil ___________________, meaning they allow air to enter the soil. o Mix the soil with their tunnels. o Worm feces are great plant food = ____________________! Class Hirudenia Includes ____________________. Usually freshwater but there are some ____________________ and terrestrial species. No __________________ between metameres No ___________________ or parapodia Have two suckers Have an extendable ____________________ for feeding Usually have a fixed number of segments (34). Each metamere consists of several annuli Lack septa between metameres, so they are incapable of moving like Oligochaetes. Instead, they use their anterior and posterior suckers to move. Reproduction o usually _________________________ o cross-fertilize by exchanging sperm Ecology o Although some leeches are parasitic blood suckers (can be temporary or permanent), many are predators. o Leeches have been used medicinally since the 19th century. o Currently they are used to increase blood flow following reconstructive surgery o _______________________ is a powerful anticoagulant that is found in the salivary glands of leeches