Exam 1
advertisement

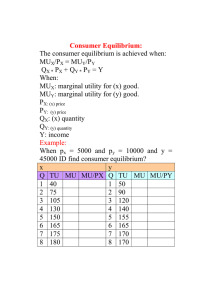
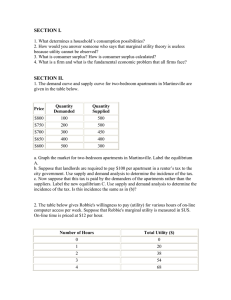
Ag Econ 1041 Exam 1, 125 points September 21, 2006 Name ______________________________ 8 a.m. Section True/False are worth one point each T T 1. 2. F 3. T F T 4. 5. 6. T 7. T 8. T 9. F T 10. 11. F 12. F F T 13. 14. 15. F 16. F T 17. 18. F 19. F T F T F F F 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. A ceteris paribus assumption is helpful in analyzing human behavior. The fallacy of consumption can lead us to assume other people are more like us than is actually true. Opportunity costs are the value of all the other choices a person gives up by making a decision to do something. Decision making is what economics is all about. It is best to use averages to make decisions. Economic theory suggests that we should all specialize in our most productive activities because of our comparative advantage. Opportunity cost is the net value of the highest valued alternative to a decision including a course of action or purchase. Land near urban areas is often sold because it has a higher opportunity cost to remain undeveloped than farmland in rural areas. Marginal utility is the utility derived from consuming additional increments of a good. Demand is always positively sloped. A person that likes something more than someone else will be willing to pay more, ceteris paribus. A person will be willing to buy a good if the ratio of marginal utility to marginal cost is less than one. Economics is primarily about the accumulation of money. Because we buy what we want there is no reason to worry about making choices. Free markets need government to enforce rules but suffer if the government tries to alter outcomes. Market demand for shoes shows the lowest price consumers are willing to pay for shoes. If water decreases in price, its demand will increase. An increase in demand means that consumers are willing to pay more for the same quantity. A friend gave me free tickets to a new movie. Using economic theory, I decided to go because there was no opportunity cost. I used the idea of opportunity cost correctly. Supply is a quantity. Demand for a normal good is always downward sloping. No one ever buys anything if prices are a little above the market equilibrium price. Scarcity affects everyone. Management skill does not affect supply. The supply of celery is not related to opportunity cost. Supply represents the highest opportunity cost facing a seller. 1 F F 27. 28. F T 29. 30. A decrease in the price of medicine will cause the supply of medicine to decrease. Demand would decrease in the current period, if suppliers expected input costs to go up in the future. Supply is equal to demand at various prices in a market equilibrium. Property rights and accurate information allow a market to operate well. Matching are valued at one point each G M H F L D K A E I O B J N C 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. Profit Marginal Price Consumer surplus Market Demand Utility Substitute Producer surplus Property rights Supply Complement Government Economics Equilibrium A) Replacement B) Consumed with another product C) No tendency to change D) Lowest opportunity cost for buyers E) Net value to sellers F) Area below demand and above price G) Attracts resources H) Measure of scarcity/relative value I) Necessary for free markets J) Referee for markets rather than participants K) Value to an individual L) Where exchange is arranged M) Change or edge N) Study of decision making O) Sellers schedule of prices and quantities Short answers are worth five points each 46. Given the following values, list the opportunity cost for each option (a, b, c, or d): a) benefits = 20, cost = 15 _____c_(25)_______ b) benefits = 10, cost = 10 ____c__(25)_______ c) benefits = 50, cost = 25 ____a__(5)_______ d) benefits = 40, cost = 45 ____c__(25)_______ 47. Complete this sentence. There is no “free lunch” because ___of opportunity cost___ 48. Given that a person has three choices, going to the movies, going to a Tigers’ game or going to a restaurant for dinner, what are their opportunity cost of going to the Tigers’ game, if they value the Tigers’ game at $100 and the other two choices at $40? $40 2 49. Show on a graph consumers’ response from an increase in the price of prescription drugs. $/Q P1 P0 D Q1 Q0 Q/t 50. Diagram the result from an increase in the price of bottled water in the market for soda. $/Q S P1 P0 D1 D0 Q0 Q1 Q/t 51. What happens to demand in the following situations? ( ↑ ↓ or ↔ ) a) Price of complement rises ___↓____ b) Own price of good increases __↔____ c) Wealth increases ___↑____ d) Utility increases ___↑___ e) Input costs decline ___----___ 3 52. Demonstrate the change in the market for houses if the price of lumber decreases. Show the change to consumer surplus. $/Q S = change CS S1 P0 P1 D Q0 Q1 Q/t 53. Draw a production possibility curve so that there are increasing marginal opportunity costs to produce more of one of the goods. A PPC B 4 54. Demonstrate the market results in the current period, if prices are expected to go down for an inferior good in the future. $/Q S S1 P0 P1 D1 Q? D Q/t 55. Complete the following sentence. Price tends to be held down in a free market because of ___competition_____________________. Longer answers are worth 10 points each 56. Diagram the change in the Production Possibility Frontier of a farmer who grows only sod for lawns and soybeans if there is an increase in land that is suitable only for soybean production. What is likely to happen to the output of each good? Output of each will likely increase sod PPC2 PPC1 soybeans 5 57. Demonstrate the change in the CD market if the music industry discovers a new, more efficient method to produce CDs and at the same time the prices of other entertainment (sports, movies, restaurants) increase. Show the market outcomes and why they happen on a diagram. $/Q S S1 P1 ? P0 D1 D Q0 Q1 Q/t 58. Diagram the situation where the government institutes a price ceiling. Show the changes in market outcome and the final levels of producer and consumer surplus. Label completely. $/Q S = CS = PS Pe Pc D Qs Qe Qd Q/t 6