Exam 3d
advertisement

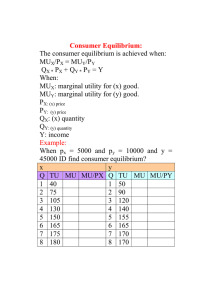
Ag Econ 1041 Exam 3, 140 points November 13, 2012 Name ______KEY__________________________ 11 a.m. Section True/False – one point each T F 1. When making decisions we face various constraints that can include income, time or others. T F 2. Demand is the aggregation of individuals’ decisions made following the decision rule. T F 3. A good decision maker would choose the action with the lowest opportunity cost. T F 4. Economics exists because scarcity means we have to not do something whenever we make a decision to do something. T F 5. Rising coffee prices due to frost in Colombia suggest demand is elastic. T F 6. Market equilibrium exists when the quantity supplied = quantity demanded. T F 7. An individual’s goal is to maximize utility. T F 8. The demand for a good is more elastic if it is a necessary good. T F 9. Subsidies are incentives provided to alter someone’s decisions or behavior. T F 10. Since I enjoy chocolate everyone must enjoy chocolate. T F 11. A rising price is a signal to buyers to buy less. T F 12. Choosing the option with the lowest opportunity cost is the same as choosing the option with the highest net benefit per dollar. T F 13. Once you pay for an all you can eat buffet, the out of pocket cost for another helping is zero but an opportunity cost still exists. T F 14. We make decisions on the margin. Using averages can mislead us when making individual decisions. T F 15. Common resources are rival in consumption. 16. If an increase in the price of peanut butter increases the demand for jelly, then the cross-price elasticity of demand for these goods is positive. any 1 T F 17. Decisions allocate resources. T F 18. A decrease in the price of hamburgers will lead to an increase in the demand for French fries. T F 19. Long run average costs (LRACs) measure the impact of the size of a business enterprise in terms of average costs. T F 20. Excise taxes tend to lower market price. T F 21. If demand decreases for houses, we expect consumer surplus to decline from home purchases. T F 22. A flood that removes land from production would shift the demand for grain to the left. T F 23. A positive cross-price elasticity tells us the demand for one good will increase because the price of another increases. T F 24. Externalities are the impact on a third party of others’ actions. T F 25. Costs that do not change once they are incurred are called explicit costs. T F 26. A deadweight loss is a measure of gain by market participants caused by government intervention. T F 27. A firm is breaking even if its AR = ATC. T F 28. The market supply curve reflects the lowest opportunity cost for each level of output and sales facing an industry. T F 29. A combination of goods beyond the production possibilities curve cannot be produced currently. T F 30. Improvements in productivity tend to benefit only producers and sellers. 2 Multiple choice – two points each __e__ 31. The marginal product multiplied by the price of the output is a) An equilibrium b) The profit maximization point c) Fixed cost d) The neutral zone e) Marginal value product __b__ 32. Production combinations on the PPC are a) Efficient but not obtainable b) Efficient and attainable c) Inefficient and sustainable d) Inefficient and not obtainable e) Useful for identifying aliens _any___ 33. When marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue, a profit-maximizing firm will a) Decrease production b) Be maximizing profit c) Increase production d) Produce nothing e) Raise price __a__ 34. How does someone decide how much of a good to buy? a) Keep buying until the net benefit of the additional good is less than or equal to the next best choice b) Only buy one unit at a time c) Keep buying until the benefit of the additional unit is equal to its price d) Buy as much as your income allows e) Keep buying until the benefit of the additional unit is less than its cost __c__ 35. The amount of satisfaction gained from purchasing an additional pair of jeans is a) Total utility b) Determined by one’s income level c) Marginal utility d) A result of the decision rule e) Never negative __b__ 36. An increase in the price of a consumption complement will cause a(n) a) Increase in demand b) Decrease in demand c) Increase in supply d) Decrease in supply e) No change in demand or supply 3 __d__ 37. An increase in the price of a production substitute will cause a(n) a) Increase in demand b) Decrease in demand c) Increase in supply d) Decrease in supply e) No change in demand or supply __d__ 38. A decrease in demand, with no change in supply, will lead to ________________ in equilibrium price and ____________________ in equilibrium quantity. a) An increase, an increase b) An increase, a decrease c) A decrease, an increase d) A decrease, a decrease e) No change, no change __c__ 39. An increase in technology, with no change in demand, will lead to _______________ in equilibrium price and ________________ in equilibrium quantity. a) An increase, an increase b) An increase, a decrease c) A decrease, an increase d) A decrease, a decrease e) No change, no change __b__ 40. The consumer’s surplus for a good is equal to a) The demand price b) The demand price minus the price paid c) The demand price plus the price paid d) The price paid minus the demand price e) The price paid plus the demand price Short answers are valued at five points each 41. What do we call a good that is rival in consumption but cannot be excluded from use by others? Common resource 42. We know a graduate who just got a high paying job. What is happening to her demand for goods she feels are inferior? Demand falls 4 43. Diagram a minimum wage set above the prevailing wage rate. Show the final consumer and producer surplus if this minimum wage is imposed. D S P1 or Mw Mw P0 D 0 Qd Q0 Qs Q 44. Declining marginal product and increasing marginal cost both result from what? Diminishing returns 45. What type of cost should not impact short run decision making? Fixed 46. a) AVC ÷ AFC = ____1 point for everyone_________________________ b) Sum of MC = ____VC___________________________ c) Average Revenue (AR) = ____D or TR ÷ Q______________________ d) Profit is maximized at the output where ___MR = MC____________________________ e) If MR is negative then demand is __inelastic___________________________ 5 47. Graph (diagram) the market for Dr. Pepper. Illustrate what happens in the market when the price of high fructose corn syrup (a major ingredient) increases. Show the new market outcomes. P S1 S P1 P0 D 0 Q1 Q0 Q 48. Diagram the market impact of technological advances in package delivery. P S S1 P0 P1 D 0 Q0 Q1 Q 49. What is the sum of marginal costs? VC 6 50. Diagram the situation where the demand for peanuts increases but the market price declines. S0 $/Q S1 P0 P1 D0 0 Q0 Q1 D1 Q 51. Show the impact of a decrease in income on the market for restaurant prepared meals. (Use a supply and demand model.) S P P0 P1 D1 0 Q1 Q0 D Q 52. What must be protected for a free market to function effectively? Property rights 53. Market solutions are efficient and the government should mimic their result is the premise of the ___Coase___________ ____Theorem________________. 7 54. Identify what happens to demand or supply under the following situations (increase, decrease or no change; i.e. utility increases, so D ↑) a) Wealth and income declines D↓ b) Government provides a subsidy to buyers of solar panels D↑ c) Input costs decline S↑ d) Population decreases D↓ e) Production technology improves S↑ 55. Diagram the situation where a percentage or ad valorem tax is applied to a market that creates negative externalities in the production and use of the good. Show the change in equilibrium and the government revenue on the graph. P = $/Q S1 S0 P1 P0 Gov’t Revenue D 0 Q1 Q0 Q 8 56. Diagram the change in the gasoline market where refineries are shut down. Show changes in prices and quantities as well as the final producer and consumer surplus. P S1 S P1 CS P0 PS D 0 Q1 Q0 Q Ten points 57. Diagram a per unit tax on gasoline. Be complete. Show the deadweight loss and the amount of tax collected. a) What is the impact on consumer surplus? ___falls____________________________ b) Why are consumers likely to eventually pay the majority of the tax assessed? __demand is inelastic_____________________________________ S1 P S P1 P0 Gov’t Revenue DWL D 0 Q1 Q0 Q 9