annelid Review Guide
advertisement
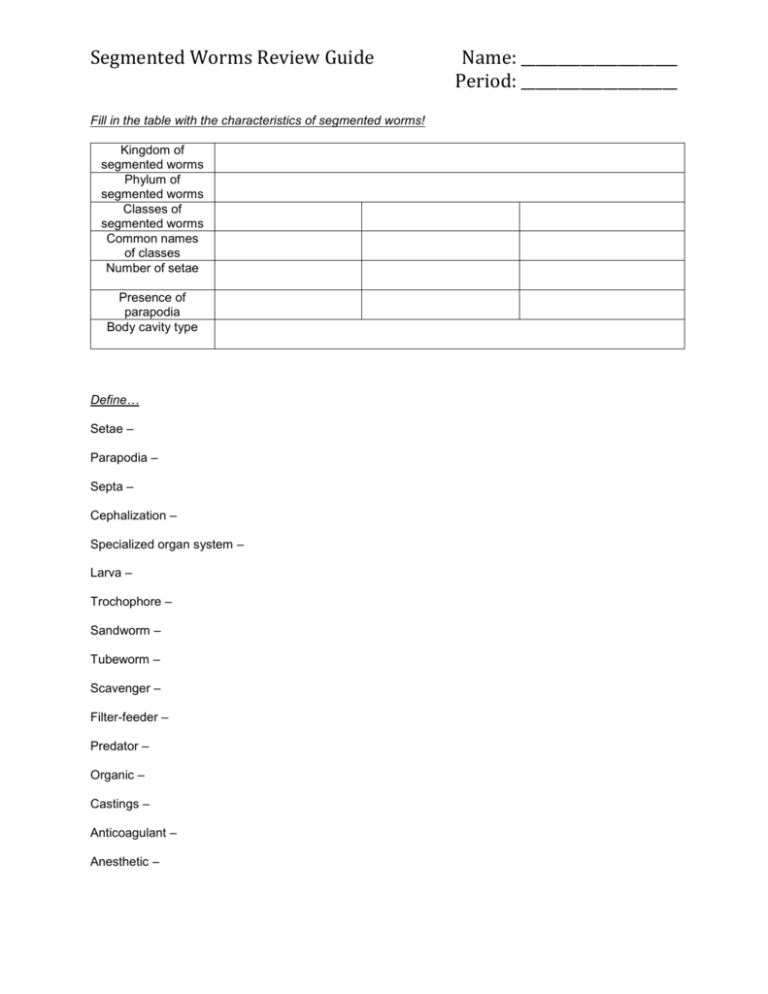
Segmented Worms Review Guide Fill in the table with the characteristics of segmented worms! Kingdom of segmented worms Phylum of segmented worms Classes of segmented worms Common names of classes Number of setae Presence of parapodia Body cavity type Define… Setae – Parapodia – Septa – Cephalization – Specialized organ system – Larva – Trochophore – Sandworm – Tubeworm – Scavenger – Filter-feeder – Predator – Organic – Castings – Anticoagulant – Anesthetic – Name: _____________________ Period: _____________________ Know… … based on what characteristics segmented worms are classified … where annelids add on new segments … where the coelom is located … where the major nerve cord is located … what earthworms can sense … through which order of organs food passes in an earthworm … where most leeches live … the difference in segmentation between leeches and earthworms … the importance of marine worms in the ecosystem … how earthworms can be used by humans … how leeches can be used by humans Be able to label the following diagram of the internal anatomy of an earthworm! A. B. C. D. E. mouth pharynx esophagus crop gizzard F. G. H. I. J. intestine brain (cerebral ganglia) ventral nerve cord seminal vesicles (testes) hearts (aortic arches) Name the anatomic directions of the worm (use the scientific terms)! a ___________________ b ___________________________ d _________________________ c______________________________ Be able to match the structures and functions of earthworm anatomy! creates vacuum and secretes mucus for swallowing thick skin ring that secrets mucus to protect the eggs pumps blood food storage sac digests food into pieces small enough to be absorbed into blood passage way to crop channels blood from heart to rest of body body opening for food to enter returns blood to heart filter toxins and waste to transport them out of the body passes waste and undigested food out of the body grinds and breaks down food into smaller pieces coordinates movement by controlling nerve cord carries information for movement to muscles and sensory stimuli to brain