Annelids
advertisement

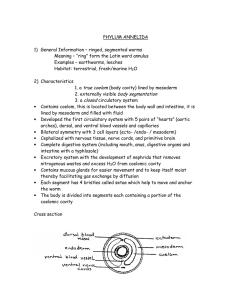
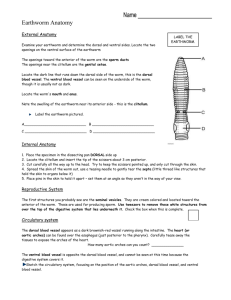
Annelidae These guys try to worm their way into all ways of life Typical dissection approach I. General Characteristics • • • • • • • • A. Bilateral symmetry B. Cephalization C. Coelom D. Complete digestive tract E. Segmentation F. Nephridia G. Circulatory system H. Hydrostatic skeleton II. Organ systems • A. Digestive System • 1. muscular pharynx • 2. esophagus • 3. crop • 4. gizzard • 5. intestine B. Nervous system • 1. ganglia • 2. ventral nerve cord C. Circulatory system • 1. closed circulatory system • 2. dorsal blood vessel • 3. five pairs of pseudohearts • 4. ventral blood vessel • 5. capillary network D. Reproductive system • 1. hermaphroditic • 2. male parts • 3. swapping of sperm • 4. clitellum • 5. female parts impossible to find for average The Great Exchange Fertilized eggs released in a cocoon E. Excretory system-nepridium • 1. almost every segment has a nepridium nephridium III. Classes of annelids • A. Oligochaets • 1. setae not huge • 2. useful for anchorage during locomotion • 3. sequence of muscle contraction B. Polychaets • 1. parapodia • 2. much more elaborate • 3. locomotion • 4. moving fluid through tubes • 5. excavation in marine worms • 6. respiratory surfaces Polychaet-feather duster worm Christmas Tree Worm C. Hirunidea-leeches • One of man’s best friends Wonderful story • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ak6MXQFRVc&NR=1 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SxZbzZ5RE40&feat ure=related Cross section • 1. coelom • 2. dorsal blood vessel • 3. ventral nerve cord • 4. muscle layers • 5. typhlosole • 6. nephridia • 7. setae